标签:
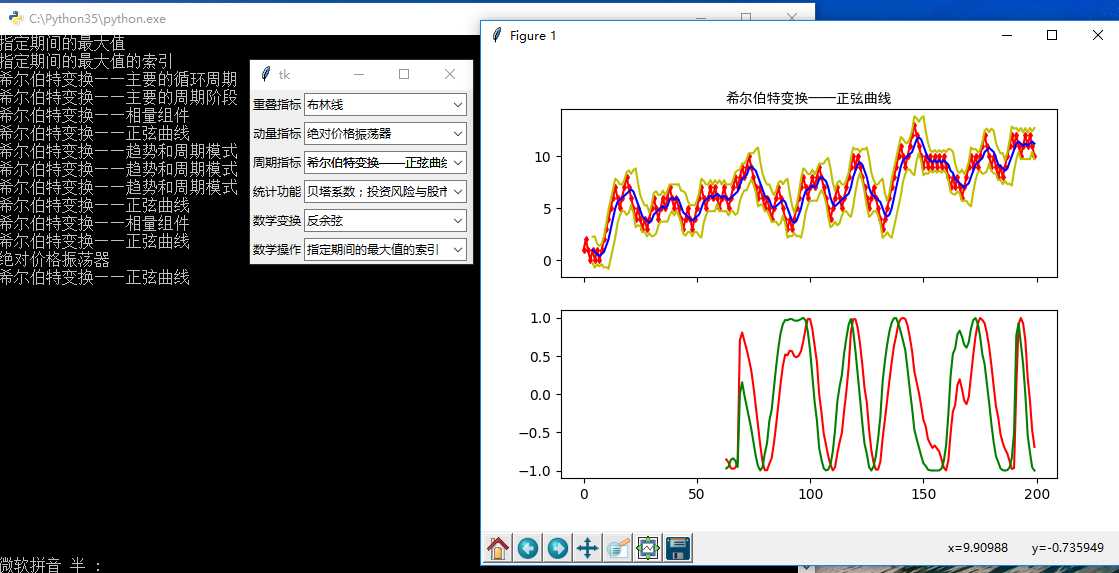
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import talib as ta series = np.random.choice([1, -1], size=200) close = np.cumsum(series).astype(float) # 重叠指标 def overlap_process(event): print(event.widget.get()) overlap = event.widget.get() upperband, middleband, lowerband = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=5, nbdevup=2, nbdevdn=2, matype=0) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True) ax1, ax2 = axes[0], axes[1] axes[0].plot(close, ‘rd-‘, markersize=3) axes[0].plot(upperband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].plot(middleband, ‘b-‘) axes[0].plot(lowerband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].set_title(overlap, fontproperties="SimHei") if overlap == ‘布林线‘: pass elif overlap == ‘双指数移动平均线‘: real = ta.DEMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘指数移动平均线 ‘: real = ta.EMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘希尔伯特变换——瞬时趋势线‘: real = ta.HT_TRENDLINE(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘考夫曼自适应移动平均线‘: real = ta.KAMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘移动平均线‘: real = ta.MA(close, timeperiod=30, matype=0) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘MESA自适应移动平均‘: mama, fama = ta.MAMA(close, fastlimit=0, slowlimit=0) axes[1].plot(mama, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(fama, ‘g-‘) elif overlap == ‘变周期移动平均线‘: real = ta.MAVP(close, periods, minperiod=2, maxperiod=30, matype=0) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘简单移动平均线‘: real = ta.SMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘三指数移动平均线(T3)‘: real = ta.T3(close, timeperiod=5, vfactor=0) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘三指数移动平均线‘: real = ta.TEMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘三角形加权法 ‘: real = ta.TRIMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif overlap == ‘加权移动平均数‘: real = ta.WMA(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) plt.show() # 动量指标 def momentum_process(event): print(event.widget.get()) momentum = event.widget.get() upperband, middleband, lowerband = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=5, nbdevup=2, nbdevdn=2, matype=0) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True) ax1, ax2 = axes[0], axes[1] axes[0].plot(close, ‘rd-‘, markersize=3) axes[0].plot(upperband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].plot(middleband, ‘b-‘) axes[0].plot(lowerband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].set_title(momentum, fontproperties="SimHei") if momentum == ‘绝对价格振荡器‘: real = ta.APO(close, fastperiod=12, slowperiod=26, matype=0) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘钱德动量摆动指标‘: real = ta.CMO(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘移动平均收敛/散度‘: macd, macdsignal, macdhist = ta.MACD(close, fastperiod=12, slowperiod=26, signalperiod=9) axes[1].plot(macd, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(macdsignal, ‘g-‘) axes[1].plot(macdhist, ‘b-‘) elif momentum == ‘带可控MA类型的MACD‘: macd, macdsignal, macdhist = ta.MACDEXT(close, fastperiod=12, fastmatype=0, slowperiod=26, slowmatype=0, signalperiod=9, signalmatype=0) axes[1].plot(macd, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(macdsignal, ‘g-‘) axes[1].plot(macdhist, ‘b-‘) elif momentum == ‘移动平均收敛/散度 固定 12/26‘: