标签:
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 16537 | Accepted: 5981 |
Description
You are given a sequence of n integers a1 , a2 , ... , an in non-decreasing order. In addition to that, you are given several queries consisting of indices i and j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n). For each query, determine the most frequent value among the integers ai , ... , aj.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers n and q (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 100000). The next line contains n integers a1 , ... , an (-100000 ≤ ai ≤ 100000, for each i ∈ {1, ..., n}) separated by spaces. You can assume that for each i ∈ {1, ..., n-1}: ai ≤ ai+1. The following q lines contain one query each, consisting of two integers i and j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n), which indicate the boundary indices for the
query.
The last test case is followed by a line containing a single 0.
Output
For each query, print one line with one integer: The number of occurrences of the most frequent value within the given range.
Sample Input
10 3 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 3 10 10 10 2 3 1 10 5 10 0
Sample Output
1 4 3
Source
先讲一下题目大意,给出一个有n个数的不下降数列,和q个问题每个问题是求[a,b]中出现次数最多的数出现的次数,
有多组测试数据,当n = 0时测试结束
方法有多种,第一种直接暴力枚举,就不讲了
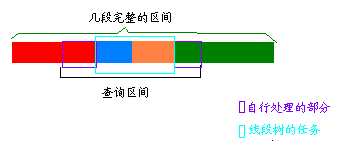
第二种用线段树,很多时候都不是完整的区间,怎么查?
左右两端不完整区间连续的个数是可以求出来的,这个就比较简单,记录一下每个区间开始的位置
,然后再弄个数组,记录第i个数属于的区间的新编号,如果a不是一个短的开始就就用下一个区间的
开始减去a (就把编号 + 1就是下一个区间的编号),结束部分就基本一样了
中间完整的区间就交给线段树查,最好是
把一个区间当成长度为1的线段,建树,查的时候就对应这个编号就行了。
由于我不想写,所以就不给代码了,可以在网上查查
第三种使用RMQ,反正又不会更新,再比较查询的时间复杂度,线段树的查询是O(log2N),而O(1)(自行忽略
log函数执行的时间或者打表的时间),线段树建树的时间复杂度貌似是O(2N)左右(大约实际有效的节点是原数组的2
倍),ST算法的预处理时间是O(nlog2n)看起来差不多
ST算法的思路和上面差不多,两端单独处理,中间交给ST算法去查。
另外:
1.用位运算时一定要加上括号,位运算优先级很低,之前没在意,RE了几次
2.每次完成一轮计算该清0的清0,该还原的还原
Code:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<cmath> 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef class MyData{ 7 private: 8 MyData(int from,int end,int _count):from(from),end(end),_count(_count){} 9 public: 10 int from; 11 int end; 12 int _count; 13 MyData(){} 14 static MyData getNULL(){ 15 return MyData(0,0,0); 16 } 17 }MyData; 18 vector<MyData> list; 19 int a = -1000000,b; 20 int *pos; 21 int count1; 22 int f[100001][20]; 23 int t; 24 int n,q; 25 void init(){ 26 const int limit = list.size(); 27 for(int i = 0;i < limit;i++) 28 f[i][0] = list[i]._count; 29 for(int j = 1; (1 << j) < limit;j++){ 30 t = 1 << j; 31 for(int i = 0; i < limit && (i + t) < limit; i++){ 32 f[i][j] = max(f[i][j - 1], f[ i + (1 << j - 1) ][j - 1]); //位运算优先级低!!!打括号 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 int main(){ 37 while(true){ 38 scanf("%d",&n); 39 if(n == 0) break; 40 scanf("%d",&q); 41 pos = new int[(const int)(n + 1)]; 42 for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){ 43 scanf("%d",&b); 44 if(a == b){ 45 list[list.size() - 1]._count++; 46 pos[i] = pos[i - 1]; 47 }else{ 48 if(!list.empty()) 49 list[list.size() - 1].end = i - 1; 50 list.push_back(MyData::getNULL()); 51 pos[i] = count1++; 52 list[list.size() - 1].from = i; 53 list[list.size() - 1]._count = 1; 54 } 55 a = b; 56 } 57 list[list.size() - 1].end = n; 58 init(); 59 for(int i = 1;i <= q;i++){ 60 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 61 if(pos[a] == pos[b]){ 62 printf("%d\n",b - a + 1); 63 continue; 64 } 65 if(pos[b] - pos[a] == 1){ 66 int result = max(list[pos[a]].end - a + 1,b - list[pos[b]].from + 1); 67 printf("%d\n",result); 68 continue; 69 } 70 int ans = 0; 71 ans = max(list[pos[a]].end-a+1,b-list[pos[b]].from+1); 72 b = pos[b] - 1; 73 a = pos[a] + 1; 74 int k = (int)(log((double)b-a+1.0)/log(2.0)); 75 int t2 = max(f[a][k],f[b-(1<<k)+1][k]); 76 ans = max(ans,t2); 77 printf("%d\n",ans); 78 } 79 delete[] pos; 80 list.clear(); 81 count1 = 0; 82 a = -1000000; 83 } 84 return 0; 85 }
[后记]
附赠调试这道题时所用的对拍器、比较程序和数据生成器
cmp.cpp:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 char buf1[1000]; 6 char buf2[1000]; 7 FILE *fin1; 8 FILE *fin2; 9 int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ 10 fin1 = fopen(argv[1],"r"); 11 fin2 = fopen(argv[2],"r"); 12 while(!(feof(fin1))&&!(feof(fin2))){ 13 fscanf(fin1,"%s",buf1); 14 fscanf(fin2,"%s",buf2); 15 if(strcmp(buf1, buf2) != 0) return 1; 16 } 17 if(feof(fin1) != feof(fin2)) return 1; 18 return 0; 19 }
md_fv.cpp:
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<cstdlib> #include<time.h> using namespace std; ofstream fout("fv.in"); int main(){ srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int n = rand()%100 + 1; int q = rand()%100 + 1; fout<<n<<" "<<q<<endl; int start = rand()%1000 - 500; for(int i =1; i<= n;i++){ start += rand()%2; fout<<start<<" "; } fout<<endl; for(int i = 0;i < q;i++){ start = rand()%n + 1; int end = min(rand()%(n - start + 1) + start,n); fout<<start<<" "<<end<<endl; } fout<<"0"<<endl; return 0; }
test_fv.cpp:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<time.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef bool boolean; 6 int statu; 7 boolean aFlag; 8 int main(){ 9 system("g++ fv.cpp -o fv.exe"); 10 system("g++ cmp.cpp -o cmp.exe"); 11 system("g++ md_fv.cpp -o md_fv.exe"); 12 system("g++ std.fv.cpp -o std.fv.exe"); 13 for(int i = 0;i < 1000;i++){ 14 aFlag = true; 15 system("md_fv"); 16 system("std.fv"); 17 clock_t begin = clock(); 18 statu = system("fv"); 19 clock_t end = clock(); 20 cout<<"测试数据#"<<i<<":"; 21 if(statu != 0){ 22 cout<<"RuntimeError"; 23 }else if(system("cmp fv1.out fv.out") != 0){ 24 cout<<"WrongAnswer"; 25 }else{ 26 cout<<"Accepted"; 27 aFlag = false; 28 } 29 cout<<"\t\tTime:"<<(end - begin)<<"ms"<<endl; 30 if(aFlag){ 31 system("pause"); 32 } 33 } 34 return 0; 35 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yyf0309/p/5676751.html