标签:
文档对象模型(Document Object Model,DOM)是一种用于HTML和XML文档的编程接口。它给文档提供了一种结构化的表示方法,可以改变文档的内容和呈现方式。我们最为关心的是,DOM把网页和脚本以及其他的编程语言联系了起来。DOM属于浏览器,而不是JavaScript语言规范里的规定的核心内容。
HTML DOM 将 HTML 文档视作树结构。这种结构被称为节点树:
通过 HTML DOM,树中的所有节点均可通过 JavaScript 进行访问。所有 HTML 元素(节点)均可被修改,也可以创建或删除节点。
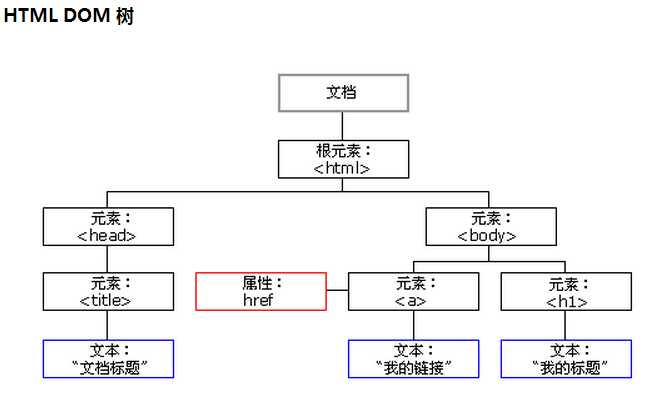
树中所有的框都是节点,文本也是一个节点
包括:<title>DOM 教程</title>,元素节点 <title>,包含值为 "DOM 教程" 的文本节点。这是一个初学者的易错点。
getElementById() 返回对拥有指定 id 的第一个对象的引用。
getElementsByName() 返回带有指定名称的对象集合。
getElementsByTagName() 返回带有指定标签名的对象集合。
获得节点node,包含所有类型的node节点。
parentNode // 父节点 childNodes // 所有子节点 firstChild // 第一个子节点 lastChild // 最后一个子节点 nextSibling // 下一个兄弟节点 previousSibling // 上一个兄弟节点
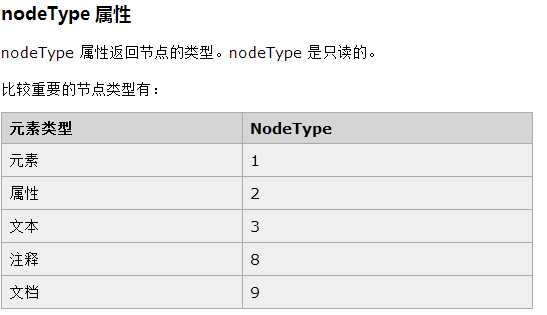
获得元素element,仅包含element标签元素的节点。
parentElement // 父节点标签元素 children // 所有子标签 firstElementChild // 第一个子标签元素 lastElementChild // 最后一个子标签元素 nextElementtSibling // 下一个兄弟标签元素 previousElementSibling // 上一个兄弟标签元素
一个例子说明上面两种方法的区别
<div id="t1">
文本
<p>123</p>
</div>

1、文本操作
innerText //所有的纯文本内容,包括子标签中的文本
innerHTML //所有子节点(包括元素、注释和文本节点)
outerHTML //返回自身节点与所有子节点
value //表单元素的值

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div> <div id="d1"><span>文本操作</span></div> </div> <input id ="d2" type="text" value="123"> <script> var e = document.getElementById("d1"); var i = document.getElementById("d2") console.log(e.innerHTML) console.log(e.outerHTML) console.log(e.innerText) console.log(i.value) </script> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>DOM元素取值操作</title> <!--表单类标签取值使用value--> </head> <body> <p id="pp">正常标签<span>span</span></p> <!-- ------------------------------------------------------> <fieldset> <legend>文本输入样例组</legend> <label>文本输入框:</label><input id=‘i1‘ type="text" value="原始字符" /> <label>密码框:</label><input id=‘i2‘ type="password" value="123" /> <label>多行文本输入:</label><textarea id="i3">value </textarea> </fieldset> <!-----------------------chexkbox-----------------------------> <fieldset> <legend>选择样例组</legend> <ul id="check-box"> <li><input type="checkbox" value="1" checked="checked"/>篮球</li> <li><input type="checkbox" value="2"/>足球</li> <li><input type="checkbox" value="3"/>排球</li> </ul> <ul id="radio-test"> <!--name一样才能同组互斥--> <li><input type="radio" value=‘11‘ name="text" checked="checked"/>男</li> <li><input type="radio" value=‘22‘ name="text"/>女</li> <li><input type="radio" value=‘33‘ name="text"/>人妖</li> </ul> <select id="select-test"> <option value="11">北京</option> <option value="22" selected="selected">上海</option> <option value="33">广州</option> <option value="44">深证</option> </select> </fieldset> <!