标签:
| 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
Value类被称为包装类,它可以将int, float, bool, unsigned, har, char等,基本数据类型可以包装成为类,也包装一些c++标准类,如std::string,std::vector<Value>, std::unordered_map<std::string, Value> 和std::unordered<int, Value>。使用Value对象的好处是,封装的基本数据类型,可以使它们具有面向对象的特性,在另一方面,也可以便于数据类型之间的转换。(即:可以将Value类型转换成基本类型,也可以将基本类型转换成Value类型)。
API中的Value常用函数:
1 /** Create a Value by an unsigned char value. */ 2 /**用无符号字符值创建一个值。*/ 3 explicit Value(unsigned char v); 4 5 /** Create a Value by an integer value. */ 6 /**用整形值创建一个值。*/ 7 explicit Value(int v); 8 9 /** Create a Value by a float value. */ 10 /**用浮点数值创建一个值。*/ 11 explicit Value(float v); 12 13 /** Create a Value by a double value. */ 14 /**用双精度值创建一个值。*/ 15 explicit Value(double v); 16 17 /** Create a Value by a bool value. */ 18 /**用bool(逻辑)值创建一个值。*/ 19 explicit Value(bool v); 20 21 /** Create a Value by a char pointer. It will copy the chars internally. */ 22 /**用字符指针创建一个值。它将复制字符内部。*/ 23 explicit Value(const char* v); 24 25 /** Create a Value by a string. */ 26 /**用字符串值创建一个值。*/ 27 explicit Value(const std::string& v); 28 29 /** Create a Value by a ValueVector object. */ 30 /**通过valuevector对象创建一个值。*/ 31 explicit Value(const ValueVector& v); 32 33 /** Create a Value by a ValueVector object. It will use std::move internally. */ 34 /**通过valuevector对象创建一个值。它将使用内部的std::move。 */ 35 explicit Value(ValueVector&& v); 36 37 /** Create a Value by a ValueMap object. */ 38 /**由ValueMap对象创建一个值。 */ 39 explicit Value(const ValueMap& v); 40 41 /** Create a Value by a ValueMap object. It will use std::move internally. */ 42 /**通过ValueMap对象创建一个值。它将使用内部的std::move。*/ 43 explicit Value(ValueMap&& v); 44 45 /** Create a Value by a ValueMapIntKey object. */ 46 /**通过ValueMapIntKey对象创建一个值。*/ 47 explicit Value(const ValueMapIntKey& v); 48 49 /** Create a Value by a ValueMapIntKey object. It will use std::move internally. */ 50 /**通过ValueMapIntKe对象创建一个值。它将使用内部的std::move。*/ 51 explicit Value(ValueMapIntKey&& v); 52 53 /** Gets as a byte value. Will convert to unsigned char if possible, or will trigger assert error.获取一个字节值。会如果有可能转换为unsigned char型,或会触发断言错误。 */ 54 unsigned char asByte() const; 55 56 /** Gets as an integer value. Will convert to integer if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 57 int asInt() const; 58 59 /** Gets as a float value. Will convert to float if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 60 float asFloat() const; 61 62 /** Gets as a double value. Will convert to double if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 63 double asDouble() const; 64 65 /** Gets as a bool value. Will convert to bool if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 66 bool asBool() const; 67 68 /** Gets as a string value. Will convert to string if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 69 std::string asString() const; 70 71 /** Gets as a ValueVector reference. Will convert to ValueVector if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 72 ValueVector& asValueVector(); 73 74 /** Gets as a const ValueVector reference. Will convert to ValueVector