标签:
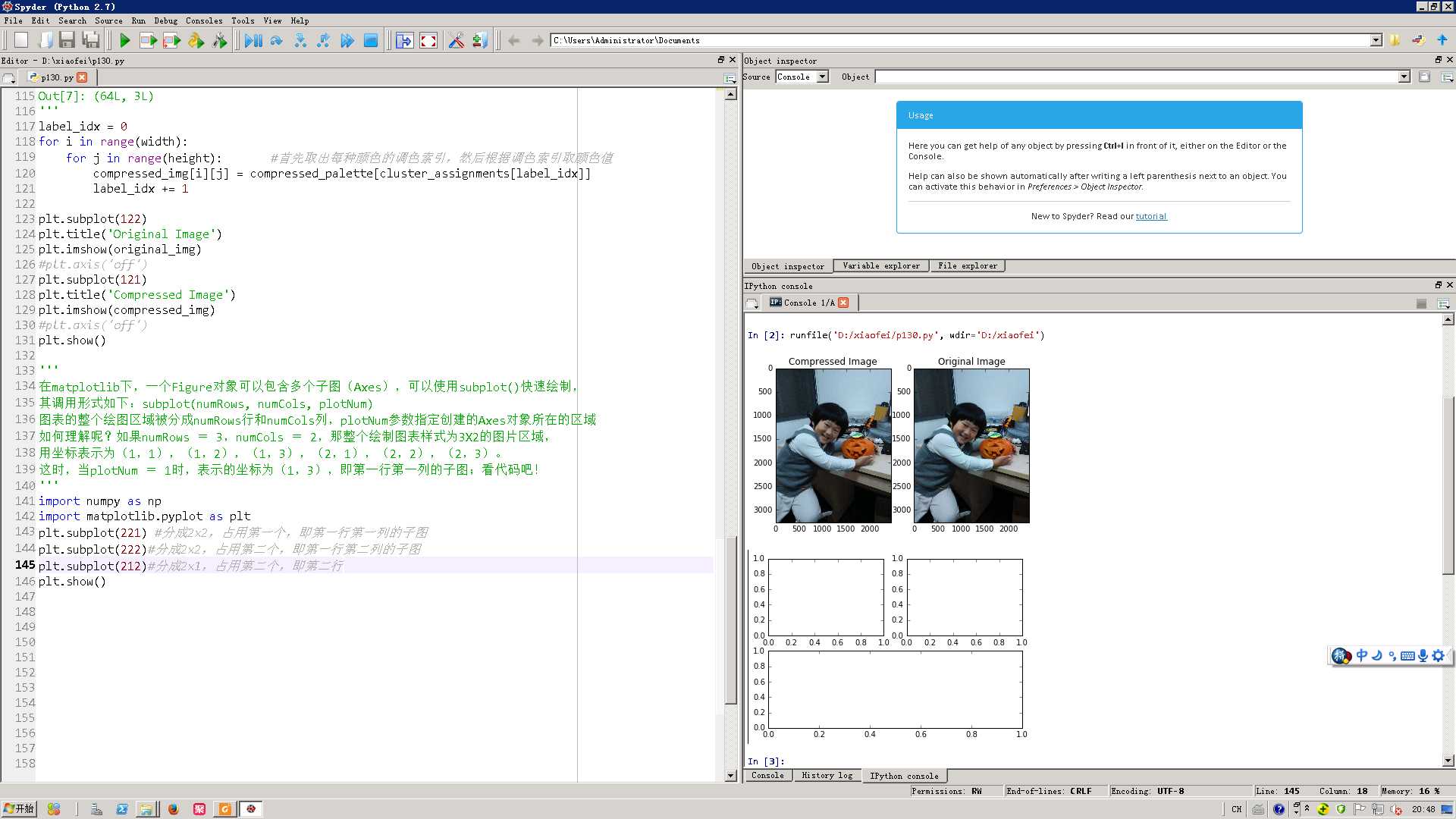
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Thu Aug 11 18:54:12 2016 @author: Administrator """ import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.cluster import KMeans from sklearn.utils import shuffle import mahotas as mh original_img = np.array(mh.imread(‘haonan.jpg‘), dtype=np.float64) / 255 original_dimensions = tuple(original_img.shape) width, height, depth = tuple(original_img.shape) #(3264L, 2448L, 3L) image_flattened = np.reshape(original_img, (width * height, depth)) #(7990272L, 3L) #将原始的图像,变成多行的样式 #打乱图像像素,选取1000个 image_array_sample = shuffle(image_flattened,random_state=0)[:1000] #聚集为64个颜色 estimator = KMeans(n_clusters=64, random_state=0) estimator.fit(image_array_sample) #Next, we predict the cluster assignment for each of the pixels in the original image: #将7990272L颜色划分为64种 cluster_assignments = estimator.predict(image_flattened) ‘‘‘ cluster_assignments.shape Out[19]: (7990272L,) ‘‘‘ #Finally, we create the compressed image from the compressed palette and cluster assignments: compressed_palette = estimator.cluster_centers_ ‘‘‘ compressed_palette.shape Out[3]: (64L, 3L) compressed_palette Out[4]: array([[ 0.54188948, 0.66987522, 0.73404635], [ 0.16122004, 0.20232389, 0.22962963], [ 0.06970588, 0.06088235, 0.06794118], [ 0.34392157, 0.46039216, 0.53215686], [ 0.68235294, 0.29254902, 0.04862745], [ 0.2619281 , 0.34901961, 0.41911765], [ 0.68074866, 0.80784314, 0.86737968], [ 0.54313725, 0.57843137, 0.57647059], [ 0.47882353, 0.36588235, 0.32117647], [ 0.11993464, 0.15108932, 0.17821351], [ 0.7745098 , 0.4745098 , 0.31372549], [ 0.62459893, 0.73698752, 0.7983066 ], [ 0.81764706, 0.95098039, 0.57843137], [ 0.0248366 , 0.01837755, 0.02568243], [ 0.28912656, 0.22816399, 0.20071301], [ 0.44456328, 0.44955437, 0.42245989], [ 0.19869281, 0.27215686, 0.33856209], [ 0.14588235, 0.12797386, 0.12130719], [ 0.51568627, 0.21372549, 0.04019608], [ 0.68333333, 0.59411765, 0.53431373], [ 0.43227753, 0.5040724 , 0.56440422], [ 0.37167756, 0.29803922, 0.26143791], [ 0.73908497, 0.86248366, 0.91477124], [ 0.55882353, 0.64215686, 0.7004902 ], [ 0.70812325, 0.72941176, 0.71820728], [ 0.75215686, 0.37098039, 0.11372549], [ 0.20980392, 0.72156863, 0.59411765], [ 0.57896613, 0.69875223, 0.75995247], [ 0.40588235, 0.08529412, 0.01372549], [ 0.55764706, 0.45490196, 0.20470588], [ 0.41921569, 0.56352941, 