标签:
Spring IOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,允许在Bean生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务。
Spring IOC容器对Bean的生命周期进行管理的过程如下:
(1).通过构造器或工厂方法创建Bean实例。
(2).为Bean的属性设置值和对其它Bean的引用。
(3).调用Bean的初始化方法。
(4).Bean的使用。
当容器关闭时,调用Bean的销毁方法。
在 Bean 的声明里设置 init-method 和 destroy-method 属性, 为 Bean 指定初始化和销毁方法。
示例:User实体类:
package com.atguigu.spring.helloworld;
import java.util.List;
public class User {
private String userName;
private List<Car> cars;
private String wifeName;
public String getWifeName() {
return wifeName;
}
public void setWifeName(String wifeName) {
System.out.println("设置wifeName属性。。。"+wifeName);
this.wifeName = wifeName;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
System.out.println("设置userName属性。。。"+userName);
this.userName = userName;
}
public List<Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
public void setCars(List<Car> cars) {
this.cars = cars;
}
// 构造方法
public User() {
System.out.println("正在使用构造方法 Construtor...");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [userName=" + userName + ", cars=" + cars + "]";
}
// 初始化方法
public void init(){
System.out.println("init method...");
}
// 销毁方法
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("destroy method...");
}
}
配置文件beans-auto.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 自动装配: 只声明 bean, 而把 bean 之间的关系交给 IOC 容器来完成 -->
<!--
byType: 根据类型进行自动装配. 但要求 IOC 容器中只有一个类型对应的 bean, 若有多个则无法完成自动装配.
byName: 若属性名和某一个 bean 的 id 名一致, 即可完成自动装配. 若没有 id 一致的, 则无法完成自动装配
-->
<!-- 在使用 XML 配置时, 自动转配用的不多. 但在基于 注解 的配置时, 自动装配使用的较多. -->
<bean id="dao" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.Dao">
<property name="dataSource" value="C3P0"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 默认情况下 bean 是单例的! -->
<!-- 但有的时候, bean 就不能使单例的. 例如: Struts2 的 Action 就不是单例的! 可以通过 scope 属性来指定 bean 的作用域 -->
<!--
prototype: 原型的. 每次调用 getBean 方法都会返回一个新的 bean. 且在第一次调用 getBean 方法时才创建实例
singleton: 单例的. 每次调用 getBean 方法都会返回同一个 bean. 且在 IOC 容器初始化时即创建 bean 的实例. 默认值
-->
<bean id="dao2" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.Dao" scope="prototype"></bean>
<bean id="service" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.Service" autowire="byName"></bean>
<bean id="action" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.Action" autowire="byType"></bean>
<!-- 导入外部的资源文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 测试 SpEL: 可以为属性进行动态的赋值(了解) -->
<bean id="girl" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User">
<property name="userName" value="周迅"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="boy" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="userName" value="高胜远"></property>
<property name="wifeName" value="#{girl.userName}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 bean 后置处理器: 不需要配置 id 属性, IOC 容器会识别到他是一个 bean 后置处理器, 并调用其方法 -->
<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<!-- 通过工厂方法的方式来配置 bean -->
<!-- 1. 通过静态工厂方法: 一个类中有一个静态方法, 可以返回一个类的实例(了解) -->
<!-- 在 class 中指定静态工厂方法的全类名, 在 factory-method 中指定静态工厂方法的方法名 -->
<bean id="dateFormat" class="java.text.DateFormat" factory-method="getDateInstance">
<!-- 可以通过 constructor-arg 子节点为静态工厂方法指定参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="2"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 2. 实例工厂方法: 先需要创建工厂对象, 再调用工厂的非静态方法返回实例(了解) -->
<!-- ①. 创建工厂对应的 bean -->
<bean id="simpleDateFormat" class="java.text.SimpleDateFormat">
<constructor-arg value="yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- ②. 有实例工厂方法来创建 bean 实例 -->
<!-- factory-bean 指向工厂 bean, factory-method 指定工厂方法(了解) -->
<bean id="datetime" factory-bean="simpleDateFormat" factory-method="parse">
