标签:
在Effective Objective-C 2.0 – 52 Specific Ways to Improve Your iOS and OS X Programs一书中,tip 11主要讲述了Objective-C中的消息传递机制。这也是Objective-C在C的基础上,做的最基础也是最重要的封装。
Static Binding And Dynamic Binding
C中的函数调用方式,是使用的静态绑定(static binding),即在编译期就能决定运行时所应调用的函数。而在Objective-C中,如果向某对象传递消息,就会使用动态绑定机制来决定需要调用的方法。而对于Objective-C的底层实现,都是C的函数。对象在收到消息之后,调用了哪些方法,完全取决于Runtime来决定,甚至可以在Runtime期间改变。
一般地,对对象发送消息,我们使用这种写法:
id returnValue = [DGObject test];
其中someObject为接收者(receiver),messageName为选择子(selector)。当Compiler看的这条语句时,会将其转换成为一条标准的消息传递的C函数,objc_msgSend,形如:
void objc_msgSend(id self, SEL cmd, ...)
其中,SEL也就是之前对应的选择子,即为此文讨论的重点。我们对应的写出之前代码在Compiler处理后的C语句:
id returnValue = objc_msgSend(DGObject, @selector(test));
@selector()
对于SEL类型,也就是我们经常使用的@selector(),在很多的书籍资料中的定义是这样:
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
而至于这个objc_selector的结构体是如何定义的,这就要取决于我们Runtime框架的类型,在iOS开发中,我们使用的是Apple的(GNU也有Runtime的framework)。在OS X中SEL被映射成为一个C字符串(char[]),这个字符串也就是方法名。
我们在lldb中,进行测试:
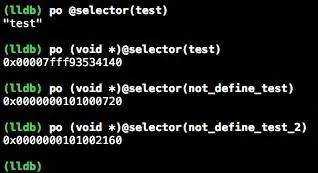
(图释:test是在DGObjectClass中已经定义的方法名,而not_define_test和not_define_test_2没有定义)
第一行我们验证了@selector是一个char[]类型。其他的结果我们可以总结出:@selector()选择子只与函数名有关。而且还有一个规律,那就是倘若选择子方法已经在编译期由Compiler进行静态绑定,则其存储的地址就会更加的具体。
发送消息所依托的选择子只与函数名有关,我们便可以猜想到为什么Objective-C中没有像C++、C#那样的函数重载特性,因为选择子并不由参数和函数名共同决定。
那么为什么要有这个选择子呢?在从源代码看 ObjC 中消息的发送一文中,作者Draveness对其原因进行了推断:
Objective-C 为我们维护了一个巨大的选择子表
在使用
@selector()时会从这个选择子表中根据选择子的名字查找对应的SEL。如果没有找到,则会生成一个SEL并添加到表中在编译期间会扫描全部的头文件和实现文件将其中的方法以及使用
@selector()生成的选择子加入到选择子表中
objc_msgSend
在选择子拿到对应的地址后,objc_msgSend会依据接收者与选择子的类型来调用适当方法。为了学习此过程,我从opensource.apple.com的git仓库中clone了Runtime源码,并在x86_64架构下macOS环境进行运行。
另外,我在整个工程中增加了一个Class:
// DGObject.h
@interface DGObject : NSObject
- (void)test;
@end
// DGObject.m
#import "DGObject.h"
@implementation DGObject
- (void)test {
printf("Hello World. ");
}
@end
并在main入口函数中进行改动:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
DGObject *obj = [[DGObject alloc]init];
NSLog(@"%p", @selector(test));
[obj test];
}
return 0;
}
然后我们在objc-runtime-new.mm中,进行debug。为了研究清楚Runtime是如何查询到调用函数,我们在lookUpImpOrForward下断点。当程序执行[obj test]后,我们发现到达断点位置,并且观察此时的调用栈情况:
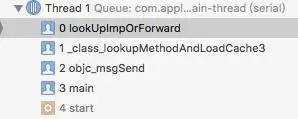
objc_msgSend并不是直接调用查询方法,而是先调用了_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3这个函数。看下它的源码:
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls){
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3就好像一个中转函数,并给出了在查询IMP指针前默认参量的几个布尔值。而由于我们的方法没有进行方法转发,则直接调用了_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3这个函数。而当对象在收到无法解读的消息之后,即启动消息转发机制,这时候应该会进入lookUpImpOrNil这个方法。这也是objc_msgSend的一种优化方式。
这里还要注意一点,就是关于Cache的默认参数是NO,因为在objc_msgSend中已经进行过缓存查询。以下是objc_msgSend的汇编实现:
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
MESSENGER_START
// NilTest:宏,判断被发送消息的对象是否为nil。
// 如果为nil直接返回。
NilTest NORMAL
// GetIsaFast快速获取isa指针地址,并放入r11寄存器
GetIsaFast NORMAL // r11 = self->isa
// 查找类缓存中selector的IMP指针,并放到r10寄存器
// 如果不存在,则在class的方法list中查询
CacheLookup NORMAL // calls IMP on success
// NilTest的许可量以及GetIsaFast的许可量
NilTestSupport NORMAL
GetIsaSupport NORMAL
// cache miss: go search the method lists
LCacheMiss:
// isa still in r11
// MethodTableLoopup这个宏是__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3函数的入口
// 调用条件是在缓存中没有查询到方法对应IMP
MethodTableLookup %a1, %a2 // r11 = IMP
cmp %r11, %r11 // set eq (nonstret) for forwarding
jmp *%r11 // goto *imp
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend
趁热打铁,再来看一下MethodTableLoopup这个宏的实现:
.macro MethodTableLookup
MESSENGER_END_SLOW
SaveRegisters
// _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(receiver, selector, class)
// 从a1, a2, a3中分别拿到对应参数
movq $0, %a1
movq $1, %a2
movq %r11, %a3
// 调用__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
call __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
// IMP is now in %rax
// 将IMP从r11挪至rax