---------------------radios-------------------> <script> pp_text_value = document.getElementById(‘pp‘).innerText //"正常标签span" pp_html_value = document.getElementById(‘pp‘).innerHTML//"正常标签<span>span</span>" // ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // text password textarea i1=document.getElementById(‘i1‘).value//要设置值直接用i1=xxx i2=document.getElementById(‘i2‘).value i3=document.getElementById(‘i3‘).value // ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // checkbox ul_box=document.getElementById(‘check-box‘) var inputs = ul_box.getElementsByTagName(‘input‘) // for(var item in inputs){ // console.log(inputs[item].value) // }这种方法有多余的数据出现 for(var index=0; index<inputs.length;index++ ){ console.log(inputs[index].value) //获取值,1 2 3 console.log(inputs[index].checked) //获取选中状态, true , false ,false } // ------------------radio-------------------------------------- var radio_test=document.getElementById(‘radio-test‘) var radios = radio_test.getElementsByTagName(‘input‘) for(var index=0;index<radios.length;index++){ console.log(radios[index].value) //获取值,11 22 33 console.log(radios[index].checked) //获取选中状态, true , false ,false } //-----------------------select------------------------------- var sel_ele=document.getElementById(‘select-test‘) var sel_value=sel_ele.value //获取当前元素值 var sel_selindex=sel_ele.selectedIndex //获取当前选中项索引 </script> </body> </html>
运行结果
2、attrbute属性操作
attributes // 获取所有标签属性
setAttribute(key,value) // 设置标签属性
getAttribute(key) // 获取指定标签属性
/*
var atr = document.createAttribute("class");
atr.nodeValue="democlass";
document.getElementById(‘n1‘).setAttributeNode(atr);
*/
3、class类操作
className // 获取所有类名
classList //获取所有类的列表 classList.remove(cls) // 删除指定类 classList.add(cls) // 添加类

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .bg-color{background-color: red} .w{width: 100px} .col{color:green} </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1" class="bg-color w col">cangsong</div> <script> var d=document.getElementById("d1") console.log(d.className) //bg-color w col console.log(d.classList) //["bg-color", "w", "col", value: "bg-color w col"] d.classList.remove("col") console.log(d.className) //bg-color w d.classList.add("col") console.log(d.className) //bg-color w col </script> </body> </html>
4、标签操作
a.创建标签
// 方式一 var tag = document.createElement(‘a‘) tag.innerText = "wupeiqi" tag.className = "c1" tag.href = "http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi" // 方式二 var tag = "<a class=‘c1‘ href=‘http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi‘>wupeiqi</a>"
b、操作标签
// 方式一 var obj = "<input type=‘text‘ />"; xxx.insertAdjacentHTML("beforeEnd",obj); xxx.insertAdjacentElement(‘afterBegin‘,document.createElement(‘p‘)) //注意:第一个参数只能是‘beforeBegin‘、 ‘afterBegin‘、 ‘beforeEnd‘、 ‘afterEnd‘ // 方式二 var tag = document.createElement(‘a‘) xxx.appendChild(tag) xxx.insertBefore(tag,xxx[1])
