标签:des style blog http color 使用 io 数据
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
思路:依次遍历链表,使用set保存已经访问过的节点的地址。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode *detectCycle( ListNode *head ) { 4 unordered_set<ListNode*> nodeSet; 5 while( head ) { 6 if( nodeSet.count( head ) ) { return head; } 7 nodeSet.insert( head ); 8 head = head->next; 9 } 10 return 0; 11 } 12 };
上述方法需要大量额外空间。为了满足常空间复杂度要求,参考网上的方法:使用两个指针slow和fast,分别以1和2的速度遍历链表。若链表中存在环,则两个指针必然会在某时刻相遇。且首次相遇时,两个指针经过的节点数目一定满足2倍关系。
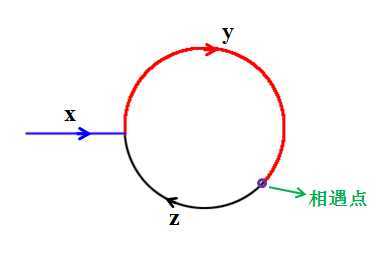
如上图:slow和fast经过的节点数目分别为:x+y和x+2*y+z,由2*(x+y)=x+2*y+z有,x = z。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode *detectCycle( ListNode *head ) { 4 if( !head || !head->next ) { return 0; } 5 ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head; 6 while( fast ) { 7 slow = slow->next; 8 fast = fast->next; 9 if( fast ) { fast = fast->next; } 10 if( fast && fast == slow ) { 11 slow = head; 12 while( slow != fast ) { 13 slow = slow->next; 14 fast = fast->next; 15 } 16 return slow; 17 } 18 } 19 return 0; 20 } 21 };
还有一种方法:依次遍历链表,将当前访问节点的地址保存到其val字段中。不过,该方法会破坏原始链表的数据,并且若原始链表的某个节点的val字段的值与其地址值本身就相同,则算法将失效。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 ListNode *detectCycle( ListNode *head ) { 4 while( head ) { 5 if( (int)head == head->val ) { return head; } 6 head->val = (int)head; 7 head = head->next; 8 } 9 return 0; 10 } 11 };
Linked List Cycle II,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:des style blog http color 使用 io 数据
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/moderate-fish/p/3905062.html