标签:
一、封装
封装:隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,仅对外公开接口,控制程序中属性的读和修改的访问级别。
person.h:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 @interface Person : NSObject 4 /** 年龄 */ 5 @property (nonatomic, assign) int age; 6 7 @end
person.m:
1 #import "Person.h" 2 3 @implementation Person 4 5 #pragma mark - 重写set方法 6 - (void)setAge:(int)age { 7 if (age < 0) { 8 NSLog(@"年龄不能为负数"); 9 return; 10 } else { 11 _age = age; 12 return; 13 } 14 } 15 16 @end
优点:
1. 隐藏内部实现细节,设置访问权限,提高了数据的安全性。
2. 任何出入的数据都要流经接口,通过重写set方法可以起到过滤数据的作用。
二、继承
继承:指一个对象直接使用另一对象的属性和方法。
Person.h:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 @interface Person : NSObject 4 /** 年龄 */ 5 @property (nonatomic, assign) int age; 6 /** 吃方法 */ 7 - (void)eat; 8 9 @end
Person.m:
1 #import "Person.h" 2 3 @implementation Person 4 5 #pragma mark - 重写set方法 6 - (void)setAge:(int)age { 7 if (age < 0) { 8 NSLog(@"年龄不能为负数"); 9 return; 10 } else { 11 _age = age; 12 return; 13 } 14 } 15 16 #pragma mark - 吃方法实现 17 - (void)eat { 18 NSLog(@"Person 吃饭"); 19 } 20 21 @end
GoodPerson.h:
1 #import "Person.h" 2 3 // 继承父类Person 4 @interface GoodPerson : Person 5 /** 姓名 */ 6 @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; 7 8 @end
GoodPerson.m:
1 #import "GoodPerson.h" 2 3 @implementation GoodPerson 4 5 - (void)eat { 6 NSLog(@"GoodPerson 吃饭"); 7 } 8 9 @end
main.m:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Person.h" 3 #import "GoodPerson.h" 4 5 6 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { 7 /** 人 */ 8 Person *p = [[Person alloc] init]; 9 p.age = 20; 10 [p eat]; 11 12 /** 好人 */ 13 GoodPerson *goodP = [[GoodPerson alloc] init]; 14 goodP.age = 30; 15 [goodP eat]; 16 17 // 好人姓名 18 goodP.name = @"Lkun"; 19 NSLog(@"好人name = %@", goodP.name); 20 21 22 return 0; 23 }
编译运行结果:
2016-08-18 17:53:37.484 01-discription[634:455001] Person 吃饭 2016-08-18 17:53:37.485 01-discription[634:455001] GoodPerson 吃饭 2016-08-18 17:53:37.485 01-discription[634:455001] 好人name = Lkun Program ended with exit code: 0
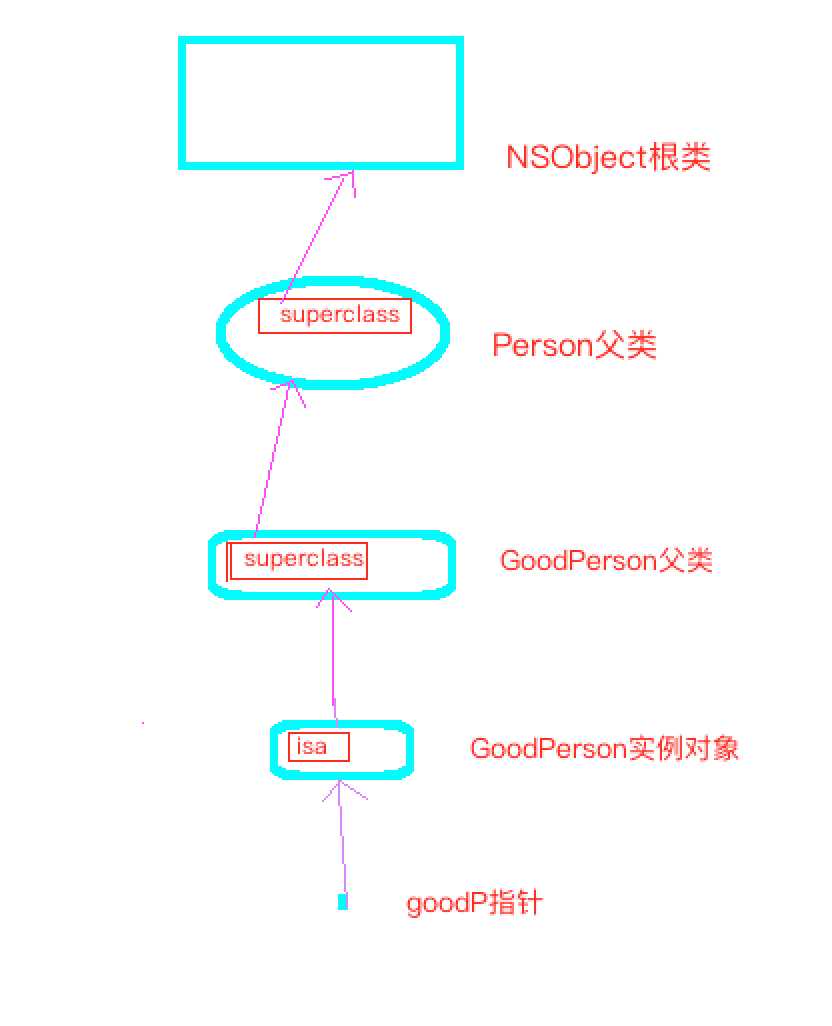
注解:
1. 大部分类都继承自NSObject父类,所以也都继承了该类的属性和方法。
