标签:
今日内容
?
在Service中使用ThreadLocal来完成事务,为将来学习Spring事务打基础!
在DAO中处理事务真是"小菜一碟"。
public void xxx() { Connection con = null; try { con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); con.setAutoCommitted(false); QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(); String sql = …; Object[] params = …; qr.update(con, sql, params); sql = …; Object[] params = …; qr.update(con, sql, params); con.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { try { if(con != null) {con.rollback();} } catch(Exception e) {} } finally { try { con.close(); } catch(Exception e) {} } }? |
?
我们要清楚一件事,DAO中不是处理事务的地方,因为DAO中的每个方法都是对数据库的一次操作,而Service中的方法才是对应一个业务逻辑。也就是说我们需要在Service中的一方法中调用DAO的多个方法,而这些方法应该在一起事务中。
怎么才能让DAO的多个方法使用相同的Connection呢?方法不能再自己来获得Connection,而是由外界传递进去。
public void daoMethod1(Connection con, …) { } public void daoMethod2(Connection con, …) { }? |
?
在Service中调用DAO的多个方法时,传递相同的Connection就可以了。
public class XXXService() { private XXXDao dao = new XXXDao(); public void serviceMethod() { Connection con = null; try { con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); con.setAutoCommitted(false); dao.daoMethod1(con, …); dao.doaMethod2(con, …); com.commint(); } catch(Exception e) { try { con.rollback(); } catch(Exception e) {} } finally { try { con.close(); } catch(Exception e) {} } } }? |
?
但是,在Service中不应该出现Connection,它应该只在DAO中出现,因为它是JDBC的东西,JDBC的东西是用来连接数据库的,连接数据库是DAO的事儿!!!但是,事务是Service的事儿,不能放到DAO中!!!
?
我们把对事务的开启和关闭放到JdbcUtils中,在Service中调用JdbcUtils的方法来完成事务的处理,但在Service中就不会再出现Connection这一"禁忌"了。
DAO中的方法不用再让Service来传递Connection了。DAO会主动从JdbcUtils中获取Connection对象,这样,JdbcUtils成为了DAO和Service的中介!
我们在JdbcUtils中添加beginTransaction()和rollbackTransaction(),以及commitTransaction()方法。这样在Service中的代码如下:
public class XXXService() { private XXXDao dao = new XXXDao(); public void serviceMethod() { try { JdbcUtils.beginTransaction(); dao.daoMethod1(…); dao.daoMethod2(…); JdbcUtils.commitTransaction(); } catch(Exception e) { JdbcUtils.rollbackTransaction(); } } }? |
?
DAO
public void daoMethod1(…) { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); } public void daoMethod2(…) { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); }? |
?
在Service中调用了JdbcUtils.beginTransaction()方法时,JdbcUtils要做准备好一个已经调用了setAuthCommitted(false)方法的Connection对象,因为在Service中调用JdbcUtils.beginTransaction()之后,马上就会调用DAO的方法,而在DAO方法中会调用JdbcUtils.getConnection()方法。这说明JdbcUtils要在getConnection()方法中返回刚刚准备好的,已经设置了手动提交的Connection对象。
?
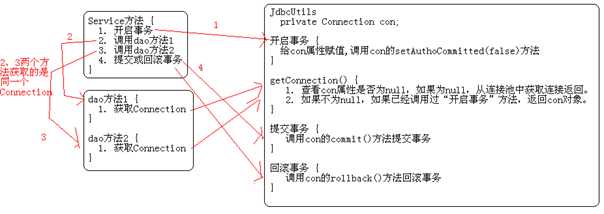
在JdbcUtils中创建一个Connection con属性,当它为null时,说明没有事务!当它不为null时,表示开启了事务。
?
beginTransaction()
判断con是否为null,如果不为null,就抛出异常!
如果con为null,那么从连接池中获取一个Connection对象,赋值给con!然后设置它为"手动提交"。
?
getConnection()
判断con是否为null,如果为null说明没有事务,那么从连接池获取一个连接返回;
如果不为null,说明已经开始了事务,那么返回con属性返回。这说明在con不为null时,无论调用多少次getConnection()方法,返回的都是同个Connection对象。
?
commitTransaction()
判断con是否为null,如果为null,说明没有开启事务就提交事务,那么抛出异常;
如果con不为null,那么调用con的commit()方法来提交事务;
调用con.close()方法关闭连接;
con = null,这表示事务已经结束!
?
rollbackTransaction()
判断con是否为null,如果为null,说明没有开启事务就回滚事务,那么抛出异常;
如果con不为null,那么调用con的rollback()方法来回滚事务;
调用con.close()方法关闭连接;
con = null,这表示事务已经结束!
?
JdbcUtils.java