macd, macdsignal, macdhist = ta.MACDFIX(close, signalperiod=9) axes[1].plot(macd, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(macdsignal, ‘g-‘) axes[1].plot(macdhist, ‘b-‘) elif momentum == ‘动量‘: real = ta.MOM(close, timeperiod=10) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘比例价格振荡器‘: real = ta.PPO(close, fastperiod=12, slowperiod=26, matype=0) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘变化率‘: real = ta.ROC(close, timeperiod=10) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘变化率百分比‘: real = ta.ROCP(close, timeperiod=10) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘变化率的比率‘: real = ta.ROCR(close, timeperiod=10) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘变化率的比率100倍‘: real = ta.ROCR100(close, timeperiod=10) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘相对强弱指数‘: real = ta.RSI(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘随机相对强弱指标‘: fastk, fastd = ta.STOCHRSI(close, timeperiod=14, fastk_period=5, fastd_period=3, fastd_matype=0) axes[1].plot(fastk, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(fastd, ‘r-‘) elif momentum == ‘三重光滑EMA的日变化率‘: real = ta.TRIX(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) plt.show() # 周期指标 def cycle_process(event): print(event.widget.get()) cycle = event.widget.get() upperband, middleband, lowerband = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=5, nbdevup=2, nbdevdn=2, matype=0) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True) ax1, ax2 = axes[0], axes[1] axes[0].plot(close, ‘rd-‘, markersize=3) axes[0].plot(upperband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].plot(middleband, ‘b-‘) axes[0].plot(lowerband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].set_title(cycle, fontproperties="SimHei") if cycle == ‘希尔伯特变换——主要的循环周期‘: real = ta.HT_DCPERIOD(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif cycle == ‘希尔伯特变换,占主导地位的周期阶段‘: real = ta.HT_DCPHASE(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif cycle == ‘希尔伯特变换——相量组件‘: inphase, quadrature = ta.HT_PHASOR(close) axes[1].plot(inphase, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(quadrature, ‘g-‘) elif cycle == ‘希尔伯特变换——正弦曲线‘: sine, leadsine = ta.HT_SINE(close) axes[1].plot(sine, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(leadsine, ‘g-‘) elif cycle == ‘希尔伯特变换——趋势和周期模式‘: integer = ta.HT_TRENDMODE(close) axes[1].plot(integer, ‘r-‘) plt.show() # 统计功能 def statistic_process(event): print(event.widget.get()) statistic = event.widget.get() upperband, middleband, lowerband = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=5, nbdevup=2, nbdevdn=2, matype=0) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True) ax1, ax2 = axes[0], axes[1] axes[0].plot(close, ‘rd-‘, markersize=3) axes[0].plot(upperband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].plot(middleband, ‘b-‘) axes[0].plot(lowerband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].set_title(statistic, fontproperties="SimHei") if statistic == ‘线性回归‘: real = ta.LINEARREG(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif statistic == ‘线性回归角度‘: real = ta.LINEARREG_ANGLE(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif statistic == ‘线性回归截距‘: real = ta.LINEARREG_INTERCEPT(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif statistic == ‘线性回归斜率‘: real = ta.LINEARREG_SLOPE(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif statistic == ‘标准差‘: real = ta.STDDEV(close, timeperiod=5, nbdev=1) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif statistic == ‘时间序列预测‘: real = ta.TSF(close, timeperiod=14) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif statistic == ‘方差‘: real = ta.VAR(close, timeperiod=5, nbdev=1) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) plt.show() # 数学变换 def math_transform_process(event): print(event.widget.get()) math_transform = event.widget.get() upperband, middleband, lowerband = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=5, nbdevup=2, nbdevdn=2, matype=0) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True) ax1, ax2 = axes[0], axes[1] axes[0].plot(close, ‘rd-‘, markersize=3) axes[0].plot(upperband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].plot(middleband, ‘b-‘) axes[0].plot(lowerband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].set_title(math_transform, fontproperties="SimHei") if math_transform == ‘反余弦‘: real = ta.ACOS(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘反正弦‘: real = ta.ASIN(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘反正切‘: real = ta.ATAN(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘向上取整‘: real = ta.CEIL(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘余弦‘: real = ta.COS(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘双曲余弦‘: real = ta.COSH(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘指数‘: real = ta.EXP(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘向下取整‘: real = ta.FLOOR(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘自然对数‘: real = ta.LN(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘常用对数‘: real = ta.LOG10(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘正弦‘: real = ta.SIN(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘双曲正弦‘: real = ta.SINH(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘平方根‘: real = ta.SQRT(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘正切‘: real = ta.TAN(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_transform == ‘双曲正切‘: real = ta.TANH(close) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) plt.show() # 数学操作 def math_operator_process(event): print(event.widget.get()) math_operator = event.widget.get() upperband, middleband, lowerband = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=5, nbdevup=2, nbdevdn=2, matype=0) fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True) ax1, ax2 = axes[0], axes[1] axes[0].plot(close, ‘rd-‘, markersize=3) axes[0].plot(upperband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].plot(middleband, ‘b-‘) axes[0].plot(lowerband, ‘y-‘) axes[0].set_title(math_operator, fontproperties="SimHei") if math_operator == ‘指定的期间的最大值‘: real = ta.MAX(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_operator == ‘指定的期间的最大值的索引‘: integer = ta.MAXINDEX(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(integer, ‘r-‘) elif math_operator == ‘指定的期间的最小值‘: real = ta.MIN(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) elif math_operator == ‘指定的期间的最小值的索引‘: integer = ta.MININDEX(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(integer, ‘r-‘) elif math_operator == ‘指定的期间的最小和最大值‘: min, max = ta.MINMAX(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(min, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(max, ‘r-‘) elif