标签:
代码如下
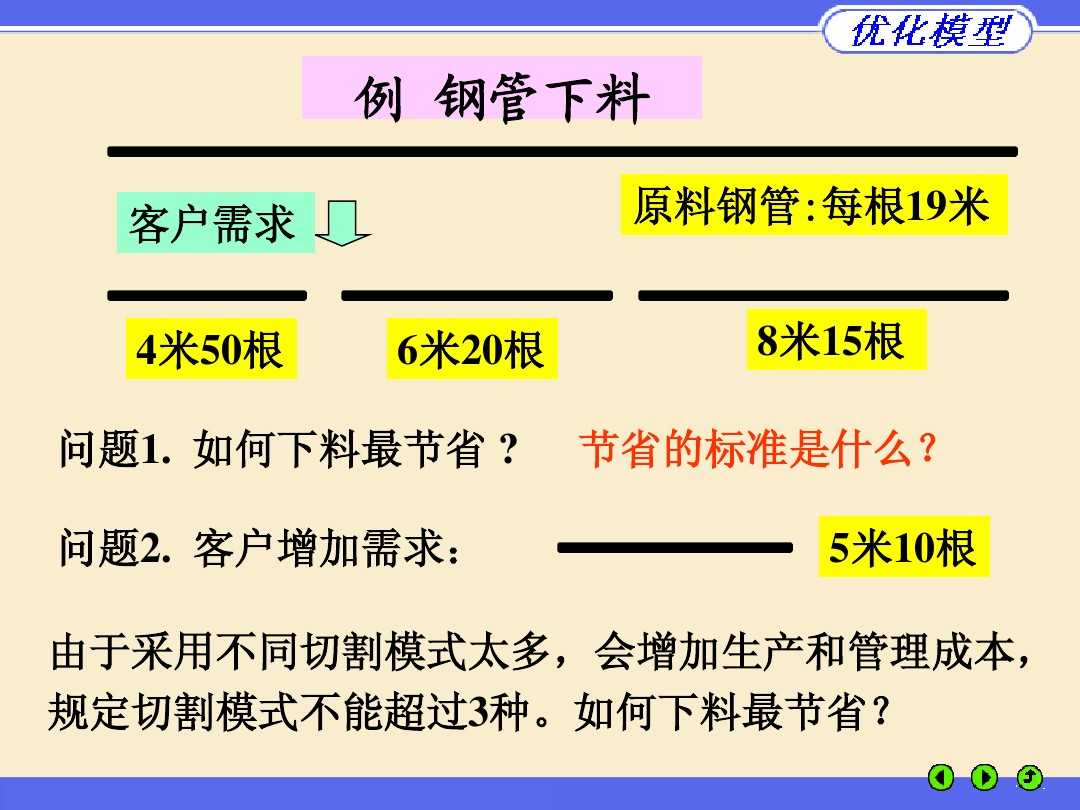
1、解决问题一的目标1:
!钢管下料,原料19m;
!客户需求:4m的50根、6m的20根、8m的15根;
!Question 1:如何下料最省? Question 2:客户增加需求5m的10根;
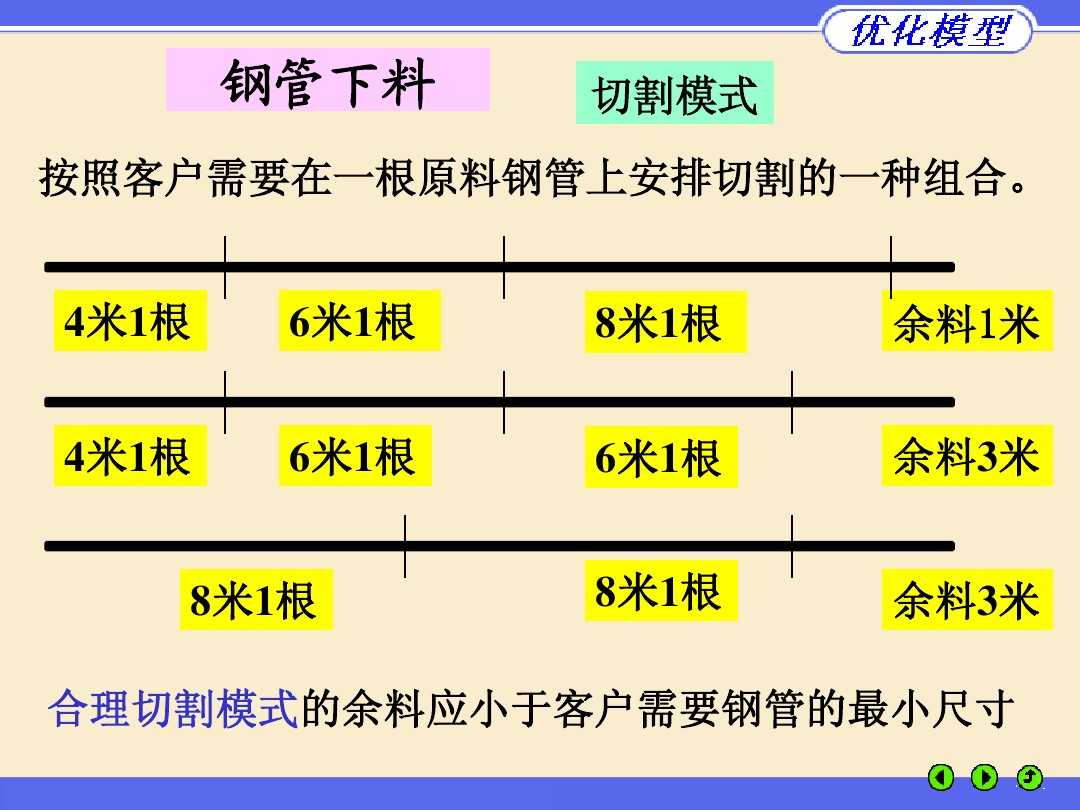
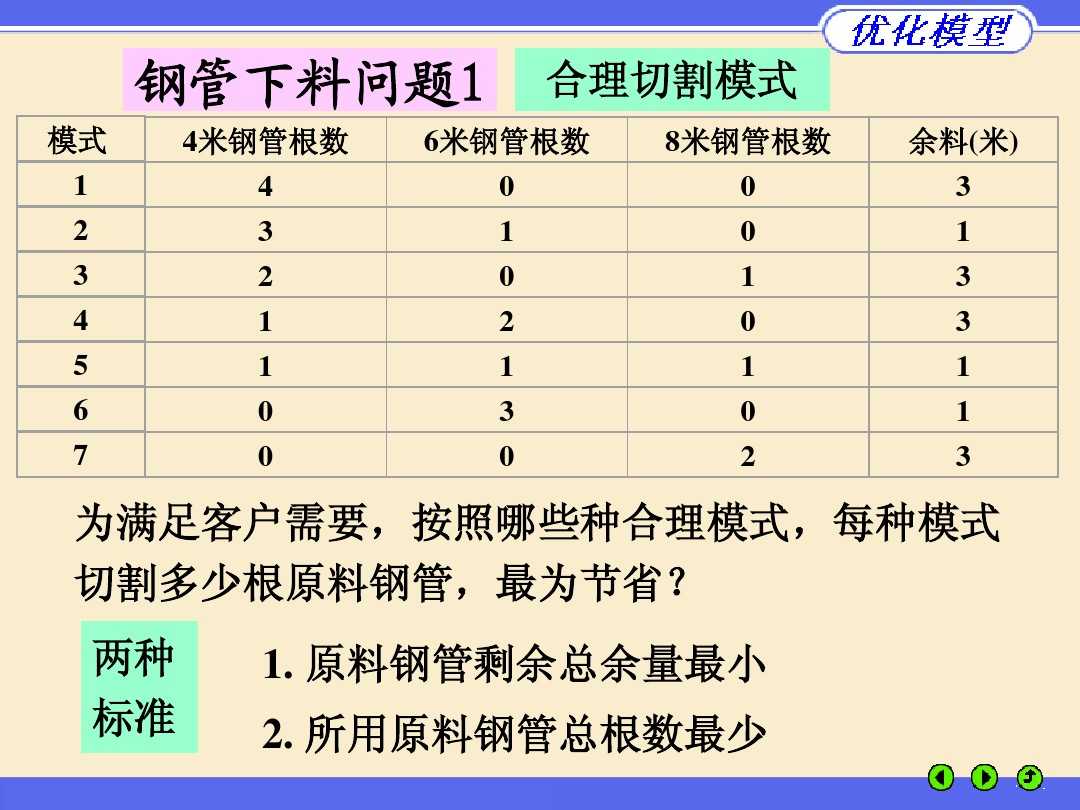
! 4 6 8 余料
Plan 1: 4 0 0
Plan 2: 3 1 0 余1
Plan 3: 2 0 1 余3
Plan 4: 1 2 0 余3
Plan 5: 1 1 1 余1
Plan 6: 0 2 0 余1
plan 7: 0 0 2 余3;
!目标一:(总余量)MIN Z1=3*x1+x2+3*x3+3*x4+x5+x6+3*x7
目标二:(总根数)MIN Z2=x1+x2+x3+x4+x5+x6+x7
约束:4*x1+3*x2+2*x3+x4+x5>=50
x2+2*x4+x5+3*x6>=20
x3+x5+2*x7>=15
整数约束:xi为整数;
MODEL:
sets:
demand/1..3/:a;!j=1,2,3;
plan/1..7/:b,x;!i=1,2,3,4,5,6,7;
link(plan,demand):c;
endsets
