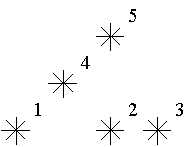Astronomers often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of the given
star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels of the stars.
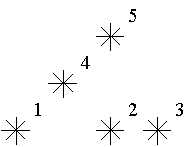
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it‘s formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level
0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
The first line of the input file contains a number of stars N (1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars (two integers X and Y per line separated by a space, 0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one
point of the plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
The output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the level N-1.
因为题目已经按照y的坐标排序,如果y相同,按x也已经排序,那么当前点进来,只要找到不大于x的坐标的点的数量就可以了,等级说白了就是有0个点小于x的坐标,有一个点小于x的坐标。。依次下去。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#define lson o<<1, l, m
#define rson o<<1|1, m+1, r
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAX=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 32222;
int sum[maxn<<2], ans[15005], n, x, y, t; // ans数组记录 该等级的数量
void up(int o) {
sum[o] = sum[o<<1] + sum[o<<1|1];
}
void in(int o, int l, int r) {
if(l == r) {
t += sum[o];
sum[o]++;
return ;
}
int m = (l+r) >> 1;
if(x <= m) {
in(lson);
} else {
t += sum[o<<1];
in(rson);
}
up(o);
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d", &n)) {
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
t = 0;
in(1, 0, 32000);
ans[t]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= n-1; i++)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}