标签:
上一篇《白话tornado源码之待请求阶段》中介绍了tornado框架在客户端请求之前所做的准备(下图1、2部分),本质上就是创建了一个socket服务端,并进行了IP和端口的绑定,但是未执行 socket的accept方法,也就是未获取客户端请求信息。
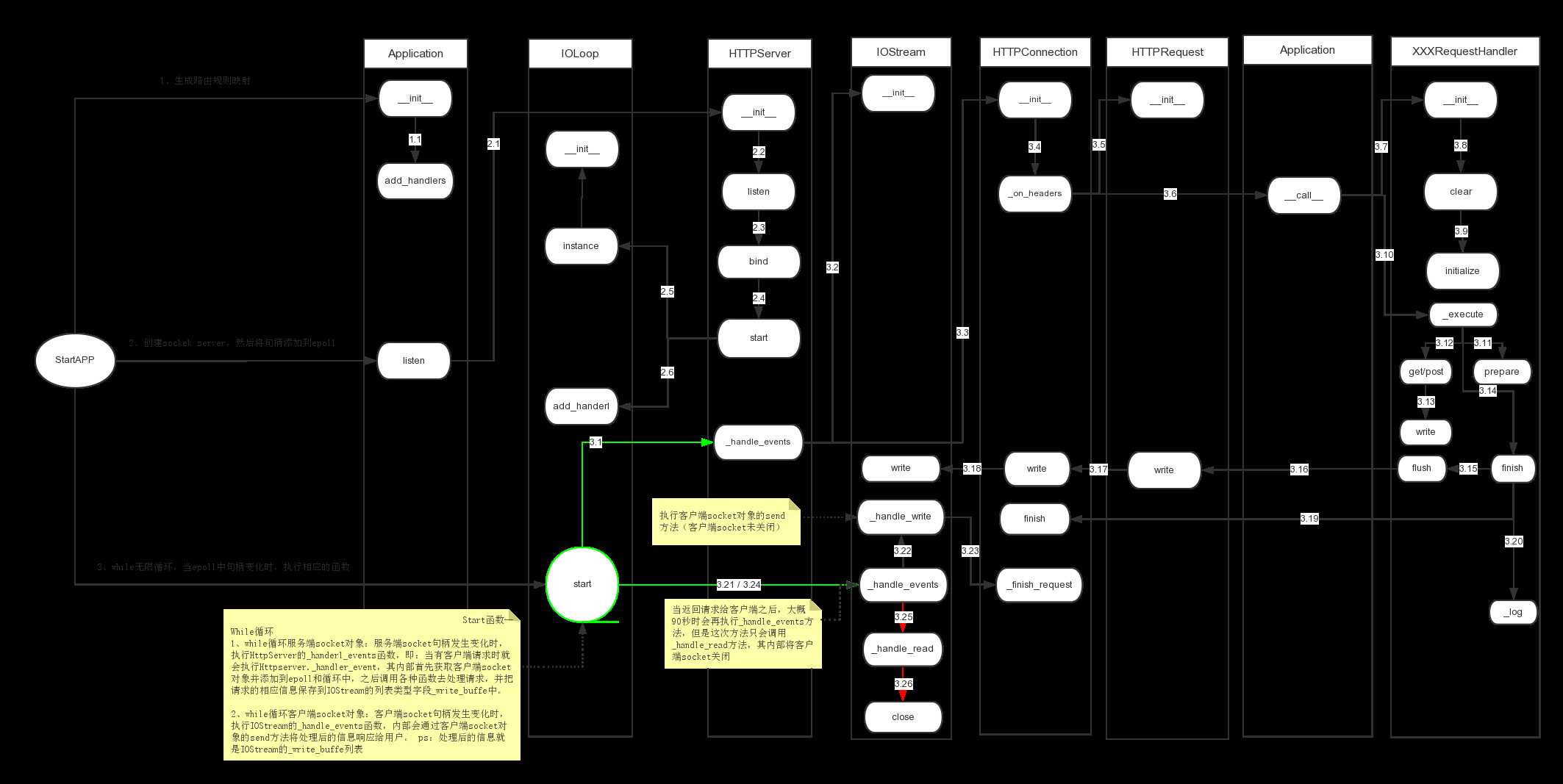
本篇就来详细介绍tornado服务器(socket服务端)是如何接收用户请求 数据以及如果根据用户请求的URL处理并返回数据,也就是上图的3系列所有步骤,如上图【start】是一个死循环,其中利用epoll监听服务端 socket句柄,一旦客户端发送请求,则立即调用HttpServer对象的_handle_events方法来进行请求的处理。
对于整个3系列按照功能可以划分为四大部分:
此处代码主要有三项任务:
1、 socket.accept() 接收了客户端请求。
2、创建封装了客户端socket对象和IOLoop对象的IOStream实例(用于之后获取或输出数据)。
3、创建HTTPConnection对象,其内容是实现整个功能的逻辑。
class HTTPServer(object):
def _handle_events(self, fd, events):
while True:
try:
#======== 获取客户端请求 =========#
connection, address = self._socket.accept()
except socket.error, e:
if e.args[0] in (errno.EWOULDBLOCK, errno.EAGAIN):
return
raise
if self.ssl_options is not None:
assert ssl, "Python 2.6+ and OpenSSL required for SSL"
try:
connection = ssl.wrap_socket(connection,
server_side=True,
do_handshake_on_connect=False,
**self.ssl_options)
except ssl.SSLError, err:
if err.args[0] == ssl.SSL_ERROR_EOF:
return connection.close()
else:
raise
except socket.error, err:
if err.args[0] == errno.ECONNABORTED:
return connection.close()
else:
raise
try:
#这是的条件是选择https和http请求方式
if self.ssl_options is not None:
stream = iostream.SSLIOStream(connection, io_loop=self.io_loop)
else:
#将客户端socket对象和IOLoop对象封装到IOStream对象中
#IOStream用于从客户端socket中读取请求信息
stream = iostream.IOStream(connection, io_loop=self.io_loop)
#创建HTTPConnection对象
#address是客户端IPdizhi
#self.request_callback是Application对象,其中包含了:url映射关系和配置文件等..
#so,HTTPConnection的构造函数就是下一步处理请求的位置了..
HTTPConnection(stream, address, self.request_callback,self.no_keep_alive, self.xheaders)
except:
logging.error("Error in connection callback", exc_info=True)
此处代码主要两项目任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
class IOStream(object): def __init__(self, socket, io_loop=None, max_buffer_size=104857600, read_chunk_size=4096): #客户端socket对象 self.socket = socket self.socket.setblocking(False) self.io_loop = io_loop or ioloop.IOLoop.instance() self.max_buffer_size = max_buffer_size self.read_chunk_size = read_chunk_size self._read_buffer = collections.deque() self._write_buffer = collections.deque() self._write_buffer_frozen = False self._read_delimiter = None self._read_bytes = None self._read_callback = None self._write_callback = None self._close_callback = None self._connect_callback = None self._connecting = False self._state = self.io_loop.ERROR with stack_context.NullContext(): #将客户端socket句柄添加的epoll中,并将IOStream的_handle_events方法添加到 Start 的While循环中 #Start 的While循环中监听客户端socket句柄的状态,以便再最后调用IOStream的_handle_events方法把处理后的信息响应给用户 self.io_loop.add_handler(self.socket.fileno(), self._handle_events, self._state) |
此处代码主要两项任务:
对于获取请求数据,其实就是执行IOStream的read_until函数来完成,其内部通过socket.recv(4096)方法获取客户端请求的数据,并以 【\r\n\r\n】作为请求信息结束符(http请求头和内容通过\r\n\r\n分割)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class HTTPConnection(object): def __init__(self, stream, address, request_callback, no_keep_alive=False,xheaders=False): self.stream = stream #stream是封装了客户端socket和IOLoop实例的IOStream对象 self.address = address #address是客户端IP地址 self.request_callback = request_callback #request_callback是封装了URL映射和配置文件的Application对象。 self.no_keep_alive = no_keep_alive self.xheaders = xheaders self._request = None self._request_finished = False #获取请求信息(请求头和内容),然后执行 HTTPConnection的_on_headers方法继续处理请求 self._header_callback = stack_context.wrap(self._on_headers) self.stream.read_until("\r\n\r\n", self._header_callback) |
请求数据格式:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8888
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2272.118 Safari/537.36
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en;q=0.6,zh-TW;q=0.4
If-None-Match: "e02aa1b106d5c7c6a98def2b13005d5b84fd8dc8"
详细代码解析:
 IOStream.read_until
IOStream.read_until IOStream._read_to_buffer
IOStream._read_to_buffer IOStream._read_from_buffer
IOStream._read_from_buffer上述代码主要有两个任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
class HTTPConnection(object): def _on_headers(self, data): try: data = native_str(data.decode(‘latin1‘)) eol = data.find("\r\n") #获取请求的起始行数据,例如:GET / HTTP/1.1 start_line = data[:eol] try: #请求方式、请求地址、http版本号 method, uri, version = start_line.split(" ") except ValueError: raise _BadRequestException("Malformed HTTP request line") if not version.startswith("HTTP/"): raise _BadRequestException("Malformed HTTP version in HTTP Request-Line") #把请求头信息包装到一个字典中。(不包括第一行) headers = httputil.HTTPHeaders.parse(data[eol:]) #把请求信息封装到一个HTTPRequest对象中 #注意:self._request = HTTPRequest, #HTTPRequest中封装了HTTPConnection #HTTPConnection中封装了stream和application self._request = HTTPRequest(connection=self, method=method, uri=uri, version=version,headers=headers, remote_ip=self.address[0]) #从请求头中获取 Content-Length content_length = headers.get("Content-Length") if content_length: content_length = int(content_length) if content_length > self.stream.max_buffer_size: raise _BadRequestException("Content-Length too long") if headers.get("Expect") == "100-continue": self.stream.write("HTTP/1.1 100 (Continue)\r\n\r\n") self.stream.read_bytes(content_length, self._on_request_body) return #**************** 执行Application对象的 __call__ 方法,也就是路由系统的入口 ******************* self.request_callback(self._request) except _BadRequestException, e: logging.info("Malformed HTTP request from %s: %s", self.address[0], e) self.stream.close() return |
 HTTPRequest.__init__
HTTPRequest.__init__此处代码主要有三个项任务:
注意:
1、执行Application的 __call__ 方法时,其参数request是HTTPRequest对象(其中封装HTTPConnetion、Stream、Application对象、请求头信息)
2、Handler泛指就是我们定义的用于处理请求的类并且她还继承自RequestHandler
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