5、style样式操作
style.cssText //可对style中的代码进行读写 style.item() //返回给定位置的CSS属性的名称 style.length //style代码块中参数个数 style.getPropertyValue() //返回给定属性的字符串值 style.getPropertyPriority() //检测给定属性是否设置了!important,设置了返回"important";否则返回空字符串 style.removeProperty() //删除指定属性 style.setProperty() //设置属性,可三个参数:设置属性名,设置属性值,是否设置为"important"

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="d1" style="background-color: yellow; width: 100px; height: 100px">style test</div> <script> var d1 = document.getElementById("d1"); console.log(d1.style.cssText); //width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: yellow; d1.style.cssText = "background-color: yellow; width: 200px; height: 200px"; //修改属性 console.log(d1.style.cssText); //width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: yellow; console.log(d1.style.item("0")); //background-color console.log(d1.style.length); //3 console.log(d1.style.getPropertyValue("background-color")); //yed1llow console.log(d1.style.getPropertyPriority("background-color")); //空字符串 console.log(d1.style.removeProperty("width")); //200px d1.style.setProperty("width","200px",""); //设置属性,第三个值为important优先值,可不写 </script> </body> </html>
6、提交表单
document.geElementById(‘form‘).submit()
7、位置相关
document.documentElement.offsetHeight //全文文档总高度
document.documentElement.clientHeight //浏览器可视区域高度。(随着窗口大小变化)
tag.offsetHeight //tag自身高度(height + padding + border)
tag.offsetTop //距离上级标签定位高度
tag.clientHeight //tag可视区域:height + padding
tag.clientTop //tag的border高度
tag.scrollHeight //tag全文文档高度(height + padding)
tag.scrollTop //tag已滚动高度(随滚动变化)
tag.offsetParent //tag相对偏移的父级标签元素

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body style="margin: 0;"> <div style="height: 900px;"> </div> <div style="padding: 10px;"> <div id="i1" style="height:190px;padding: 2px;border: 1px solid red;margin: 8px;overflow: scroll"> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> <p>asdf</p> </div> </div> <script> var i1 = document.getElementById(‘i1‘); console.log(document.documentElement.clientHeight) //窗口可视区域高度 console.log(document.documentElement.offsetHeight) //全文文档总高度 console.log(‘=====‘); console.log(i1.clientHeight); // 可见区域:height + padding console.log(i1.clientTop); // border高度 console.log(‘=====‘); console.log(i1.offsetHeight); // 可见区域:height + padding + border console.log(i1.offsetTop); // 上级定位标签的高度 console.log(‘=====‘); console.log(i1.scrollHeight); //全文高:height + padding console.log(i1.scrollTop); // 已滚动高度 </script> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style type="text/css"> .container{ height:2000px; width:100%; } #top{ background-color: aqua; height: 50px; width:50px; padding:10px; position: fixed; bottom:30px; right: 30px; } .hide{ display: none; } </style> <title>返回顶部</title> </head> <body onscroll="scroll()"> <div class="container"> <div id="top" class="hide" onclick="gotop()"> <a href="javascript:void(0)" >返回顶部</a> </div> <div class="content"> <h1>本实例知识点:</h1> <p>1、 onscroll="gotop()"要要用在监听的元素上。