public class JdbcUtils { ????private static DataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); ????private static Connection con = null; ? ????public static DataSource getDataSource() { ????????return dataSource; ????} ? ????public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { ????????if(con == null) { ????????????return dataSource.getConnection(); ????????} ????????return con; ????} ???? ????public static void beginTranscation() throws SQLException { ????????if(con != null) { ????????????throw new SQLException("事务已经开启,在没有结束当前事务时,不能再开启事务!"); ????????} ????????con = dataSource.getConnection(); ????????con.setAutoCommit(false); ????} ???? ????public static void commitTransaction() throws SQLException { ????????if(con == null) { ????????????throw new SQLException("当前没有事务,所以不能提交事务!"); ????????} ????????con.commit(); ????????con.close(); ????????con = null; ????} ???? ????public static void rollbackTransaction() throws SQLException { ????????if(con == null) { ????????????throw new SQLException("当前没有事务,所以不能回滚事务!"); ????????} ????????con.rollback(); ????????con.close(); ????????con = null;???????? ????} } |
?
现在JdbcUtils有个问题,如果有两个线程!第一个线程调用了beginTransaction()方法,另一个线程再调用beginTransaction()方法时,因为con已经不再为null,所以就会抛出异常了。
我们希望JdbcUtils可以多线程环境下被使用!这说明最好的方法是为每个线程提供一个Connection,这样每个线程都可以开启自己的事务了。
还记得ThreadLocal类么?
public class JdbcUtils { ????private static DataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); ????private static ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>(); ? ????public static DataSource getDataSource() { ????????return dataSource; ????} ? ????public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { ????????Connection con = tl.get(); ????????if(con == null) { ????????????return dataSource.getConnection(); ????????} ????????return con; ????} ???? ????public static void beginTranscation() throws SQLException { ????????Connection con = tl.get(); ????????if(con != null) { ????????????throw new SQLException("事务已经开启,在没有结束当前事务时,不能再开启事务!"); ????????} ????????con = dataSource.getConnection(); ????????con.setAutoCommit(false); ????????tl.set(con); ????} ???? ????public static void commitTransaction() throws SQLException { ????????Connection con = tl.get(); ????????if(con == null) { ????????????throw new SQLException("当前没有事务,所以不能提交事务!"); ????????} ????????con.commit(); ????????con.close(); ????????tl.remove(); ????} ???? ????public static void rollbackTransaction() throws SQLException { ????????Connection con = tl.get(); ????????if(con == null) { ????????????throw new SQLException("当前没有事务,所以不能回滚事务!"); ????????} ????????con.rollback(); ????????con.close(); ????????tl.remove(); ????} } |
?
public class AccountDao { ????public void updateBalance(String name, double balance) throws SQLException { ????????String sql = "update account set balance=balance+? where name=?"; ????????Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); ????????QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(); ????????qr.update(con, sql, balance, name); ????} } |
public class AccountService { ????private AccountDao dao = new AccountDao(); ???? ????public void transfer(String from, String to, double balance) { ????????try { ????????????JdbcUtils.beginTranscation(); ????????????dao.updateBalance(from, -balance); ????????????dao.updateBalance(to, balance); ????????????JdbcUtils.commitTransaction(); ????????} catch(Exception e) { ????????????try { ????????????????JdbcUtils.rollbackTransaction(); ????????????} catch (SQLException e1) { ????????????????throw new RuntimeException(e); ????????????} ????????} ????} } |
????????AccountService as = new AccountService(); ????????as.transfer("zs", "ls", 100); |
?
?
?
?
?
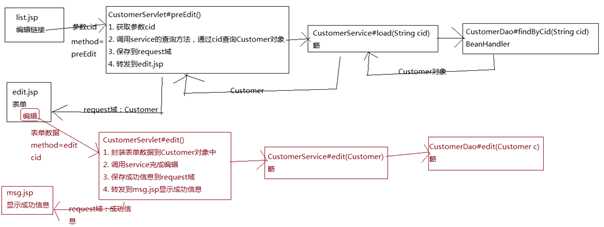
编辑分为两步:
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
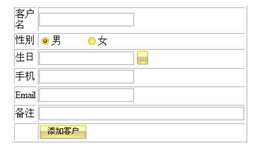
添加客户