<!-- 通过 constructor-arg 执行调用工厂方法需要传入的参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="1990-12-12 12:12:12"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 配置通过 FactroyBean 的方式来创建 bean 的实例(了解) -->
<bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.UserBean"></bean>
</beans>
测试Main函数:
package com.atguigu.spring.ref;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-auto.xml");
//测试 spEL
User boy = (User) ctx.getBean("boy");
System.out.println(boy);
ctx.close();
}
}
测试结果:

说明:首先通过构造函数来创建bean的实例,然后通过setter方法设置属性,在使用bean实例之前,执行了init初始化方法,使用之后又执行了destroy方法。
Bean后置处理允许在调用初始化方法前后对Bean进行额外的处理,Bean后置处理器对IOC容器的所有Bean实例逐一处理,而非单一实例。其典型应用是:检查Bean属性的正确性或根据特定的标准更改Bean的属性。
对Bean后置处理器而言,需要实现接口BeanPostProcessor,在初始化方法被调用前后,Spring将把每个Bean实例分别传递给上述接口的以下两个方法:
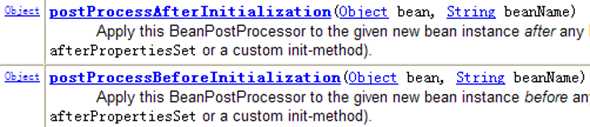
添加Bean后置处理器后,Spring IOC容器对Bean的生命周期管理的过程为:
示例演示Bean的后置处理器:
先定义MyBeanPostProcessor类并实现BeanPostProcessor接口:
package com.atguigu.spring.ref;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
//该方法在 init 方法之后被调用
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
if(arg1.equals("boy")){
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..." + arg0 + "," + arg1);
User user = (User) arg0;
user.setUserName("李大齐");
}
return arg0;
}
//该方法在 init 方法之前被调用
//可以工作返回的对象来决定最终返回给 getBean 方法的对象是哪一个, 属性值是什么
/**
* @param arg0: 实际要返回的对象
* @param arg1: bean 的 id 值
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
if(arg1.equals("boy"))
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..." + arg0 + "," + arg1);
return arg0;
}
}
bean-auto.xml文件中配置Bean的后置处理器bean,<bean class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>在上面的配置文件中已标注,不再赘述。
main函数测试类在与上文相同,测试结果如下:
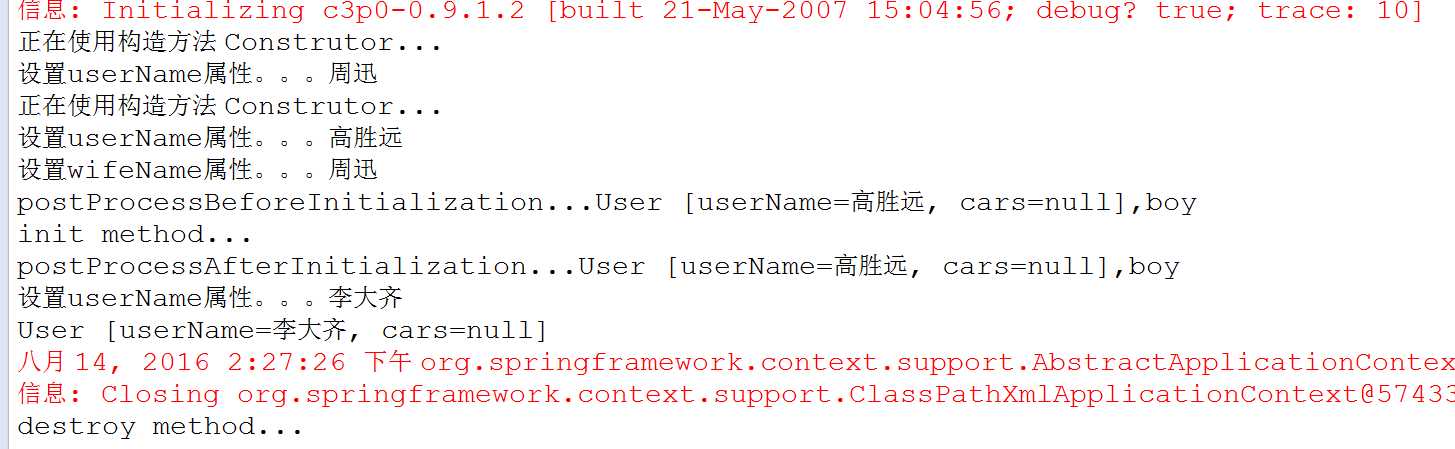
说明:和上面的测试结果对比可以看出,多了一个在bean初始化方法之前将 Bean 实例传递给 Bean 后置处理器的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法和在执行bean初始化方法之后将 Bean 实例传递给 Bean 后置处理器的 postProcessAfterInitialization方法
创建Car实体类:
package com.atguigu.spring.ref;
public class Car {
private String company;
private String brand;
private int maxSpeed;
private float price;
public Car() {
}
public Car(String company,float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [company=" + company + ", brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed="
+ maxSpeed + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
创建静态工厂方法:
package com.atguigu.spring.ref;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class StaticCarFactory {
private static Map<String, Car> cars = new HashMap<String, Car>();
static {
cars.put("Audi", new Car("Audi", 300000));
cars.put("Ford", new Car("Ford", 500000));
}
// 静态工厂方法
public static Car getCar(String name) {
return cars.get(name);
}
}
bean-auto.xml配置静态工厂方法bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 通过工厂方法的方式来配置 bean -->
<!-- 1. 通过静态工厂方法: 一个类中有一个静态方法, 可以返回一个类的实例(了解) -->
<!-- 在 class 中指定静态工厂方法的全类名, 在 factory-method 中指定静态工厂方法的方法名 -->
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<!-- 可以通过 constructor-arg 子节点为静态工厂方法指定参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="Audi"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dateFormat" class="java.text.DateFormat" factory-method="getDateInstance">
<!-- 可以通过 constructor-arg 子节点为静态工厂方法指定参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="2"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 2. 实例工厂方法: 先需要创建工厂对象, 再调用工厂的非静态方法返回实例(了解) -->
<!-- ①. 创建工厂对应的 bean -->
<bean id="simpleDateFormat" class="java.text.SimpleDateFormat">
<constructor-arg value="yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- ②. 有实例工厂方法来创建 bean 实例 -->