data:
a=50,20,15;
b=3,1,3,3,1,1,3;
c=4 0 0 3 1 0 2 0 1 1 2 0 1 1 1 0 3 0 0 0 2;
enddata
min=@sum(plan(i):x(i)*b(i));
@for(demand(j):@sum(plan(i):x(i)*c(i,j))>a(j););!3行约束,@for(demand(j):),按照j循环3次,即j=1,2,3;
@for(plan(i):@gin(x(i)););
END
2、解决问题一的目标2:
MODEL:
sets:
demand/1..3/:a;!j=1,2,3;
plan/1..7/:b,x;!i=1,2,3,4,5,6,7;
link(plan,demand):c;
endsets
data:
a=50,20,15;
b=3,1,3,3,1,1,3;
c=4 0 0 3 1 0 2 0 1 1 2 0 1 1 1 0 3 0 0 0 2;
enddata
min=@sum(plan(i):x(i));
@for(demand(j):@sum(plan(i):x(i)*c(i,j))>a(j););!3行约束,@for(demand(j):),按照j循环3次,即j=1,2,3;
@for(plan(i):@gin(x(i)););
END
3、解决再加额外10根5m的需求:
MODEL:
sets:
type/1..4/:a,b;!i=1, 2,3,4;
plan/1..3/:x;!j=1,2,3;
link(type,plan):r;
endsets
data:
a=4 5 6 8;
b=50 10 20 15;
enddata
min=@sum(plan(j):x(j));
@sum(plan(j):x(j))>26;
@for(type(i):@sum(plan(j):r(i,j)*x(j))>b(i););
@for(plan(j):@sum(type(i):r(i,j)*a(i))>=16;);
@for(plan(j):@sum(type(i):r(i,j)*a(i))<=19;);
@for(plan(j):@gin(x(j)););
@for(link(i,j):@gin(r(i,j)););
END
这期就到这里啦,小编未来将在自己的blog里发表一些有关MATLAB、C语言、Python、LINGO、R、SPSS、EVIEWS and Multisim,and so on,还有一些单片机、电子设计等有关知识。
不要问小编为什么会这么多,因为小编学的是电子信息工程!一个难到爆炸的专业,上到天文电磁波,下到量子微机电路板,外加各种编程,2333.
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lemonCyu/p/5791182.html