?


?
?
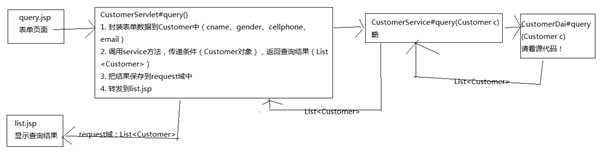
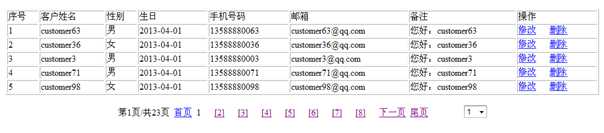
查看客户


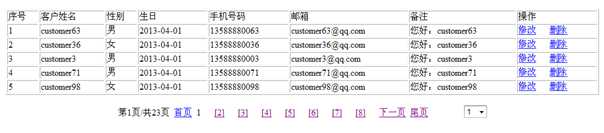
?
修改客户
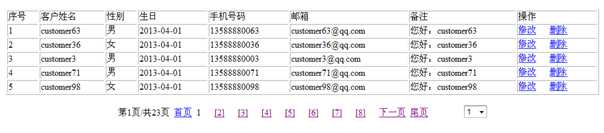
?

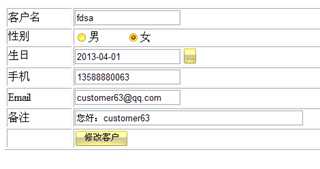

?
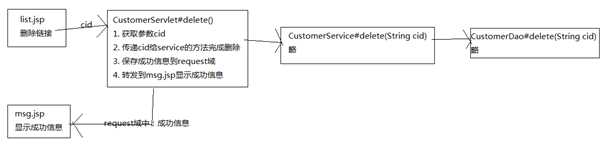
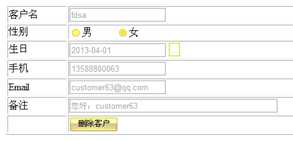
删除客户
?


?
?
?
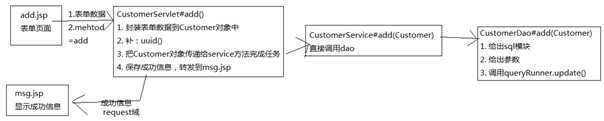
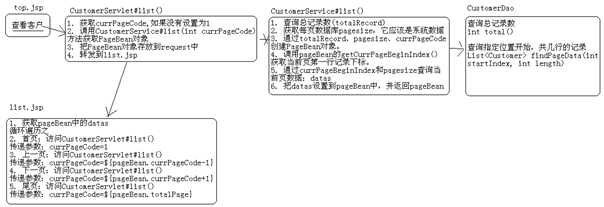
编写CustomerServlet,处理页面跳转问题!
?
?
customer
customer? | ? | ? |
字段 | 类型 | 说明 |
cid? | char(32)? | 主键 |
cname? | varchar(30)? | 客户姓名 |
gender? | varchar(6)? | 客户性别 |
birthday? | date? | 客户生日 |
cellphone? | varchar(20)? | 客户手机 |
email? | varchar(30)? | 客户邮箱 |
description? | varchar(200)? | 客户描述 |
?
CREATE TABLE customer( cid CHAR(32) PRIMARY KEY, cname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, gender VARCHAR(6) NOT NULL, birthday DATE, cellphone VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(30), description VARCHAR(200) ); |
?
Customer类这里就省略了!
?
?
?
?
?
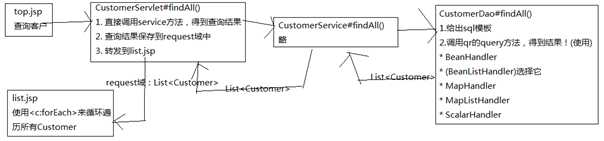
页面需要什么数据:
?
Servlet需要什么数据:
?
把分布数据封装成PageBean类对象
public class PageBean<T> { ????private List<T> datas;// 当前页记录数, 需要传递 ????private int totalRecord;// 总记录数, 需要传递 ????private int currPageCode;// 当前页码, 需要传递 ????private int pagesize;// 每页记录数, 需要传递 ????private int totalPage;// 总页数, 计算 ????private int currPageBeginIndex; //需要计算 ????public PageBean(int currPageCode, int totalRecord, int pagesize) { ????????this.currPageCode = currPageCode; ????????this.totalRecord = totalRecord; ????????this.pagesize = pagesize; ???????? ????????init(); ????} ???? ????private void init() { ????????this.totalPage = totalRecord / pagesize; ????????if(totalRecord % pagesize != 0) { ????????????this.totalPage++; ????????} ????????this.currPageBeginIndex = (this.currPageCode-1) * this.pagesize; ????} ... } |
?
?