class Application(object): def __call__(self, request): """Called by HTTPServer to execute the request.""" transforms = [t(request) for t in self.transforms] handler = None args = [] kwargs = {} #根据请求的目标主机,匹配主机模版对应的正则表达式和Handlers handlers = self._get_host_handlers(request) if not handlers: handler = RedirectHandler( self, request, url="http://" + self.default_host + "/") else: for spec in handlers: match = spec.regex.match(request.path) if match: # None-safe wrapper around url_unescape to handle # unmatched optional groups correctly def unquote(s): if s is None: return s return escape.url_unescape(s, encoding=None) handler = spec.handler_class(self, request, **spec.kwargs) #创建RquestHandler对象 # Pass matched groups to the handler. Since # match.groups() includes both named and unnamed groups, # we want to use either groups or groupdict but not both. # Note that args are passed as bytes so the handler can # decide what encoding to use. kwargs = dict((k, unquote(v)) for (k, v) in match.groupdict().iteritems()) if kwargs: args = [] else: args = [unquote(s) for s in match.groups()] break if not handler: handler = ErrorHandler(self, request, status_code=404) # In debug mode, re-compile templates and reload static files on every # request so you don‘t need to restart to see changes if self.settings.get("debug"): if getattr(RequestHandler, "_templates", None): for loader in RequestHandler._templates.values(): loader.reset() RequestHandler._static_hashes = {} #==== 执行RequestHandler的_execute方法 ==== handler._execute(transforms, *args, **kwargs) return handler |
 Application._get_host_handlers
Application._get_host_handlers RequestHandler.__init__
RequestHandler.__init__上述过程中,首先根据请求的URL去路由规则中匹配,一旦匹配成功,则创建路由相 对应的handler的实例。例如:如果请求 的url是【/index/11】则会创建IndexHandler实例,然后再执行该对象的 _execute 方法。由于所有的 xxxHandler 类是RequestHandler的派生类,所以会默认执行 RequestHandler的 _execute 方法。
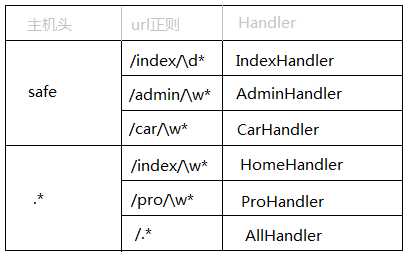
此处代码主要有三项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
class RequestHandler(object): def _execute(self, transforms, *args, **kwargs): """Executes this request with the given output transforms.""" self._transforms = transforms with stack_context.ExceptionStackContext( self._stack_context_handle_exception): if self.request.method not in self.SUPPORTED_METHODS: raise HTTPError(405) # If XSRF cookies are turned on, reject form submissions without # the proper cookie if self.request.method not in ("GET", "HEAD") and \ self.application.settings.get("xsrf_cookies"): self.check_xsrf_cookie() self.prepare() if not self._finished: #通过反射的方法,执行 RequestHandler 派生类的的 get、post、put方法 getattr(self, self.request.method.lower())(*args, **kwargs) if self._auto_finish and not self._finished: self.finish() |
例:用户发送get请求
 MyHandler.get
MyHandler.get RequestHandler.write
RequestHandler.write上述在执行RequestHandler的write方法时,讲数据保存在 Handler对象的 _write_buffer 列表中,在之后执行finish时再讲数据写到IOStream对象的_write_buffer字段中,其类型是双向队列 collections.deque()。
此段代码主要有两项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
