标签:
原型模式是用于创建重复的对象,同时又能保证性能。
原型模式用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
主要解决: 利用已有的一个原型对象,快速地生成和原型对象一样的实例
关键代码 : 实现克隆操作,在 JAVA 继承 Cloneable,重写 clone()
使用场景:
类初始化需要消化非常多的资源,这个资源包括数据、硬件资源等。
类图:
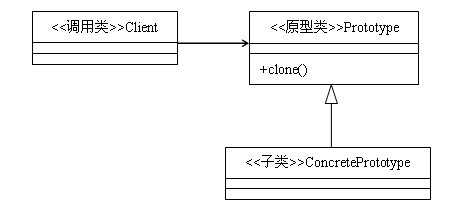
原型模式主要用于对象的复制,它的核心是就是类图中的原型类Prototype。Prototype类需要具备以下两个条件:
个人理解:
原型类实现了Cloneable接口
public class Prototype implements Cloneable { public Prototype clone() { Prototype prototype = null; try { prototype = (Prototype) super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return prototype; } }
具体原型类
public class ConcretePrototype extends Prototype { public void show(){ System.out.println("原型模式实现类,address="+this); } }
测试运行:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcretePrototype cp = new ConcretePrototype();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ConcretePrototype clonecp = (ConcretePrototype) cp.clone();
clonecp.show();
}
}
生成一个实现了Cloneable接口,并重写了clone()方法的模型原型类。这个原型类有一个大头像的属性,可以存储大对象。
public class People implements Cloneable { private String name; private byte[] profile; public People() { File profile = new File("E:testJavaTool/car.jpg"); byte[] profileBytes = ToolHelper.getBytesFromFile(profile); this.setProfile(profileBytes); } public People clone() { People prototype = null; try { prototype = (People) super.clone(); prototype.profile = this.profile.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return prototype; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public byte[] getProfile() { return profile; } public void setProfile(byte[] profile) { this.profile = profile; } public void debugInfo() { System.out.println("--- people debugInfo ---"); System.out.println("name=" + name); System.out.println("profile length=" + profile.length); }
测试运行:
1. 测试创建普通对象占用的系统资源
for(double j=0;j< 100000000000l;j++){ People people = new People(); people.debugInfo(); }
2. 测试创建拷贝对象占用的系统资源
for(double j=0;j< 100000000000l;j++){ People p = new People(); People clonePeople = (People)p.clone(); clonePeople.debugInfo(); }
使用原型模式创建对象比直接new一个对象在性能上要好的多,因为Object类的clone方法是一个本地方法,它直接操作内存中的二进制流,特别是复制大对象时,性能的差别非常明显。
使用原型模式的另一个好处是简化对象的创建,使得创建对象就像我们在编辑文档时的复制粘贴一样简单。
因为以上优点,所以在需要重复地创建相似对象时可以考虑使用原型模式。比如需要在一个循环体内创建对象,假如对象创建过程比较复杂或者循环次数很多的话,使用原型模式不但可以简化创建过程,而且可以使系统的整体性能提高很多。
1)使用原型模式复制对象不会调用类的构造方法。因为对象的复制是通过调用Object类的clone方法来完成的,它直接在内存中复制数据,因此不会调用到类的构造方法
2)深拷贝与浅拷贝。Object类的clone方法只会拷贝对象中的基本的数据类型,对于数组、容器对象、引用对象等都不会拷贝,这就是浅拷贝。如果要实现深拷贝,必须将原型模式中的数组、容器对象、引用对象等另行拷贝。
public class Prototype implements Cloneable { private ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); public Prototype clone(){ Prototype prototype = null; try{ prototype = (Prototype)super.clone(); prototype.list = (ArrayList) this.list.clone(); }catch(CloneNotSupportedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return prototype; } }
3)深拷贝与浅拷贝问题中,会发生深拷贝的有java中的8中基本类型以及他们的封装类型,另外还有String类型。其余的都是浅拷贝。
4)深拷贝是通过实现 Serializable 读取二进制流。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangshuo1/p/5761145.html