movq %rax, %r11
RestoreRegisters
.endmacro
而在objc-msg-x86_64.s中有多个以objc_msgSend为前缀的方法,这个是根据返回值类型和调用者类型分别处理的,我列举三个常用的
| OBJC_MSGSEND_STRET | 待发送的消息要返回结构体前提是只有当CPU的寄存器能够容纳的下消息返回类型。 |
|---|---|
| objc_msgSend_fpret | 消息返回的是浮点数。因为某些架构的CPU调用函数,需要对浮点数寄存器做特殊处理。 |
| objc_msgSendSuper | 需要向superClass发送消息时调用。 |
lookUpImpOrForward
之后我们随着调用栈往上看,在接受到消息入口的命令后,Runtime要开始进行查找方法的操作,源码如下:
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver) {
Class curClass;
IMP imp = nil;
Method meth;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// 检查是否添加缓存锁,如果没有进行缓存查询。
// 查到便返回IMP指针
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// 通过调用realizeClass方法,分配可读写`class_rw_t`的空间
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
rwlock_writer_t lock(runtimeLock);
realizeClass(cls);
}
// 倘若未进行初始化,则初始化
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
}
// 保证方法查询,并进行缓存填充(cache-fill)
retry:
runtimeLock.read();
// 是否忽略GC垃圾回收机制(仅用在macOS中)
if (ignoreSelector(sel)) {
imp = _objc_ignored_method;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
goto done;
}
// 当前类的缓存列表中进行查找
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// 从类的方法列表中进行查询
meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
// 从父类中循环遍历
curClass = cls;
while ((curClass = curClass->superclass)) {
// 父类的缓存列表中查询
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// 如果在父类中发现方法,则填充到该类缓存列表
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
break;
}
}
// 从父类的方法列表中查询
meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// 进入method resolve过程
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
// 调用_class_resolveMethod,解析没有实现的方法
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
// 进行二次尝试
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// 没有找到方法,启动消息转发
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
}
以上就是整个的查找方法流程,然后我们再对其中的一些方法逐一解读。
static method_t *getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel) {
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// 遍历所在类的methods,这里的methods是List链式类型,里面存放的都是指针
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(), end = cls->data()->methods.endLists(); mlists != end; ++mlists) {
method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
这里的对于 class 存储方式,我在以后的博文中会分析其存储结构。
而对于没有实现方法的解析过程中,会有以下过程:
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst) {
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
// 针对于对象方法的操作
// 这个方法是动态方法解析中,当收到无法解读的消息后调用。
// 这个方法也会用在@dynamic,以后会在消息转发机制的源码分析中介绍
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
// 针对于类方法的操作,说明同上
_class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
// 再次启动查询,并且判断是否拥有缓存中消息标记_objc_msgForward_impcache
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/)) {
// 说明可能不是 metaclass 的方法实现,当做对象方法尝试
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}
来单步调试一下程序,由于我们的test方法属于正常的类方法,所以会进入正常地查询类方法列表中查到,进入done函数块,返回到objc_msgSend方法,最终会到我们的函数调用位置:
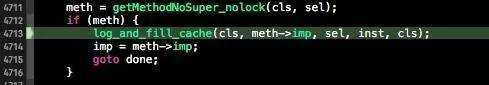
IMP in Method List Flow
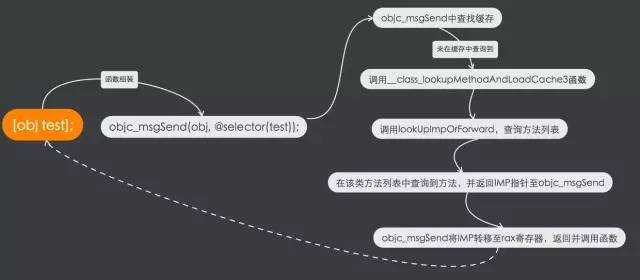
来简单总结一下在第一次调用某个对象方法的消息传递流程:当代码执行到某个对象(第一次)调用某个方法后,首先会确定这个方法的接收者和选择子,并组装成C的objc_msgSend函数形式,启动消息传递机制。
objc_msgSend函数是使用汇编语言实现的,其中我们先尝试的从缓存表中(也就是常说的快速映射表)查询缓存,倘若查询失败,则会将具体的类对象、选择子、接收者在指定的内存单元中存储,并调用__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3函数。__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3我们俗称为在方法列表中查询的入口函数,他会直接调用lookUpImpOrForward进行查询方法对应的IMP指针。由于我们是方法函数,在获取方法列表后,即可查询到IMP指针。由于是第一次调用,则会把我们的方法加入缓存,并goto到done代码块,返回IMP指针。当objc_msgSend接收到IMP指针后存储至rax寄存器,返回调用函数位置,完成整个消息传递流程。
写在最后
其实消息传递及转发流程是一个相对来说比较复杂的机制。本文所讲述的流程是我们最常见的一种形式。在之后的消息传递与转发的博文中,还会更加深入的探讨这一机制相关流程并深入的阅读源码。
若想查看更多的iOS Source Probe文章,收录在这个Github仓库中。
https://github.com/Desgard/iOS-Source-Probe
objc_msgSend消息传递学习笔记 – 对象方法消息传递流程
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/fengmin/p/5820453.html