class RequestHandler: def finish(self, chunk=None): """Finishes this response, ending the HTTP request.""" assert not self._finished if chunk is not None: self.write(chunk) if not self._headers_written: if (self._status_code == 200 and self.request.method in ("GET", "HEAD") and "Etag" not in self._headers): hasher = hashlib.sha1() for part in self._write_buffer: hasher.update(part) etag = ‘"%s"‘ % hasher.hexdigest() inm = self.request.headers.get("If-None-Match") if inm and inm.find(etag) != -1: self._write_buffer = [] self.set_status(304) else: self.set_header("Etag", etag) if "Content-Length" not in self._headers: content_length = sum(len(part) for part in self._write_buffer) self.set_header("Content-Length", content_length) if hasattr(self.request, "connection"): self.request.connection.stream.set_close_callback(None) if not self.application._wsgi: #将处理请求返回的数据发送到IOStream的_write_buffer队列中 self.flush(include_footers=True) self.request.finish() #纪录日志 self._log() self._finished = True |
此处代码主要有一项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
def flush(self, include_footers=False): """Flushes the current output buffer to the network.""" if self.application._wsgi: raise Exception("WSGI applications do not support flush()") chunk = "".join(self._write_buffer) self._write_buffer = [] if not self._headers_written: self._headers_written = True for transform in self._transforms: self._headers, chunk = transform.transform_first_chunk( self._headers, chunk, include_footers) headers = self._generate_headers() else: for transform in self._transforms: chunk = transform.transform_chunk(chunk, include_footers) headers = "" # Ignore the chunk and only write the headers for HEAD requests if self.request.method == "HEAD": if headers: self.request.write(headers) return if headers or chunk: #执行HTTPReqeust的write方法 self.request.write(headers + chunk) |
 HTTPRequest.write
HTTPRequest.write IOStream.write
IOStream.write以上代码执行完成之后,请求的处理基本上就完成了。下面就是等待监听客户端socket句柄的epoll触发,然后执行IOStream的_handle_event方法来将 响应数据发送给客户端。
此处代码主要有一项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
|
class RequestHandler: def _log(self): self.application.log_request(self) |
 Application.log_request
Application.log_request由于epoll中不但监听了服务器socket句柄还监听了客户端sokcet句柄,所以当客户端socket对象变化时,就会去调用之前指定的IOStream的_handler_events方法。
此段代码主要有一项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
class IOStream(object): def _handle_events(self, fd, events): if not self.socket: logging.warning("Got events for closed stream %d", fd) return try: if events & self.io_loop.READ: self._handle_read() if not self.socket: return if events & self.io_loop.WRITE: if self._connecting: self._handle_connect() #执行_handle_write方法,内部调用socket.send将数据响应给客户端 self._handle_write() if not self.socket: return if events & self.io_loop.ERROR: self.close() return state = self.io_loop.ERROR if self.reading(): state |= self.io_loop.READ if self.writing(): state |= self.io_loop.WRITE if state != self._state: self._state = state self.io_loop.update_handler(self.socket.fileno(), self._state) except: logging.error("Uncaught exception, closing connection.", exc_info=True) self.close() raise |
此段代码主要有两项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