math_operator == ‘指定的期间的最小和最大值的索引‘: minidx, maxidx = ta.MINMAXINDEX(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(minidx, ‘r-‘) axes[1].plot(maxidx, ‘r-‘) elif math_operator == ‘合计‘: real = ta.SUM(close, timeperiod=30) axes[1].plot(real, ‘r-‘) plt.show() root = tk.Tk() # 第一行:重叠指标 rowframe1 = tk.Frame(root) rowframe1.pack(side=tk.TOP, ipadx=3, ipady=3) tk.Label(rowframe1, text="重叠指标").pack(side=tk.LEFT) overlap_indicator = tk.StringVar() # 重叠指标 combobox1 = ttk.Combobox(rowframe1, textvariable=overlap_indicator) combobox1[‘values‘] = [‘布林线‘,‘双指数移动平均线‘,‘指数移动平均线 ‘,‘希尔伯特变换——瞬时趋势线‘, ‘考夫曼自适应移动平均线‘,‘移动平均线‘,‘MESA自适应移动平均‘,‘变周期移动平均线‘, ‘简单移动平均线‘,‘三指数移动平均线(T3)‘,‘三指数移动平均线‘,‘三角形加权法 ‘,‘加权移动平均数‘] combobox1.current(0) combobox1.pack(side=tk.LEFT) combobox1.bind(‘<<ComboboxSelected>>‘, overlap_process) # 第二行:动量指标 rowframe2 = tk.Frame(root) rowframe2.pack(side=tk.TOP, ipadx=3, ipady=3) tk.Label(rowframe2, text="动量指标").pack(side=tk.LEFT) momentum_indicator = tk.StringVar() # 动量指标 combobox2 = ttk.Combobox(rowframe2, textvariable=momentum_indicator) combobox2[‘values‘] = [‘绝对价格振荡器‘,‘钱德动量摆动指标‘,‘移动平均收敛/散度‘,‘带可控MA类型的MACD‘, ‘移动平均收敛/散度 固定 12/26‘,‘动量‘,‘比例价格振荡器‘,‘变化率‘,‘变化率百分比‘, ‘变化率的比率‘,‘变化率的比率100倍‘,‘相对强弱指数‘,‘随机相对强弱指标‘,‘三重光滑EMA的日变化率‘] combobox2.current(0) combobox2.pack(side=tk.LEFT) combobox2.bind(‘<<ComboboxSelected>>‘, momentum_process) # 第三行:周期指标 rowframe3 = tk.Frame(root) rowframe3.pack(side=tk.TOP, ipadx=3, ipady=3) tk.Label(rowframe3, text="周期指标").pack(side=tk.LEFT) cycle_indicator = tk.StringVar() # 周期指标 combobox3 = ttk.Combobox(rowframe3, textvariable=cycle_indicator) combobox3[‘values‘] = [‘希尔伯特变换——主要的循环周期‘,‘希尔伯特变换——主要的周期阶段‘,‘希尔伯特变换——相量组件‘, ‘希尔伯特变换——正弦曲线‘,‘希尔伯特变换——趋势和周期模式‘] combobox3.current(0) combobox3.pack(side=tk.LEFT) combobox3.bind(‘<<ComboboxSelected>>‘, cycle_process) # 第四行:统计功能 rowframe4 = tk.Frame(root) rowframe4.pack(side=tk.TOP, ipadx=3, ipady=3) tk.Label(rowframe4, text="统计功能").pack(side=tk.LEFT) statistic_indicator = tk.StringVar() # 统计功能 combobox4 = ttk.Combobox(rowframe4, textvariable=statistic_indicator) combobox4[‘values‘] = [‘贝塔系数;投资风险与股市风险系数‘,‘皮尔逊相关系数‘,‘线性回归‘,‘线性回归角度‘, ‘线性回归截距‘,‘线性回归斜率‘,‘标准差‘,‘时间序列预测‘,‘方差‘] combobox4.current(0) combobox4.pack(side=tk.LEFT) combobox4.bind(‘<<ComboboxSelected>>‘, statistic_process) # 第五行:数学变换 rowframe5 = tk.Frame(root) rowframe5.pack(side=tk.TOP, ipadx=3, ipady=3) tk.Label(rowframe5, text="数学变换").pack(side=tk.LEFT) math_transform = tk.StringVar() # 数学变换 combobox5 = ttk.Combobox(rowframe5, textvariable=math_transform_process) combobox5[‘values‘] = [‘反余弦‘,‘反正弦‘,‘反正切‘,‘向上取整‘,‘余弦‘,‘双曲余弦‘,‘指数‘,‘向下取整‘, ‘自然对数‘,‘常用对数‘,‘正弦‘,‘双曲正弦‘,‘平方根‘,‘正切‘,‘双曲正切‘] combobox5.current(0) combobox5.pack(side=tk.LEFT) combobox5.bind(‘<<ComboboxSelected>>‘, math_transform_process) # 第六行:数学操作 rowframe6 = tk.Frame(root) rowframe6.pack(side=tk.TOP, ipadx=3, ipady=3) tk.Label(rowframe6, text="数学操作").pack(side=tk.LEFT) math_operator = tk.StringVar() # 数学操作 combobox6 = ttk.Combobox(rowframe6, textvariable=math_operator_process) combobox6[‘values‘] = [‘指定期间的最大值‘,‘指定期间的最大值的索引‘,‘指定期间的最小值‘,‘指定期间的最小值的索引‘, ‘指定期间的最小和最大值‘,‘指定期间的最小和最大值的索引‘,‘合计‘] combobox6.current(0) combobox6.pack(side=tk.LEFT) combobox6.bind(‘<<ComboboxSelected>>‘, math_operator_process) root.mainloop()
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hhh5460/p/5602357.html