标签:
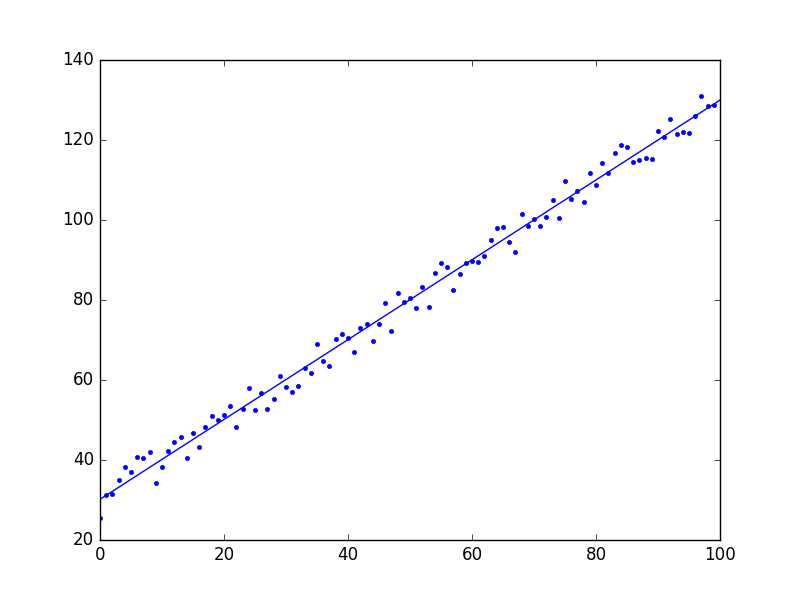
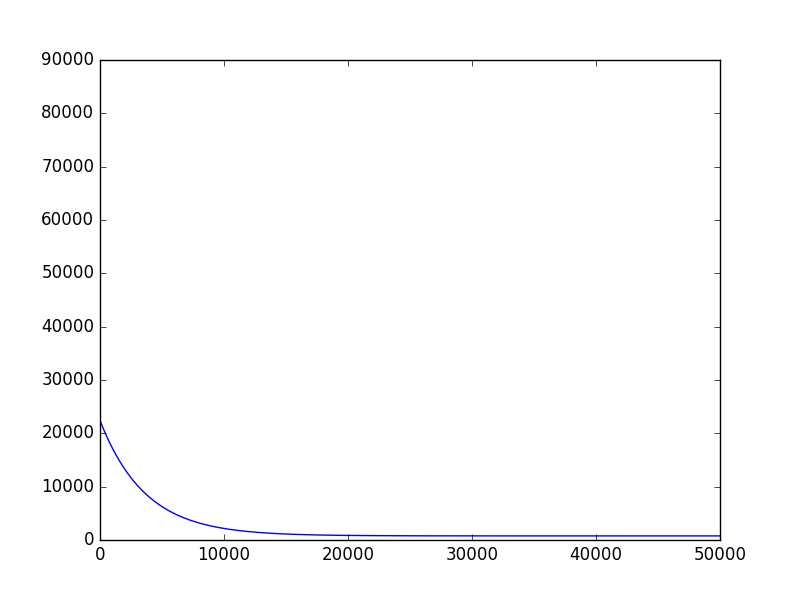
1 # coding:utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 5 def dataN(length): 6 x = np.zeros(shape = (length,2)) 7 y = np.zeros(shape = length) 8 for i in range(0,length): 9 x[i][0] = 1 10 x[i][1] = i 11 y[i] = (i + 25) + np.random.uniform(0,1) *10 12 return x,y 13 14 def alphA(x,y): #选取前20次迭代cost最小的alpha 15 c=float("inf") 16 for k in range(1,1000): 17 a=1.0/k**3 18 f=gD(x,y,20,a)[1][-1] 19 if f>c: 20 break 21 c=f 22 alpha=a 23 return alpha 24 25 def gD(x,y,iter,alpha):#梯度下降 26 theta=np.ones(2) 27 cost=[] 28 for i in range(iter): 29 hypothesis = np.dot(x,theta) 30 loss = hypothesis - y 31 cost.append(np.sum(loss ** 2)) 32 gradient = np.dot(x.transpose(),loss) 33 theta = theta -alpha * gradient 34 return theta,cost 35 36 def sgD(x,y,iter,alpha):#随机梯度下降 37 theta=np.ones(2) 38 cost=[] 39 40 for i in range(iter): 41 l=0 42 for j in range(0,len(y)): 43 loss=theta[1]*x[j][1]+theta[0]-y[j] 44 theta[1]=theta[1]-alpha*x[j][1]*loss 45 theta[0]=theta[0]-alpha*loss 46 l=l+loss**2 47 cost.append(l) 48 return theta,cost 49 50 def eQ(x,y):#正则方程组 51 x=np.matrix(x) 52 y=np.matrix(y).T 53 a=np.dot(x.T,x).I 54 b=np.dot(a,x.T) 55 c=np.dot(b,y) 56 return c 57 58 def exP(x,y):#一元线性回归拟合方程 59 xmean=np.mean(x) 60 ymean=np.mean(y) 61 b=np.sum([(x1-xmean)*(y1-ymean)for x1,y1 in zip(x,y)])/np.sum([(x1-xmean)**2 for x1 in x]) 62 a=ymean-b*xmean 63 return a,b 64 65 length=100 66 iter=50000 67 x,y=dataN(length) 68 #theta,cost=sgD(x,y,iter,alphA(x,y)) #[ 30.24623439 0.99707473] 69 theta,cost=gD(x,y,iter,alphA(x,y)) #[ 30.17228028 0.99806093] 70 print theta 71 print eQ(x,y) #[[ 30.20320097][ 0.99759475]] 72 print exP(x[:,1],y) #与正则方程组结果一致 73 74 plt.figure(1) 75 plt.plot(range(iter),cost) 76 plt.figure(2) 77 plt.plot(x[:,1],y,‘b.‘) 78 plt.plot([0,length],[theta[0],theta[0]+length*theta[1]]) 79 plt.show()
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qw12/p/5638970.html