class IOStream(object): def _handle_write(self): while self._write_buffer: try: if not self._write_buffer_frozen: _merge_prefix(self._write_buffer, 128 * 1024) #调用客户端socket对象的send方法发送数据 num_bytes = self.socket.send(self._write_buffer[0]) self._write_buffer_frozen = False _merge_prefix(self._write_buffer, num_bytes) self._write_buffer.popleft() except socket.error, e: if e.args[0] in (errno.EWOULDBLOCK, errno.EAGAIN): self._write_buffer_frozen = True break else: logging.warning("Write error on %d: %s", self.socket.fileno(), e) self.close() return if not self._write_buffer and self._write_callback: callback = self._write_callback self._write_callback = None #执行回调函数关闭客户端socket连接(HTTPConnection的_on_write_complete方法) self._run_callback(callback) |
 IOStream._run_callback
IOStream._run_callback注:IOStream的_run_callback方法内部调用了HTTPConnection的_on_write_complete方法
此处代码主要有一项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
class HTTPConnection(object): def _on_write_complete(self): if self._request_finished: self._finish_request() def _finish_request(self): if self.no_keep_alive: disconnect = True else: connection_header = self._request.headers.get("Connection") if self._request.supports_http_1_1(): disconnect = connection_header == "close" elif ("Content-Length" in self._request.headers or self._request.method in ("HEAD", "GET")): disconnect = connection_header != "Keep-Alive" else: disconnect = True self._request = None self._request_finished = False if disconnect: self.stream.close() return self.stream.read_until("\r\n\r\n", self._header_callback) |
 IOStream.read_until
IOStream.read_until IOStream._add_io_state
IOStream._add_io_state IOLoop.update_handler
IOLoop.update_handler此段代码主要有一项任务:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
class IOStream(object): def _handle_events(self, fd, events): if not self.socket: logging.warning("Got events for closed stream %d", fd) return try: #由于在 2.23 步骤中已经将epoll的状态更新为READ,所以这次会执行_handle_read方法 if events & self.io_loop.READ: self._handle_read() #执行完_handle_read后,客户端socket被关闭且置空,所有此处就会执行return if not self.socket: return #===============================终止=========================== if events & self.io_loop.WRITE: if self._connecting: self._handle_connect() self._handle_write() if not self.socket: return if events & self.io_loop.ERROR: self.close() return state = self.io_loop.ERROR if self.reading(): state |= self.io_loop.READ if self.writing(): state |= self.io_loop.WRITE if state != self._state: self._state = state self.io_loop.update_handler(self.socket.fileno(), self._state) except: logging.error("Uncaught exception, closing connection.", exc_info=True) self.close() raise |
 IOStream._handle_read
IOStream._handle_read IOStream._read_from_socket
IOStream._read_from_socket IOStream.close
IOStream.close IOLoop.remove_handler
IOLoop.remove_handler以上就是tornado源码针对请求的主要内容,另外,大家可能注意到我们返回给用户的只是一个简单的“hello world”,tornado返回复杂的内容时又需要使用模板语言,至于如何生成复杂的页面,我们会在下一篇再会剖析。
读者如果觉得那里错误或不适,请与我联系!!!
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/maozhr/p/5840677.html