标签:
http://classfoo.com/ccby/article/jnevK
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> // sort, max_element, random_shuffle, remove_if, lower_bound #include <functional> // greater, bind2nd // 用在此处是为了方便简洁, 在实际编程中慎用 using namespace std; int main() { int arr[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; // 用上述数组初始化向量 vector<int> foo(arr, arr + 4); // 插入更多的元素 foo.push_back(5); foo.push_back(6); foo.push_back(7); foo.push_back(8); // 此时的向量内容为 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} // 随机移动元素 random_shuffle(foo.begin(), foo.end()); // 定位最大的元素, O(n) vector<int>::const_iterator largest = max_element(foo.begin(), foo.end()); cout << "当前最大元素是: " << *largest << "\n"; cout << "它的索引位置是: " << largest - foo.begin() << "\n"; // 排序元素 sort(foo.begin(), foo.end()); // 用二分查找法找出向量中值为5的元素 vector<int>::const_iterator five = lower_bound(foo.begin(), foo.end(), 5); cout << "值为5的元素的索引位置是: " << five - foo.begin() << "\n"; // 删除所有值大于4的元素 foo.erase(remove_if(foo.begin(), foo.end(), bind2nd(greater<int>(), 4)), foo.end()); // 打印所有剩余元素的值 for (vector<int>::const_iterator it = foo.begin(); it != foo.end(); ++it) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << "\n"; return 0; }

对象
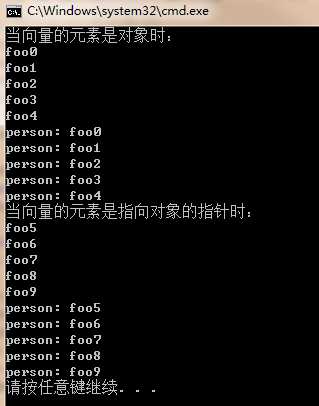
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> #include <sstream> namespace ClassFoo{ using namespace std; class Person { private: std::string name; static int n; public: Person() { std::stringstream ss; std::string snum; ss << n++; ss >> snum; name = "foo" + snum; } void print() const { std::cout << name << std::endl; } void printWithPrefix(std::string prefix) const { std::cout << prefix << name << std::endl; } }; int Person::n = 0; void foo(const std::vector<Person>& coll) { // 对每个元素对象调用成员函数 print() for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(), mem_fun_ref(&Person::print)); // 对每个元素对象调用成员函数 printWithPrefix() // - "person: " 作为参数传递给成员函数 for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(), bind2nd(mem_fun_ref(&Person::printWithPrefix), "person: ")); } void ptrfoo(const std::vector<Person*>& coll) { // 对每个指针指向的元素对象调用成员函数 print() for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(), mem_fun(&Person::print)); // 对每个指针指向的元素对象调用成员函数 printWithPrefix() // - "person: " 作为参数传递给成员函数 for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(), bind2nd(mem_fun(&Person::printWithPrefix), "person: ")); } } int main() { std::cout << "当向量的元素是对象时:" << std::endl; std::vector<ClassFoo::Person> coll(5); ClassFoo::foo(coll); std::cout << "当向量的元素是指向对象的指针时:" << std::endl; std::vector<ClassFoo::Person*> coll2; coll2.push_back(new ClassFoo::Person); coll2.push_back(new ClassFoo::Person); coll2.push_back(new ClassFoo::Person); coll2.push_back(new ClassFoo::Person); coll2.push_back(new ClassFoo::Person); ClassFoo::ptrfoo(coll2); }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuguangyuan/p/5845516.html