其中红框中的就是页码列表!
?
4.1 页面需要的数据:
例如开始页码为11,结束页码为18,那么就显示:
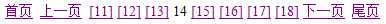
对于页面,它只需要beginIndex和endIndex,然后使用<c:forEach>就可以循环显示了!然后再判断一下遍历的数字如果与pageBean.currPageCode相等,那么就不要显示为链接即可。
?
4.2 PageBean
页面需要的数据由PageBean来提供,即为pageBean添加两个方法:
?
但是,PageBean想计算这两个值,也要需要两个系统数据:
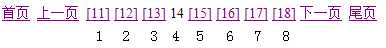
?
4.3 计算beginIndex
计算beginIndex分为4步:
例如,当前数据一共5页,那么列表的开始页码一定是1。
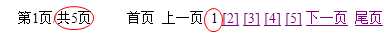
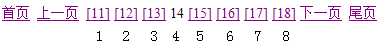
上图中当前页码(currPageCode)为14,当前页码位置为4(currPageCodeListIndex),推算出beginIndex为11,即beginIndex = currPageCode- currPageCodeListIndex+1;
第2步的计算可能会出现问题,例如在当前页码(currPageCode)为1时,那么上面的计算就会出现beginIndex小于1的情况!这种beginIndex小于1的情况,只有在currPageCode为1、2、3时会出现。你可以去套用一下第2步的公式,会发现这个问题的!
也就是说,beginIndex的最小值就是1
?
当cuarrPageCode为30时,那么通过第2步计算出的beginIndex为27,但是如果totalPage为30呢?因为一共就30页,总不能显示31出来吧。那么显示:27、28、29、30,这就只有4个页码,但列表长度应该为8,所以出错。
我们为了验证第2步是否出现这个错误,需要通过得到的beginIndex来推算endIndex。例如currPageCode为30,计算出beginIndex为27,再通过beginIndex计算出endIndex为34。然后查看endIndex是否大于totalPage,如果大于了totalPage,那么应该使用totalPage减去pageCodeListSize再加1,得到正确的beginIndex。
int endIndex = beginIndex+pageCodeListSize-1;
if(endIndex > totalPage) beginIndex = totalPage-pageCodeListSize + 1;
?
????public int getBeginIndex() { ????????if(totalPage <= pageCodeListSize) return 1; ????????int begin = currPageCode – currPageCodeListIndex+1; ????????if(begin < 1) begin = 1; ????????int end = begin + pageCodeListSize-1; ????????if(end > totalPage) begin = totalPage – pageCodeListSize+1; ????????return begin; ????} |
?
4.4 计算endIndex
计算endIndex也是分为4步
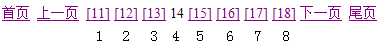
currPageCode=14,pageCodeListSize=8,currPageCodeListIndex=4,所以
endIndex = currPageCode+(pageCodeListSize=currPagecodeListIndex)=18。
如果currPageCode为30,那么通过第2步计算出的endIndex为34,但是如果totalPage为30呢?那么就让endIndex=totalPage。
当currPageCode为27、28、29、30时,如果totalPage=30,那么第2步都会计算出错。这时就把endIndex=totalPage
当currPageCode为1时,那么通过第2步计算的endIndex为5,即列表为1、2、3、4、5,但列表长度应该为8,所以当第2步计算出的endIndex< pageCodeListSize,那么让endIndex等于列表长度。
????public int getEndIndex() { ????????if(totalPage <= pageCodeListSize) return totalPage; ????????int end = currPageCode + (pageCodeListSize-currPageCodeListIndex); ????????if(end > totalPage) end = totalPage; ????????if(end < pageCodeListSize) end = pageCodeListSize; ????????return end; ????} |
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Prozhu/p/5721631.html