标签:
Description
在一个平面上有N 个首位相连的杠杆.初始所有杠杆都为1 个单位长度。第一根杠杆左
侧位于(0,0)处。所有杠杆水平放置。
现在我会对这些杠杆进行以下两种操作:
1.拉伸
此操作标号为1,意为将某根杠杆沿原放向伸长x 个单位.
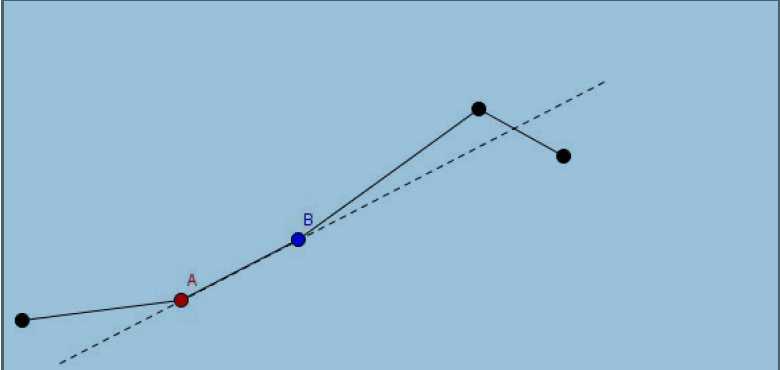
2.旋转
此标号操作为2,意为将某根杠杆逆时针伸长x 度.
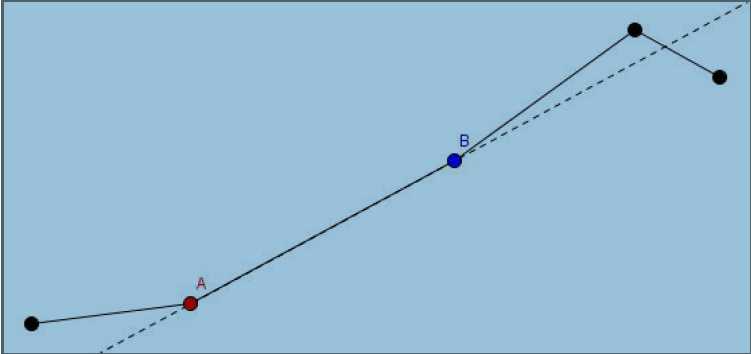
现在,我关心的是每次操作后第N 个杠杆的右侧在哪里呢?
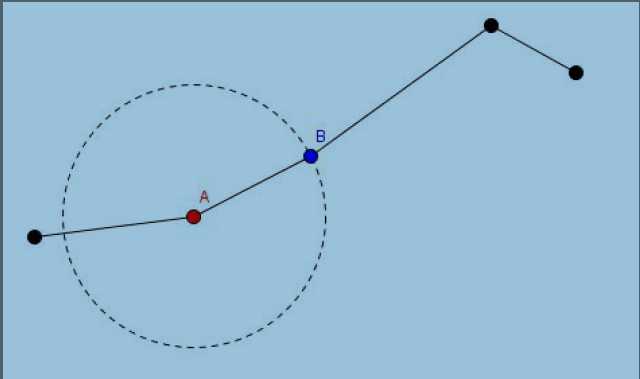
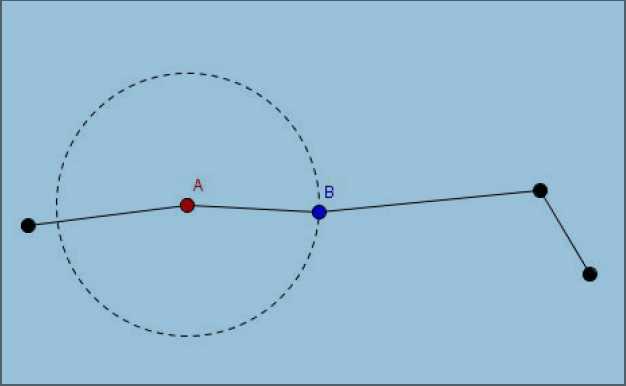
Input
第一行两个整数N,M 表示杠杆数和操作数.
接下来若干行,每行三个数x,y,z.
若x=1,表示对第y 根杠杆伸长z 个单位.
若x=2,表示对第y 根杠杆逆时针旋转z 度
Output
对于每个操作,输出一个坐标x,y 表示第N 根杠杆右侧的位置.精确到6 位小数.
Sample Input
5 4
1 1 3
2 3 90
2 5 48
1 4 1
Sample Output
8.000000 0.000000
5.000000 -3.000000
4.256855 -2.669131
4.256855 -3.669131
Hint
30%数据有n,m<=100
60%数据有n,m<=2000
100%数据保证n,m<=300000 1<=x<=2 1<=y<=n 1<=z<=359
题的意思是有一排小木棍水平放置,有两种操作,1:单点修改1根小木棍的长度,2:修改某一个木棍的旋转角度。
维护小木棍的每一个末尾的点,分别有与x的夹角angle,因为angle可以直接相加减,然后每一次操作都要输出最后的那一个的横坐标纵坐标,那么我们就可以维护一个支点相对于前一个支点的dx值,那么最后一个点就是sigma(dx),那么索性就直接维护sigma(dx)——>sx好了,sy同理.
