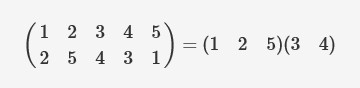As
a unicorn, the ability of using magic is the distinguishing feature
among other kind of pony. Being familiar with composition and
decomposition is the fundamental course for a young unicorn. Twilight
Sparkle is interested in the decomposition of permutations. A
permutation of a set S = {1, 2, ..., n} is a bijection from S to itself.
In the great magician —— Cauchy‘s two-line notation, one lists the
elements of set S in the first row, and then for each element, writes
its image under the permutation below it in the second row. For
instance, a permutation of set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} σ can be written as:

Here σ(1) = 2, σ(2) = 5, σ(3) = 4, σ(4) = 3, and σ(5) = 1.
Twilight
Sparkle is going to decompose the permutation into some disjoint
cycles. For instance, the above permutation can be rewritten as:
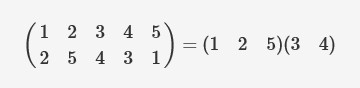
Help Twilight Sparkle find the
lexicographic smallest solution. (Only considering numbers).Input
contains multiple test cases (less than 10). For each test case, the
first line contains one number n (1<=n<=10^5). The second line
contains n numbers which the i-th of them(start from 1) is σ(i).
For each case, output the corresponding result.
(1 2 5)(3 4)
(1)(2)(3)
= = 把a数组设为bool 型,无限WA。。。我真是。。。本来1A的
题意:就是找循环。比如说 1 ->2 -> 5->1 所以 (1,2,5)是一个循环。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
bool vis[N];
int res[N],a[N];
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int j=i;
if(vis[j]) continue;
int id = 0;
while(!vis[j]){
res[id++] = j;
vis[j]=true;
j = a[j];
}
printf("(");
for(int i=0;i<id-1;i++){
printf("%d ",res[i]);
}
printf("%d)",res[id-1]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}