标签:
二叉树基础:
刚看到堆排序,顺便记录一下关于树的一些基本概念:
前面介绍的栈、队列都是线性结构(linear structure)。而树是非线性结构(non-linear structure)。因此,树中的元素之间一般不存在类似于线性结构的一对一的关系,更多地表现为多对多的关系。直观地看,它是数据元素(在树中称为节点)按分支关系组织起来的结构。显然,树形结构是比线性结构更复杂的一种数据结构类型。
树的定义:树是含有n个节点的有穷集合,其中有一个节点比较特殊称为根节点。在图示树时,用一条边连接两个有逻辑关系的节点,这个关系被称为父子关系。
二叉树(Binary Tree)由节点的有限集合构成。这个集合或者为空集,或者为由一个根节点(root)和两棵互不相交,分别称为这个根的左子树(left subtree)和右子树(right subtree)的二叉树组成的集合。
一棵二叉树的示意图:
 个结点。若共有k层,则最多有节点
个结点。若共有k层,则最多有节点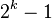 个。
个。 ,即logn向下取整,高度从0计数。
,即logn向下取整,高度从0计数。 ,层数从0计数。这个量在选择排序:树形选择中用到了。
,层数从0计数。这个量在选择排序:树形选择中用到了。
二叉树遍历:
在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。

一颗简单的二叉树
二叉树的遍历分为三种:前(先)序、中序、后序遍历。
设L、D、R分别表示二叉树的左子树、根结点和遍历右子树,则先(根)序遍历二叉树的顺序是DLR,中(根)序遍历二叉树的顺序是LDR,后(根)序遍历二叉树的顺序是LRD。还有按层遍历二叉树。这些方法的时间复杂度都是O(n),n为结点个数。
假设我们有一个包含值的value和指向两个子结点的left和right的树结点结构。我们可以写出这样的过程:
先序遍历(递归实现): 中序遍历(递归实现):
visit(node)
if node.left != null then visit(node.left)
print node.value
if node.right != null then visit(node.right)
后序遍历(递归实现):
visit(node)
if node.left != null then visit(node.left)
if node.right != null then visit(node.right)
print node.value
二叉树创建和遍历:
public class BinaryTree {
private Node root;
/**
*
* 内部节点类
* @author yhh
*/
private class Node{
private Node left;
private Node right;
private int data;
public Node(int data){
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
public BinaryTree(){
root = null;
}
/**
* 递归创建二叉树
* @param node
* @param data
*/
public void buildTree(Node node,int data){
if(root == null){
root = new Node(data);
}else{
if(data < node.data){
if(node.left == null){
node.left = new Node(data);
}else{
buildTree(node.left,data);
}
}else{
if(node.right == null){
node.right = new Node(data);
}else{
buildTree(node.right,data);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 前序遍历
* @param node
*/
public void preOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
System.out.println(node.data);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
* @param node
*/
public void inOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.println(node.data);
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历
* @param node
*/
public void postOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2,4,12,45,21,6,111};
BinaryTree bTree = new BinaryTree();
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
bTree.buildTree(bTree.root, a[i]);
}
bTree.preOrder(bTree.root);
bTree.inOrder(bTree.root);
bTree.postOrder(bTree.root);
}
} 插入操作
二叉树查找树b插入操作x的过程如下:
具体代码:
public void insert(T t)
{
rootTree = insert(t, rootTree);
}
public BinaryNode insert(T t,BinaryNode node)
{
if(node==null)
{
//新构造一个二叉查找树
return new BinaryNode(t, null, null);
}
int result = t.compareTo(node.data);
if(result<</SPAN>0)
node.left= insert(t,node.left);
else if(result>0)
node.right= insert(t,node.right);
else
;//doNothing
return node;
} 


具体代码:
public void remove(T t)
{
rootTree = remove(t,rootTree);
}
public BinaryNode remove(T t,BinaryNode node)
{
if(node == null)
return node;//没有找到,doNothing
int result = t.compareTo(node.data);
if(result>0)
node.right = remove(t,node.right);
else if(result<</SPAN>0)
node.left = remove(t,node.left);
else if(node.left!=null&&node.right!=null)
{
node.data = findMin(node.right).data;
node.right = remove(node.data,node.right);
}
else
node = (node.left!=null)?node.left:node.right;
return node;
}
查找二叉树节点:
在二叉查找树中查找x的过程如下:
1、若二叉树是空树,则查找失败。
2、若x等于根结点的数据,则查找成功,否则。
3、若x小于根结点的数据,则递归查找其左子树,否则。
4、递归查找其右子树。
具体代码:
public TreeNode search(int Key) {
TreeNode node = root;
// 首先定义一个节点让其指向根,在下面的循环中
// 只要节点值不等于要查找的节点值就进入循环如果没有找到则返回null
while (node.keyValue != Key) {
if (Key < node.keyValue) { // 如果要查找的值小于节点值则指向左节点
node = node.leftNode;
} else { // 否则指向右节点
node = node.rightNode;
}
if (node == null) { // 如果节点为空了则返回null
return null;
}
}
return node;
}
思路:最大值一直往右走,最小值一直往左走。
具体代码:
public int max() {
TreeNode node = root;
TreeNode parent = null;
while (node != null) {
parent = node;
node = node.rightNode;
}
return parent.keyValue;
}
public int min() {
TreeNode node = root;
TreeNode parent = null;
while (node != null) {
parent = node;
node = node.leftNode;
}
return parent.keyValue;
} 具体代码:
int length(Node root){
int depth1;
int depth2;
if(root == null) return 0;
//左子树的深度
depth1 = length(root.right);
//右子树的深度
depth2 = length(root.left);
if(depth1>depth2)
return depth1+1;
else
return depth2+1;
}
参考链接:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_401823210101f8t6.html
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_937cbcc10101dmqm.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/wuchanming/p/4067951.html
http://blog.csdn.net/fansongy/article/details/6798278
http://www.cricode.com/3489.html
http://www.cricode.com/3212.html
http://blog.csdn.net/sjf0115/article/details/8645991
http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei/archive/2013/03/17/2962290.html
http://blog.csdn.net/sysu_arui/article/details/7865876
http://blog.163.com/xiaopengyan_109/blog/static/14983217320108168618624/
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/laokdidiao/article/details/51860741