<!-- factory-bean 指向工厂 bean, factory-method 指定工厂方法(了解) -->
<bean id="datetime" factory-bean="simpleDateFormat" factory-method="parse">
<!-- 通过 constructor-arg 执行调用工厂方法需要传入的参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="1990-12-12 12:12:12"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 配置通过 FactroyBean 的方式来创建 bean 的实例(了解) -->
<bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.UserBean"></bean>
</beans>
测试函数:
package com.atguigu.spring.ref;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-auto.xml");
Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car+"**********");
ctx.close();
}
}
执行结果:
![]()
实例工厂方法: 将对象的创建过程封装到另外一个对象实例的方法里. 当客户端需要请求对象时, 只需要简单的调用该实例方法而不需要关心对象的创建细节。
要声明通过实例工厂方法创建的 Bean
(1).在 bean 的 factory-bean 属性里指定拥有该工厂方法的 Bean
(2).在 factory-method 属性里指定该工厂方法的名称
(3).使用 construtor-arg 元素为工厂方法传递方法参数
也可以通过实现FactoryBean接口来创建Bean的实例:
创建UserBean并实现FactoryBean接口:
package com.atguigu.spring.ref;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.Car;
import com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User;
public class UserBean implements FactoryBean<User>{
/**
* 返回的 bean 的实例
*/
@Override
public User getObject() throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("abc");
user.setWifeName("ABC");
List<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>();
cars.add(new Car("ShangHai", "BuiKe", 180, 300000));
cars.add(new Car("ShangHai", "CRUZE", 130, 150000));
user.setCars(cars);
return user;
}
/**
* 返回的 bean 的类型
*/
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
/**
* 返回的 bean 是否为单例的
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
bean-auto.xml文件中配置bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 通过工厂方法的方式来配置 bean -->
<!-- 1. 通过静态工厂方法: 一个类中有一个静态方法, 可以返回一个类的实例(了解) -->
<!-- 在 class 中指定静态工厂方法的全类名, 在 factory-method 中指定静态工厂方法的方法名 -->
<bean id="car" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<!-- 可以通过 constructor-arg 子节点为静态工厂方法指定参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="Audi"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dateFormat" class="java.text.DateFormat" factory-method="getDateInstance">
<!-- 可以通过 constructor-arg 子节点为静态工厂方法指定参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="2"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 2. 实例工厂方法: 先需要创建工厂对象, 再调用工厂的非静态方法返回实例(了解) -->
<!-- ①. 创建工厂对应的 bean -->
<bean id="simpleDateFormat" class="java.text.SimpleDateFormat">
<constructor-arg value="yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- ②. 有实例工厂方法来创建 bean 实例 -->
<!-- factory-bean 指向工厂 bean, factory-method 指定工厂方法(了解) -->
<bean id="datetime" factory-bean="simpleDateFormat" factory-method="parse">
<!-- 通过 constructor-arg 执行调用工厂方法需要传入的参数 -->
<constructor-arg value="1990-12-12 12:12:12"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 配置通过 FactroyBean 的方式来创建 bean 的实例(了解) -->
<bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring.ref.UserBean"></bean>
</beans>
scope用来声明容器中的对象所应该处的限定场景或者说该对象的存活时间。
1、singleton
标记为拥有singleton的对象定义,在Spring的IOC容器中只存在一个实例,所有对该对象的引用将共享这个实例。该实例从容器启动,并因为第一次请求而初始化之后,将一直存活到容器退出。
2、prototype
拥有prototype的bean定义,容器在接到该类型对象的请求的时候,会每次都重新生成一个新的对象实例给请求方,虽然这种类型的对象的实例化以及属性设置等工作都是由容器负责的,但是只要准备完毕,并且对象实例返回给请求方之后,容器就不在拥有当前返回对象的引用。
3、request、session和global session
这三类只适用于Web应用程序,通常是与XmlWebApplicationContext共同使用。request:XmlWebApplicationContext会为每个http请求创建一个全新的request-processor对象供当前请求使用,当请求结束后,该对象实例的生命周期即告结束。request可以看做是prototype的一种特例,除了应用场景更加具体。
session:Spring容器会为每个独立的session创建属于他们自己的全新的对象实例,与request相比,除了拥有更长的存活时间,其他没什么差别。
global session:只在基于portlet的web应用程序中才有意义
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ablejava/p/5770378.html