标签:
1.我们在网站上注册账号时,当填好用户名后,系统都会判断用户名是否已被使用,如果已被使用,系统就会提示该用户名已被注册。系统是如何检测用户名是否被使用的?
可以用哈希表来解决这个问题。哈希表又叫散列表,关键值通过哈希函数映射到数组上,查找时通过关键值直接访问数组。在上面的例子里,我们将用户名通过哈希函数映射成一个整数,也就是数组的存储位置,在检测时用同样方法计算出存储位置,如果位置上已有元素则表示用户名已经被注册。
哈希函数指的是关键值和存储位置建立的对应关系,查找时只要根据这个关系就能找到目标位置。一般我们只要通过一次查找就能找到目标位置,但有些关键字需要多次比较和查找才能找到,这是为什么呢?因为哈希表里,可能存在关键字不同但是哈希地址相同的情况,也就是冲突。一般情况下,冲突是不可避免的,因为关键字集合往往比哈希地址集合大很多。
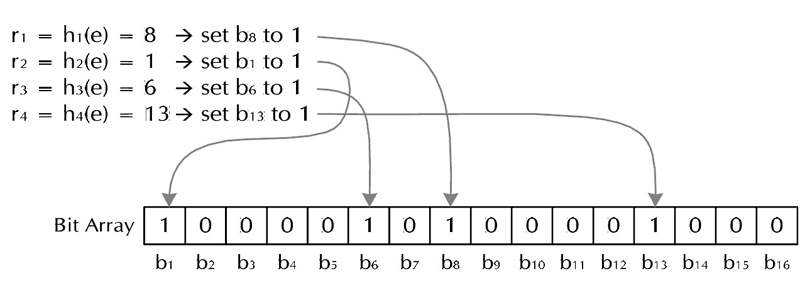
提高哈希表的查找效率,关键在与哈希函数的构造和解决冲突的方法。哈希函数的构造方法有很多种,我们应该如何构造优秀的哈希函数来减少冲突呢?如果发生了冲突,我们该如何处理冲突,减少比较次数提高查找效率呢?
2.性质
3.设计哈希函数没有统一的方法,同一个哈希函数不一定能适用所有问题,其产生的影响也是不一样的。哈希函数的设计又是至关重要的,那么我们该如何设计呢?一般来说,设计哈希函数时要达到两个要求:计算简单,计算复杂的哈希函数会增加查询的时间;关键字尽可能地均分到存储地址上,这样可以减少冲突。
4.哈希表的构造,插入,查询,和重建
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 class HashTable { 5 private: 6 string *elem; 7 int size; 8 public: 9 HashTable() { 10 size = 2000; 11 elem = new string[size]; 12 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 13 elem[i] = "#"; 14 } 15 } 16 ~HashTable() { 17 delete[] elem; 18 } 19 int hash(string& index) { 20 int code = 0; 21 for (size_t i = 0; i < index.length(); i++) { 22 code = (code * 256 + index[i] + 128) % size; //避免负数所以加上128,相加时用的ASCII码的值 23 } 24 return code; 25 } 26 bool search(string& index, int& pos, int& times) { //开放地址法 27 pos = hash(index); 28 times = 0; //记录冲突次数 29 while (elem[pos] != "#" && elem[pos] != index) { 30 times++; 31 if (times < size) { 32 pos = (pos + 1) % size; 33 } else { 34 return false; 35 } 36 } 37 if (elem[pos] == index) { 38 return true; 39 } else { 40 return false; 41 } 42 } 43 int insert(string& index) { 44 int pos, times; 45 if (search(index, pos, times)) { 46 return 2; 47 } else if (times < size / 2) { 48 elem[pos] = index; 49 return 1; 50 } else { 51 recreate(); 52 return 0; 53 } 54 } 55 void recreate(){ 56 string *temp_elem; 57 temp_elem=new string[size]; 58 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 59 temp_elem[i]=elem[i]; 60 } 61 int copy_size=size; 62 size=size*2; 63 delete[]elem; 64 elem=new string[size]; 65 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 66 elem[i]="#"; 67 } 68 for(int i=0;i<copy_size;i++){ 69 if(temp_elem[i]!="#"){ 70 insert(temp_elem[i]); 71 } 72 } 73 delete[]temp_elem; 74 } 75 }; 76 int main() { 77 HashTable hashtable; 78 string buffer; 79 int n; 80 cin >> n; 81 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 82 cin >> buffer; 83 int ans = hashtable.insert(buffer); 84 if (ans == 0) { 85 cout << "insert failed!" << endl; 86 } else if (ans == 1) { 87 cout << "insert success!" << endl; 88 } else if (ans == 2) { 89 cout << "It already exists!" << endl; 90 } 91 } 92 int temp_pos, temp_times; 93 cin >> buffer; 94 if (hashtable.search(buffer, temp_pos, temp_times)) { 95 cout << "search success!" << endl; 96 } else { 97 cout << "search failed!" << endl; 98 } 99 return 0; 100 }
5.应用:忽略大小写筛选用户名
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cctype> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 class HashTable { 7 private: 8 string *elem; 9 int size; 10 public: 11 HashTable() { 12 size = 300000; 13 elem = new string[size]; 14 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 15 elem[i] = "#"; 16 } 17 } 18 ~HashTable() { 19 delete[] elem; 20 } 21 int hash(string& index) { 22 int code = 0; 23 for (size_t i = 0; i < index.length(); i++) { 24 code = (code * 256 + index[i] + 128) % size; 25 } 26 return code; 27 } 28 bool search(string& index, int& pos, int& times) { 29 pos = hash(index); 30 times = 0; 31 while (elem[pos] != "#" && elem[pos] != index) { 32 times++; 33 if (times < size) { 34 pos = (pos + 1) % size; 35 } else { 36 return false; 37 } 38 } 39 if (elem[pos] == index) { 40 return true; 41 } else { 42 return false; 43 } 44 } 45 int insert(string& index) { 46 int pos, times; 47 if (search(index, pos, times)) { 48 return 2; 49 } else if (times < size / 2) { 50 elem[pos] = index; 51 return 1; 52 } else { 53 recreate(); 54 return 0; 55 } 56 } 57 void recreate(){ 58 string *temp_elem; 59 temp_elem=new string[size]; 60 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 61 temp_elem[i]=elem[i]; 62 } 63 int copy_size=size; 64 size=size*2; 65 delete[]elem; 66 elem=new string[size]; 67 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 68 elem[i]="#"; 69 } 70 for(int i=0;i<copy_size;i++){ 71 if(temp_elem[i]!="#"){ 72 insert(temp_elem[i]); 73 } 74 } 75 delete[]temp_elem; 76 } 77 }; 78 int main() { 79 HashTable hashtable; 80 string buffer; 81 int n; 82 cin >> n; 83 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 84 cin >> buffer; 85 transform(buffer.begin(),buffer.end(),buffer.begin(),::tolower); 86 int ans = hashtable.insert(buffer); 87 if (ans == 0) { 88 cout << "No" << endl; 89 } else if (ans == 1) { 90 cout << "No" << endl; 91 } else if (ans == 2) { 92 cout << "Yes" << endl; 93 } 94 } 95 96 return 0; 97 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Reindeer/p/5674575.html