本例为body边标签。</p> <p>2、document.body.scrollTop监听离元素滚轮顶部的距离。</p> <p>3、 a href="javascript:void(0)",使得点击a标签不刷新页面。</p> <p>4、返回顶部设置document.body.scrollTop=0</p> </div> </div> <script> function scroll() { var scrolltop=document.body.scrollTop if (scrolltop>100){ document.getElementById("top").classList.remove("hide") }else { document.getElementById("top").classList.add("hide") } } function gotop() { document.body.scrollTop=0 } </script> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style> .clearfix:after{ content: ‘clearfix‘; display: block; height: 0; visibility: hidden; clear: both; } .header{ height:50px; background-color: black; } .container{ width: 1100px; margin: 0 auto; } .menu{ width: 200px; float: left; background-color: coral; } .content{ width: 870px; background-color: blanchedalmond; margin-left: 20px; float: right; } .fixed{ position: fixed; top:10px; } .section{ border: 1px solid red; height: 300px; width: 865px; } </style> </head> <body onscroll="scrollEvent()"> <div class="header"></div> <div class="container clearfix"> <div id="menu" class="menu"> <ul> <li>第一章</li> <li>第二章</li> <li>第三章</li> </ul> </div> <div class="content"> <div class="section">第一章内容</div> <div class="section">第二章内容</div> <div class="section">第三章内容</div> </div> </div> <script> function scrollEvent() { var sh= document.body.scrollTop // 滚轮已滚高度 var menu=document.getElementById("menu") if (sh>50){ menu.classList.add("fixed") }else { menu.classList.remove("fixed") } } </script> </body> </html>
 (接固定菜单往下做)
(接固定菜单往下做)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style> .clearfix:after{ content: ‘clearfix‘; display: block; height: 0; visibility: hidden; clear: both; } .header{ height:50px; background-color: black; } .container{ width: 1100px; margin: 0 auto; } .menu{ width: 200px; float: left; background-color: coral; } .content{ width: 870px; background-color: blanchedalmond; margin-left: 20px; float: right; } .fixed{ position: fixed; top:10px; } .section{ border: 1px solid red; height: 300px; width: 865px; } .active{ background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body onscroll="scrollEvent()"> <div class="header"></div> <div class="container clearfix"> <div id="menu" class="menu"> <ul> <li>第一章</li> <li>第二章</li> <li>第三章</li> </ul> </div> <div class="content"> <div class="section">第一章内容</div> <div class="section">第二章内容</div> <div class="section">第三章内容</div> </div> </div> <script> function scrollEvent() { var sh= document.body.scrollTop // 滚轮已滚高度 var menu=document.getElementById("menu") if (sh>50){ menu.classList.add("fixed") }else { menu.classList.remove("fixed") }//实现菜单固定显示 var sections = document.getElementsByClassName("section") var menu_section=document.getElementsByTagName("li") for (i=0;i<sections.length;i++){ var secParent=sections[i].offsetParent // 章节相对偏移的父元素。