标签:
intellj idea的强大之处就不多说了,相信每个用过它的人都会体会到,但是我们也会被他的复杂搞的晕头转向,尤其刚从eclipse转过来的童鞋,相信刚开始的那段经历都是不堪回首的,我也是一步步这么走过来的。
今天讲的一个主题是如何实现类似eclipse的Code Templates那样的功能,进行文件级别的方法级别注释的实现。
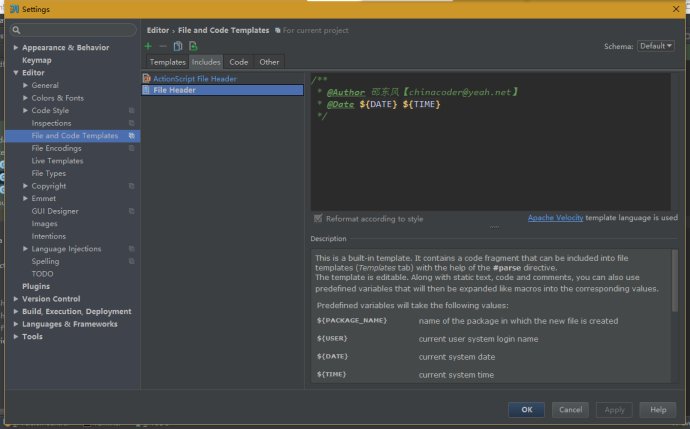
一:文件级别的注释
文件级别的注释网上已经很多介绍了,本文不做多介绍,主要是通过File--》Setting--》File and Code Template中来设置
二:方法级别的注释
文件级别的注释网上其实已经有很多了,但是方法级别的注释讲解的却很少,很多人不知道如何实现。我分享的这种方法也是个人在使用Intellj过程中自己的一些技巧,如果你有更好的方式,可以在评论中给予更多的思路。主要就是通过intellj强大的Live Template来做。
下面简单介绍一下Live Template(下面这段话摘自网络,点击这里进入原文-- 更为详细的Live Template的使用介绍和高级进阶,请参考文章底部链接 ):
用惯了Eclipse快捷键的人可能会不习惯,sysout、foreach等快捷方式找不到了,main方法也无法自动补全了,其实这个在IntelliJ中有一个异常强大的模块Live Template来实现。
例如,在class中尝试psvm+tab,则会发现main方法产生了;输入iter+tab,则生成了foreach语句。
live template还有一个surround的用法,选中某个变量,键入ctl+alt+j两次,则会出现自动补全的菜单。
此外,还可以自定义Live Template。Code Snippet技术应用也挺普遍的,IntelliJ的Live Template优点是内置了一些智能的变量和函数,可以做到一些语义级别的分析和运用
下面为具体步骤:
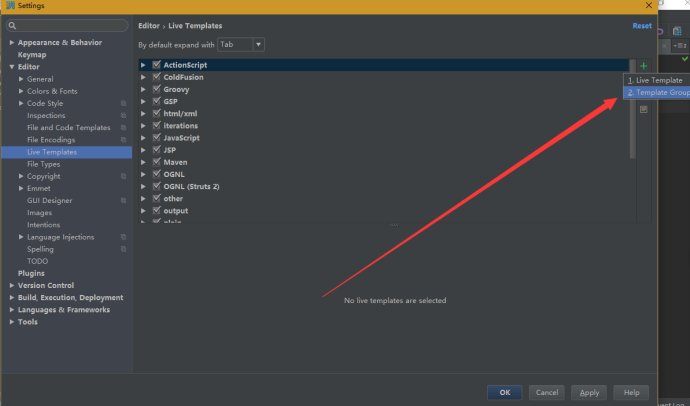
1、点击File--》Setting--》Live Template,点击右侧的+号,选择Template Group
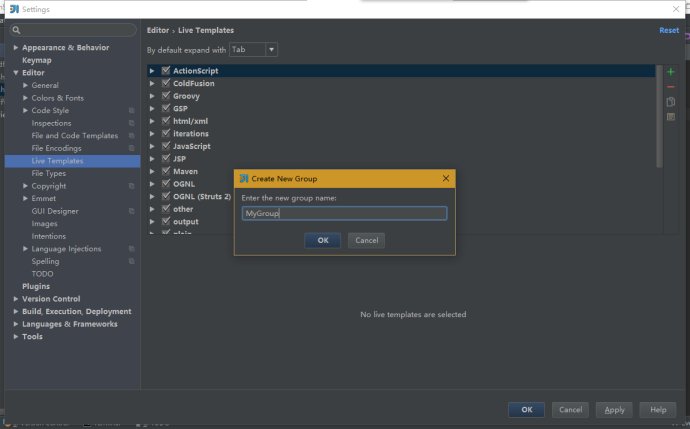
2、输入MyGroup(你也可以输入其他自定义的名称),然后点击OK。
3、选中MyGroup之后,再次点击右侧的+号,选择Live Template
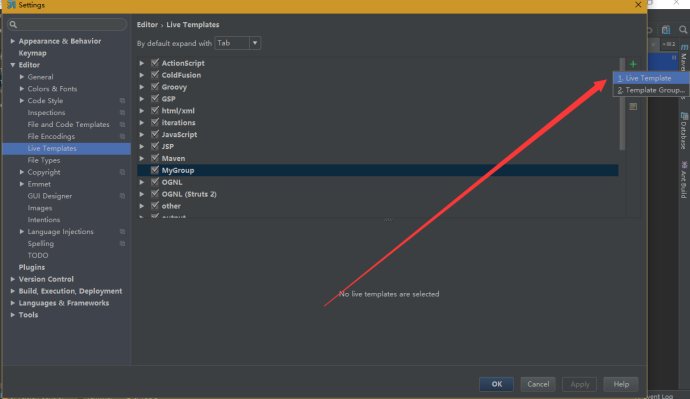