2. GoodPerson虽继承了父类Person的属性age和方法eat,但却有其独特的方法name,且重写了父类的方法eat。
3. 当子类对象收到方法消息时则逐层查找,找到即执行。如setName方法在GoodPerson父类就可以找到,而setAge类得在Person父类才能找到
优点:抽取重复代码、建立联系
缺点:耦合性强
继承:狗是动物,所以狗继承动物类
组合:学生拥有狗,所以把狗作为学生类的一个属性
三、多态
多态:父类指针指向子类对象,父类类型参数可以接收子类类型参数的传入
Person.h:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Animal.h" 3 4 @interface Person : NSObject 5 // 喂食动物的方法 6 - (void)feedAnimal:(Animal *)animal; 7 8 @end
Person.m:
1 #import "Person.h" 2 3 @implementation Person 4 5 - (void)feedAnimal:(Animal *)animal { 6 [animal eat]; 7 } 8 9 @end
Animal.h:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 @interface Animal : NSObject 4 /** 吃方法 */ 5 - (void)eat; 6 7 @end
Animal.m:
1 #import "Animal.h" 2 3 @implementation Animal 4 5 - (void)eat { 6 NSLog(@"Animal eat"); 7 } 8 9 @end
Cat.h:
1 #import "Animal.h" 2 3 @interface Cat : Animal 4 5 @end
Cat.m:
1 #import "Cat.h" 2 3 @implementation Cat 4 #pragma mark - 重写父类的吃方法 5 - (void)eat { 6 NSLog(@"Cat eat"); 7 } 8 9 @end
Dog.h:
1 #import "Animal.h" 2 3 @interface Dog : Animal 4 5 @end
Dog.m:
1 #import "Dog.h" 2 3 @implementation Dog 4 #pragma mark - 重写父类吃方法 5 - (void)eat { 6 NSLog(@"Dog eat"); 7 } 8 9 @end
main.m:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Person.h" 3 #import "Animal.h" 4 #import "Cat.h" 5 #import "Dog.h" 6 7 8 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { 9 /** 人 */ 10 Person *p = [[Person alloc] init]; 11 12 /** 动物 */ 13 Animal *a = [[Animal alloc] init]; 14 15 /** 猫 */ 16 Cat *c = [[Cat alloc] init]; 17 18 // 父类指针指向Dog实例对象 19 Animal *d = [[Dog alloc] init]; 20 21 22 // 动态检测真正对象是Dog 23 [d eat]; 24 25 // 父类指针类型的参数也可以接收子类指针类型的参数 26 [p feedAnimal:a]; 27 [p feedAnimal:c]; 28 29 30 return 0; 31 }
编译运行结果:
2016-08-18 19:42:59.467 01-discription[759:669325] Dog eat 2016-08-18 19:42:59.468 01-discription[759:669325] Animal eat 2016-08-18 19:42:59.468 01-discription[759:669325] Cat eat Program ended with exit code: 0
注解:
1. oc语言是编译的时候才动态检测,调用真正的对象,而不管是指针是什么类型。
2. 父类子针作为参数类型时,其子类子针参数都可以传入
3. 父类指针指向子类对象不能使用子类独有的方法,但可以使用强制转换类型,进而调用
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/gzhu-lkun/p/5785181.html