content //sections[i].offsetTop章节元素偏移高度+父元素偏移高度secParent.offsetTop-滑动的高度=章节元素相对于视口顶部的高度。 //小于0,说明章节元素顶部即将超出视口,可以激活。 var secOffect= sections[i].offsetTop+secParent.offsetTop-sh var secHeight=sections[i].offsetHeight //章节元素自身高度 var secBottomOffect=secOffect+secHeight //章节元素底部距离浏览器视口高度。 //元素顶部偏移超出视口,底部偏移还未超出是,机会该章节。一旦有章节匹配不再往下判断,break if(secOffect<0 && secBottomOffect>0){ curr_menu_section= menu_section[i] curr_menu_section.classList.add("active"); //清除其他章节的active for(j=0;j<menu_section.length;j++){ if(curr_menu_section!=menu_section[j]){ menu_section[j].classList.remove("active"); }else {} } break; } } } </script> </body> </html>
8、定时器
setInterval //多次定时器(毫秒计时)
clearInterval //清除多次定时器
setTimeout //单次定时器
clearTimeout //清除单次定时器

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="Interval" onclick="Interval();" /> <input type="button" value="StopInterval" onclick="StopInterval();" /> <script> function Interval() { s1 = setInterval(function () { console.log(123); }, 1000); s2 = setInterval(function () { console.log(456); }, 2000); console.log(1); } function StopInterval() { clearInterval(s1); clearInterval(s2); } </script> </body> </html>
9、弹出框
console.log //输出框
alert //弹出框
confirm //确认框

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="consolelog" onclick="console_log();" /> <input type="button" value="alert" onclick="test_alert();" /> <input type="button" value="confirm" onclick="test_confirm();" /> <script> function console_log() { console.log("后台输出数据")//要在后台调试界面console界面看到 } function test_alert() { alert("测试alert") } function test_confirm() { confirm("测试confirm") } </script> </body> </html>
location.href = "url" 获取URL重定向
location.assign("http://www.cnblogs.com/suoning") 重定向到URL
location.search = "wd=suoning" 修改查询字符串(百度搜索)
location.hostname 服务主机名,例:www.cnblogs.com
location.pathname 路径,例:suoning
location.port 端口号
location.reload() 重新加载
11、其他BOM相关
navigator 包含有关浏览器的信息
screen 包含有关客户端显示屏幕的信息
history 包含用户(在浏览器窗口中)访问过的 URL
window.print(); 显示打印对话框

//后退一页
history.go(-1)
//前进一页
history.go(1);
//前进两页
history.go(2);
//无参数时,刷新当前页面
history.go()
//后退一页
history.back()
//前进一页
history.forward()
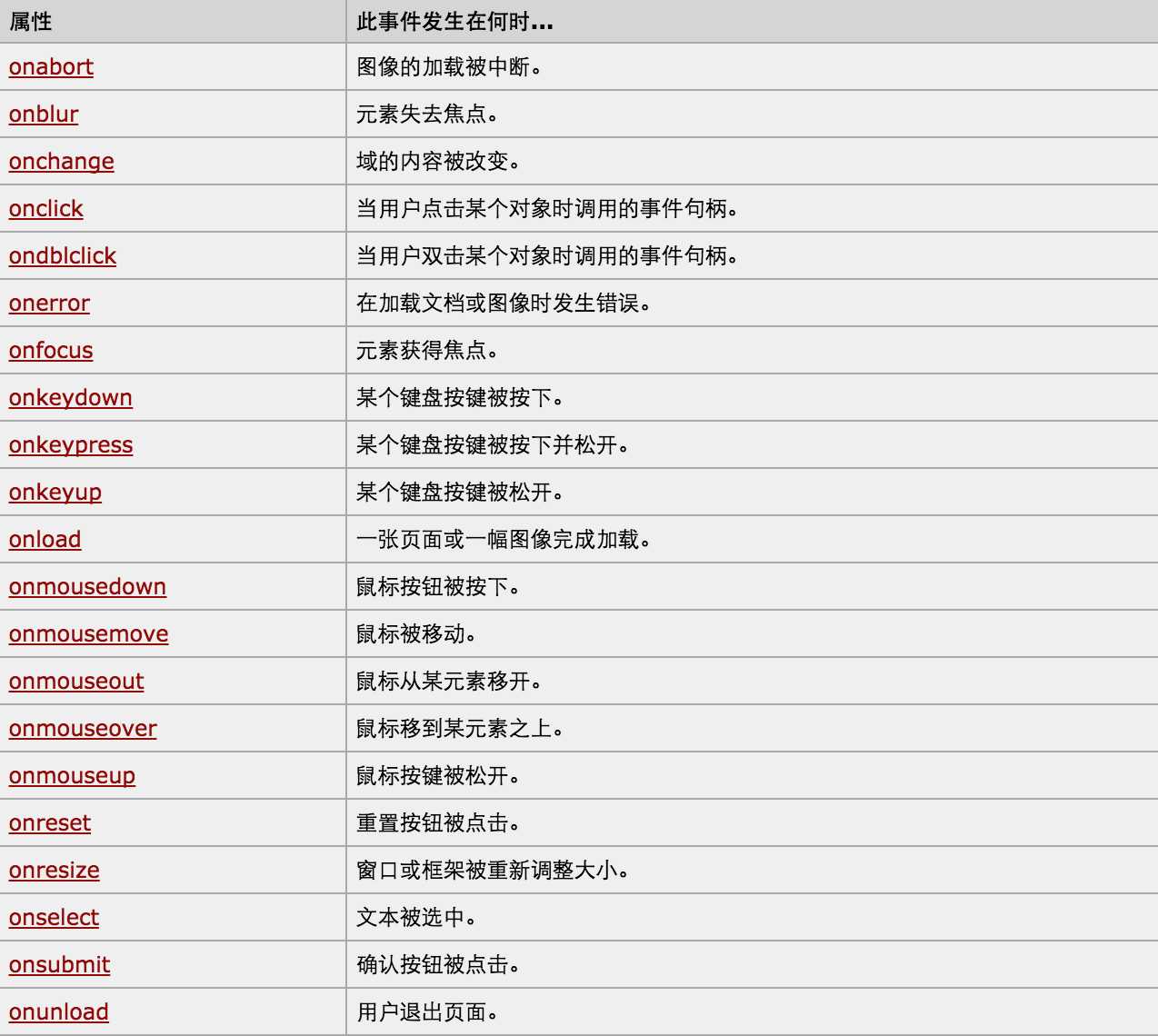
对于事件需要注意的要点:
this标签当前正在操作的标签,event封装了当前事件的内容。