0.65411765], [ 0.29877451, 0.4129902 , 0.4877451 ], [ 0.08686275, 0.12215686, 0.16686275], [ 0.30532213, 0.32156863, 0.34117647], [ 0.51980392, 0.61686275, 0.66823529], [ 0.51078431, 0.51666667, 0.50686275], [ 0.16642157, 0.24730392, 0.30514706], [ 0.0629156 , 0.07212276, 0.09445865], [ 0.6373366 , 0.75955882, 0.82295752], [ 0.13777778, 0.17934641, 0.20836601], [ 0.65098039, 0.65588235, 0.66176471], [ 0.49338235, 0.57867647, 0.63578431], [ 0.33823529, 0.37205882, 0.37745098], [ 0.2047619 , 0.30532213, 0.38207283], [ 0.20980392, 0.04313725, 0.02941176], [ 0.19758673, 0.2361991 , 0.26033183], [ 0.59215686, 0.26143791, 0.01699346], [ 0.24145658, 0.17086835, 0.13893557], [ 0.50532213, 0.49971989, 0.43417367], [ 0.79215686, 0.45196078, 0.21372549], [ 0.12529412, 0.20078431, 0.26431373], [ 0.59691028, 0.71895425, 0.78193702], [ 0.51764706, 0.2745098 , 0.17647059], [ 0.62058824, 0.51911765, 0.46911765], [ 0.60952381, 0.68095238, 0.73977591], [ 0.11687812, 0.0946559 , 0.09265667], [ 0.28627451, 0.25359477, 0.25294118], [ 0.08411765, 0.09392157, 0.11764706], [ 0.74845938, 0.76246499, 0.77983193], [ 0.62287582, 0.26339869, 0.09607843], [ 0.84313725, 0.94901961, 0.42745098], [ 0.43267974, 0.41045752, 0.36601307], [ 0.65918833, 0.77756498, 0.84012768], [ 0.04037763, 0.03384168, 0.04139434]]) ‘‘‘ #生成一个新的图像,全部是0,深度和原来图像相等 compressed_img = np.zeros((width, height, compressed_palette.shape[1])) ‘‘‘ compressed_palette.shape Out[7]: (64L, 3L) ‘‘‘ label_idx = 0 for i in range(width): for j in range(height): #首先取出每种颜色的调色索引,然后根据调色索引取颜色值 compressed_img[i][j] = compressed_palette[cluster_assignments[label_idx]] label_idx += 1 plt.subplot(122) plt.title(‘Original Image‘) plt.imshow(original_img) #plt.axis(‘off‘) plt.subplot(121) plt.title(‘Compressed Image‘) plt.imshow(compressed_img) #plt.axis(‘off‘) plt.show() ‘‘‘ 在matplotlib下,一个Figure对象可以包含多个子图(Axes),可以使用subplot()快速绘制, 其调用形式如下:subplot(numRows, numCols, plotNum) 图表的整个绘图区域被分成numRows行和numCols列,plotNum参数指定创建的Axes对象所在的区域 如何理解呢?如果numRows = 3,numCols = 2,那整个绘制图表样式为3X2的图片区域, 用坐标表示为(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3)。 这时,当plotNum = 1时,表示的坐标为(1,3),即第一行第一列的子图;看代码吧! ‘‘‘ import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.subplot(221) #分成2x2,占用第一个,即第一行第一列的子图 plt.subplot(222)#分成2x2,占用第二个,即第一行第二列的子图 plt.subplot(212)#分成2x1,占用第二个,即第二行 plt.show()
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qqhfeng/p/5762538.html