单点修改某一根木棍的len,那么那一个点的sx = cos(angle/180*pi)*len,sy = sin(angle/180*pi)*len.
把一根木棍旋转了,那么以后的所有木棍与x轴成的角都会增加,也就是区间修改角度.
我们知道sx = cos(a1)*l1 + cos(a2)*l2 + cos(a3)*l3 + ...cos(an)*ln,sy = sin(a1)*l1 + sin(a2)*l2 + sin(a3)*l3 + ...sin(an)*ln
增加f的角度
sx = cos(a1+f)*l1 + cos(a2+f)*l2 + cos(a3+f)*l3 + ...cos(an+f)*ln
把余弦打开,sx = cos(f)*(cos(a1)*l1 + cos(a2)*l2 + cos(a3)*l3 + ...cos(an)*ln)-sin(f)*(sin(a1)*l1 + sin(a2)*l2 + sin(a3)*l3 + ...sin(an)*ln)
所以,sx = cos(f)*sx - sin(f)*sy
同理,sy = cos(f)*sx + sin(f)*sy
那么我们需要维护的值有sx(sigma(dx)),sy(sigma(dy)),每一个与x轴成的角度,每一个木棒的长度,区间修改的角度的懒惰标记.
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 300010;
const double pi = acos(-1.0);
struct node{
double angle,sx,sy,sl,rk;
}tree[N<<2];
#define lson k<<1,l,mid
#define rson k<<1|1,mid+1,r
void pushup(int k){
tree[k].sx = tree[k<<1].sx+tree[k<<1|1].sx;
tree[k].sy = tree[k<<1].sy+tree[k<<1|1].sy;
}
void processdown(int k){
double sx,sy;
double &res = tree[k].rk;
if(res == 0)return;
sx = tree[k<<1].sx;
sy = tree[k<<1].sy;
tree[k<<1].rk += res;
tree[k<<1].sx = cos(tree[k<<1].rk/180.0*pi)*sx-sin(tree[k<<1].rk/180.0*pi)*sy;
tree[k<<1].sy = sin(tree[k<<1].rk/180.0*pi)*sx+cos(tree[k<<1].rk/180.0*pi)*sy;
sx = tree[k<<1|1].sx;
sy = tree[k<<1|1].sy;
tree[k<<1|1].rk += res;
tree[k<<1|1].sx = cos(tree[k<<1|1].rk/180.0*pi)*sx-sin(tree[k<<1|1].rk/180.0*pi)*sy;
tree[k<<1|1].sy = sin(tree[k<<1|1].rk/180.0*pi)*sx+cos(tree[k<<1|1].rk/180.0*pi)*sy;
res = 0;
}
void build(int k,int l,int r){
if(l == r){
tree[k].sx = tree[k].sl = 1;
tree[k].sy = tree[k].angle = 0;
return;
}
processdown(k);
int mid = (l+r)>>1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
pushup(k);
}
void updateLen(int k,int l,int r,int x,double value){
if(l == r){
tree[k].sl += value;
tree[k].angle += tree[k].rk;
tree[k].rk = 0;
tree[k].sx = cos(tree[k].angle/180.0*pi)*tree[k].sl;
tree[k].sy = sin(tree[k].angle/180.0*pi)*tree[k].sl;
return;
}
processdown(k);
int mid = (l+r)>>1;
if(x <= mid)updateLen(lson,x,value);
else if(x > mid)updateLen(rson,x,value);
pushup(k);
}
void updateAngle(int k,int l,int r,int ql,int qr,double value){
if(l == ql && r == qr){
tree[k].rk -= value;
double sx = tree[k].sx,sy = tree[k].sy;
tree[k].sx = cos(-value/180.0*pi)*sx-sin(-value/180.0*pi)*sy;
tree[k].sy = sin(-value/180.0*pi)*sx+cos(-value/180.0*pi)*sy;
return;
}
processdown(k);
int mid = (l+r)>>1;
if(qr <= mid)updateAngle(lson,ql,qr,value);
else if(ql > mid)updateAngle(rson,ql,qr,value);
else updateAngle(lson,ql,mid,value),updateAngle(rson,mid+1,qr,value);
pushup(k);
}
int main(){
freopen("stick.in","r",stdin);
freopen("stick.out","w",stdout);
double x;int n,m,flag,id;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m;
build(1,1,n);
while(m--){
cin>>flag>>id>>x;
if(flag == 1){
updateLen(1,1,n,id,x);
}
if(flag == 2){
updateAngle(1,1,n,id,n,x);
}
printf("%.6lf %.6lf\n",tree[1].sx,tree[1].sy);
}
return 0;
}
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xgtao984/p/5719816.html