实例:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset=‘utf-8‘ /> <title></title> <style> .gray{ color:gray; } .black{ color:black; } </style> <script type="text/javascript"> function Enter(){ var id= document.getElementById("tip") id.className = ‘black‘; if(id.value==‘请输入关键字‘||id.value.trim()==‘‘){ id.value = ‘‘ } } function Leave(){ var id= document.getElementById("tip") var val = id.value; if(val.length==0||id.value.trim()==‘‘){ id.value = ‘请输入关键字‘ id.className = ‘gray‘; }else{ id.className = ‘black‘; } } </script> </head> <body> <input type=‘text‘ class=‘gray‘ id=‘tip‘ value=‘请输入关键字‘ onfocus=‘Enter();‘ onblur=‘Leave();‘/> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <style type="text/css"> ul { margin:0; padding:0; } ul li{ line-height: 44px; text-align: center; list-style: none; float: left; margin:0; padding-left: 10px; padding-right: 10px; } .clearfix:after{ display: block; content:‘.‘; height:0; visibility: hidden; clear: both; } .hide{ display:none; } .active{ background-color: white; border-bottom: none; } .container{ width: 100%; } .title{ height:44px; background-color: bisque; border:1px solid black; border-bottom: none; margin: auto 10% ; } #content{ margin: auto 10%; background-color: white; border: 1px solid black; border-top: none; max-height:500px; min-height:100px; overflow: scroll; } </style> <title>Tab菜单实例</title> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="title" class="clearfix"> <ul id="i1"> <!--this表示元素本身--> <li title="1" onclick="show(this)" class="active">title1</li> <li title="2" onclick="show(this)">title2</li> <li title="3" onclick="show(this)">title3</li> </ul> </div> <div id="content"> <div content="1" > <h1>本例知识点:</h1> <p>1/onclick="show(this)" this特质本元素。</p> <p>2、classList.remove(‘active‘) 移除class中的active,用于class操作</p> <p>3、ths.className获取class名,设置值直接ths.className="active"</p> <p>3、tag.getAttribute("content")获取tag标签中:“content"属性的值。标题和内容关联用标签值来关联。</p> <h1>4、max-height:500px;最大高度min-height:100px;最小高度</h1> <h1>content1</h1> <h1>content1</h1> <h1>content1</h1> <h1>content1</h1> <h1>content1</h1> </div> <div content="2" class="hide">content2</div> <div content="3" class="hide">content3</div> </div> </div> <script> function show(ths) { // ths表示元素自身,本函数点击自身添加active样式,兄弟节点移除active样式、 ths.className="active" var brothers = ths.parentElement.children for(var i=0;i<brothers.length;i++){ if (ths==brothers[i]){ continue }else { brothers[i].classList.remove(‘active‘) } } var title_tab=ths.getAttribute("title") var father =document.getElementById("content") var contents = father.children // console.log(contents) for(var i=0;i<contents.length;i++){ if(contents[i].getAttribute("content")==title_tab){ contents[i].classList.remove("hide") }else { contents[i].classList.add("hide") } } } </script> </body> </html>
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tkqasn/p/5737608.html