if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 75 const ValueVector& asValueVector() const; 76 77 /** Gets as a ValueMap reference.Will convert to ValueMap if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 78 ValueMap& asValueMap(); 79 80 /** Gets as a const ValueMap reference. Will convert to ValueMap if possible, or will trigger assert error. */ 81 const ValueMap& asValueMap() const; 82 83 /** Gets as a ValueMapIntKey reference. Will convert to ValueMapIntKey if possible, or will trigger assert error. 获取作为一个ValueMapinTKEY参考。会如果有可能转换为ValueMap TKEY,或会触发断言错误。*/ 84 ValueMapIntKey& asIntKeyMap(); 85 86 /** Gets as a const ValueMapIntKey reference. Will convert to ValueMapIntKey if possible, or will trigger assert error.作为获取一个const值PrIntKey参考。会如果有可能转换为ValueMapIntKey,或会触发断言错误 */ 87 const ValueMapIntKey& asIntKeyMap() const; 88 89 /** Checks if the Value is null.@return True if the Value is null, false if not.*/ 90 inline bool isNull() const { return _type == Type::NONE; }
实例:
.h files
#ifndef _VALUETEST_SCENE_H_
#define _VALUETEST_SCENE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
class valueTest : public cocos2d::Layer
{
private:
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
void valTest();
CREATE_FUNC(valueTest);
};
#endif // _VALUETEST_SCENE_H_
.cpp files
val2.getDescription().c_str();这条语句的意思是,输出val2对象所描述的信息。
#include "ValueTest.h"
USING_NS_CC;
Scene* valueTest::createScene()
{
// ‘scene‘ is an autorelease object
auto scene = Scene::create();
// ‘layer‘ is an autorelease object
auto layer = valueTest::create();
// add layer as a child to scene
scene->addChild(layer);
// return the scene
return scene;
}
bool valueTest::init()
{
if (!Layer::init())
{
return false;
}
valTest();
return true;
}
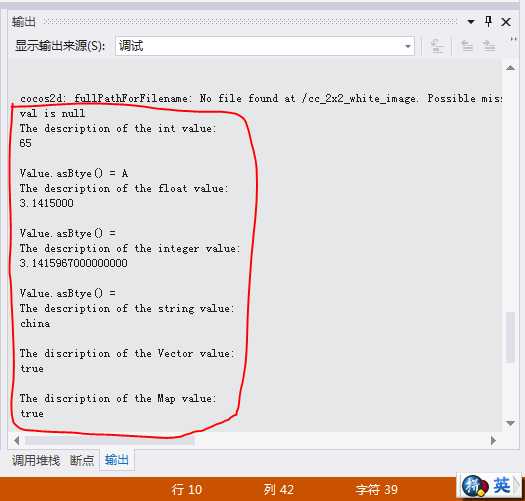
void valueTest::valTest()
{
//1. 调用默认的构造方法
Value val;
//2. 判断val是否为空
if (val.isNull())
{
log("val is null");
}
else
{
std::string str = val.getDescription();
log("The description of val: %s", str.c_str());
}
//3. 使用int初始化
Value val1(65);
log("The description of the int value: %s", val1.getDescription().c_str());
log("Value.asBtye() = %c", val1.asByte());
//4. 使用float初始化
Value val2(3.1415f);
log("The description of the float value: %s", val2.getDescription().c_str());
log("Value.asBtye() = %c", val2.asByte());
//5. 使用double初始化
Value val3(3.1415967);
log("The description of the integer value: %s", val3.getDescription().c_str());
log("Value.asBtye() = %c", val3.asByte());
//6. 使用字符串初始化
std::string str1 = "china";
Value val4(str1);
log("The description of the string value: %s", val4.getDescription().c_str());
//7. 使用Vector初始化
auto spr = Sprite::create();
Vector<Object*>* vec = new Vector<Object*>();
vec->pushBack(spr);
Value val5(vec);
log("The discription of the Vector value: %s", val5.getDescription().c_str());
delete vec;
//8. 使用Map初始化
Map<std::string, Object*>* map = new Map<std::string, Object*>();
map->insert(str1, spr);
//初始化map
Value val6(map);
log("The discription of the Map value:%s", val6.getDescription().c_str());
delete map;
}
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/geore/p/5799168.html