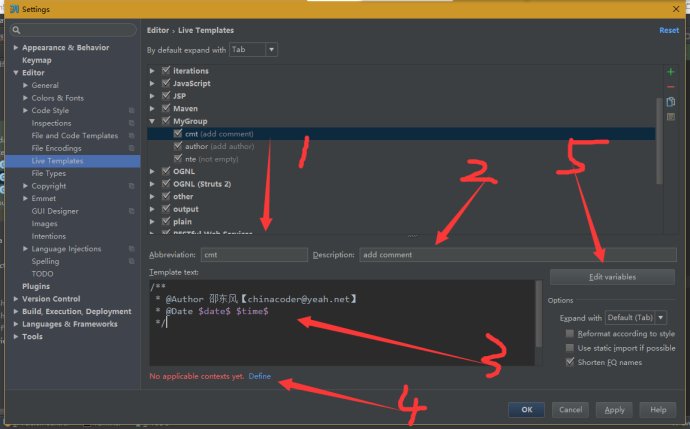
其中abbreviation
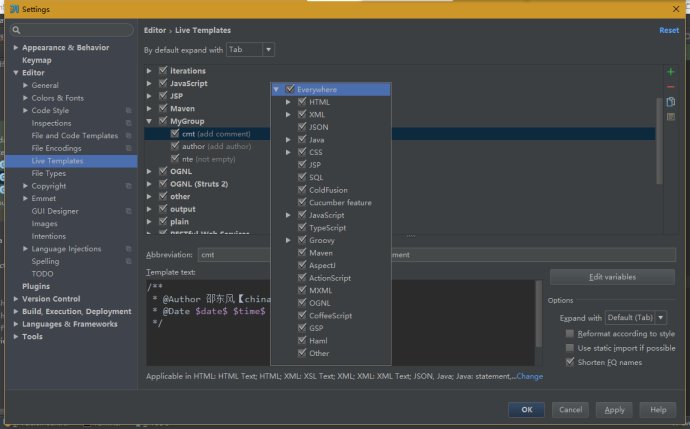
4、点击第四步的Define,选择EveryWhere
5、点击右边的Edit variables
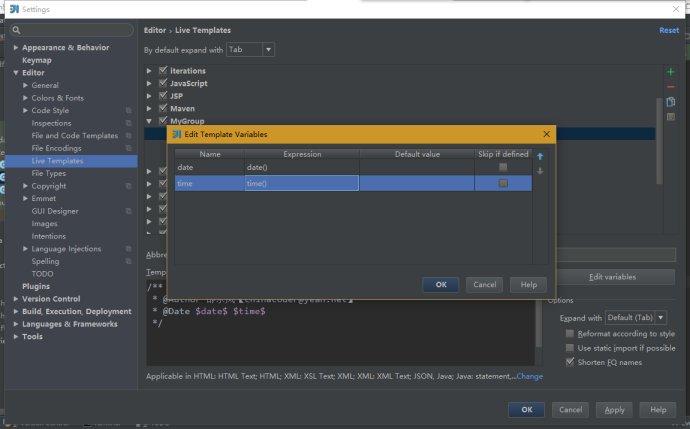
6、点击OK,Apply,退出,大功告成。在方法前面按 Ctrl+J ,然后选择自定义的方法注解,进行体验吧
我的上面的这个小技巧只是个人在使用Intellj时的一个小技巧而已,Live Template的使用,可以参考以下链接,建议大家仔细阅读,对自己的常用编码很有帮助。
IntelliJ下使用Code/Live Template加快编码速度:程序员的工作不是写程序,而是写程序解决问题
Intellj Live Template中的预定义函数列表
备注:
注意点:
不知道怎样可以带回参数和返回值等信息,但是我知道为啥不显示了。
user()和date()能显示内容,是因为这两个方法在其有效的作用域执行。
而关于Method的方法(如methodName()、methodParameters()、methodReturnType())没有起作用是因为你在方法外执行的mc快捷操作,这些方法的作用域是在方法内。
看下methodName()方法的解释:Returns the name of the embracing method (where the template is expanded).返回起作用的方法的名称。
| This is a built-in template. It contains a code fragment that can be included into file templates (Templates tab) with the help of the #parsedirective. The template is editable. Along with static text, code and comments, you can also use predefined variables that will then be expanded like macros into the corresponding values. |
| Predefined variables will take the following values: | ||
| ${PACKAGE_NAME} | name of the package in which the new file is created | |
| ${USER} | current user system login name | |
| ${DATE} | current system date | |
| ${TIME} | current system time | |
| ${YEAR} | current year | |
| ${MONTH} | current month | |
| ${MONTH_NAME_SHORT} | first 3 letters of the current month name. Example: Jan, Feb, etc. | |
| ${MONTH_NAME_FULL} | full name of the current month. Example: January, February, etc. | |
| ${DAY} | current day of the month | |
| ${HOUR} | current hour | |
| ${MINUTE} | current minute | |
| ${PROJECT_NAME} | the name of the current project |
注意点二:多个参数换行,可以使用 groovyScript
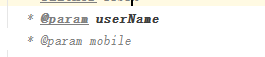
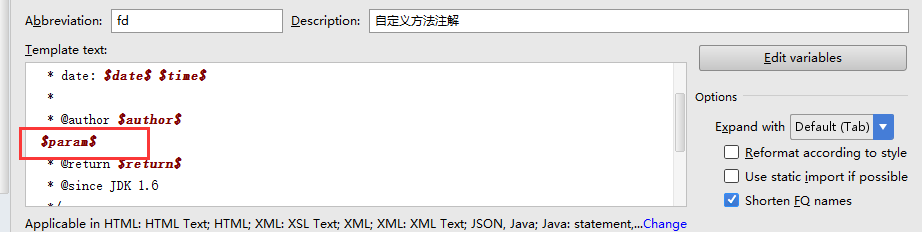
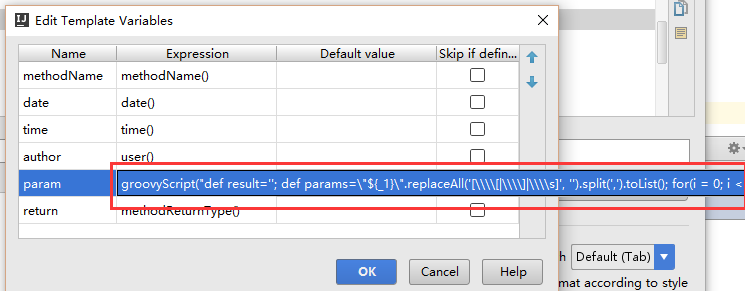
其中脚本值:
groovyScript("def result=‘‘; def params=\"${_1}\".replaceAll(‘[\\\\[|\\\\]|\\\\s]‘, ‘‘).split(‘,‘).toList(); for(i = 0; i < params.size(); i++) {result+=‘ * @param ‘ + params[i] + ((i < params.size() - 1) ? ‘\\n\\b‘ : ‘‘)}; return result", methodParameters())
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/duwanjiang/p/5875743.html