标签:
题目:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1036
给一个词典dict,词典中包含了一些单词words。要求判断给定的一个文本串text中是否包含这个字典中的单词words。
相关基础的理解
1. 与用KMP解决的问题的差别
KMP:输入原串S和一个模式串T,判断T是否出现在S中。通过对T计算next数组,避免原串S的回溯。
现在的问题:输入文本串text和多个单词words,判断words中是否有出现在text中。同样希望输入的text不用进行回溯。那么解决方案?
2. trie树识别
把所有的单词构建成trie树,输入ab的识别过程如下:每个节点会通过a/b/c到达下一个节点,当识别到终点(单词的最后一个字母,图中用两个圆表示)时说明整个单词都匹配成功
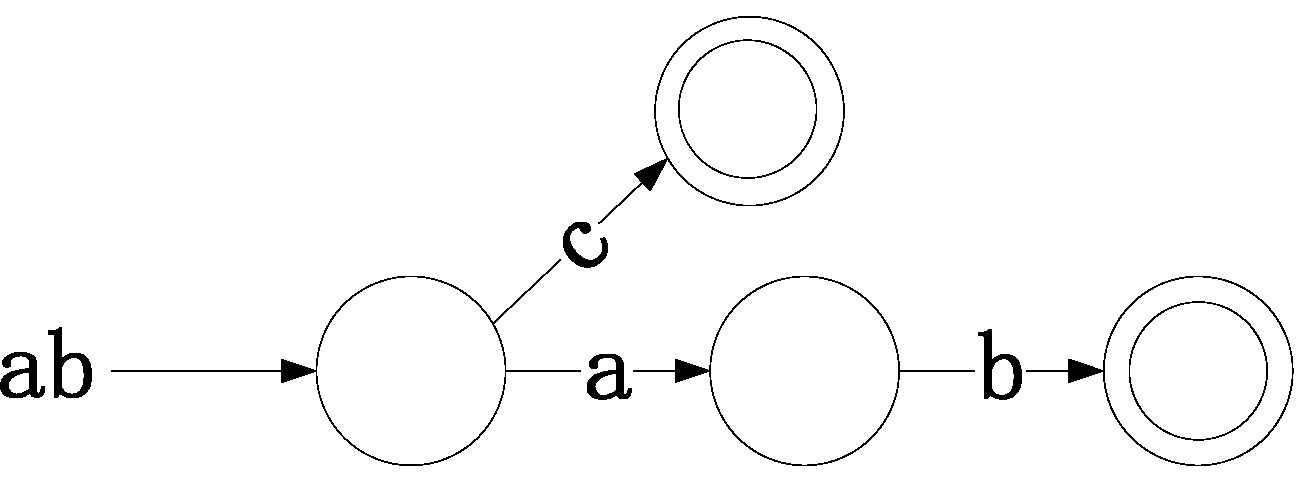
以上面的trie树为例,如果输入的text串为 ac
| 顺序 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 路径 | 1->2 | 2->3 | 1-4 | |
| 过程说明 | a-a匹配成功 | c-b失配 | text在c处失配,下一个用c再去匹配(不回溯) | c-c匹配成功 |
3. trie图(最关键的)
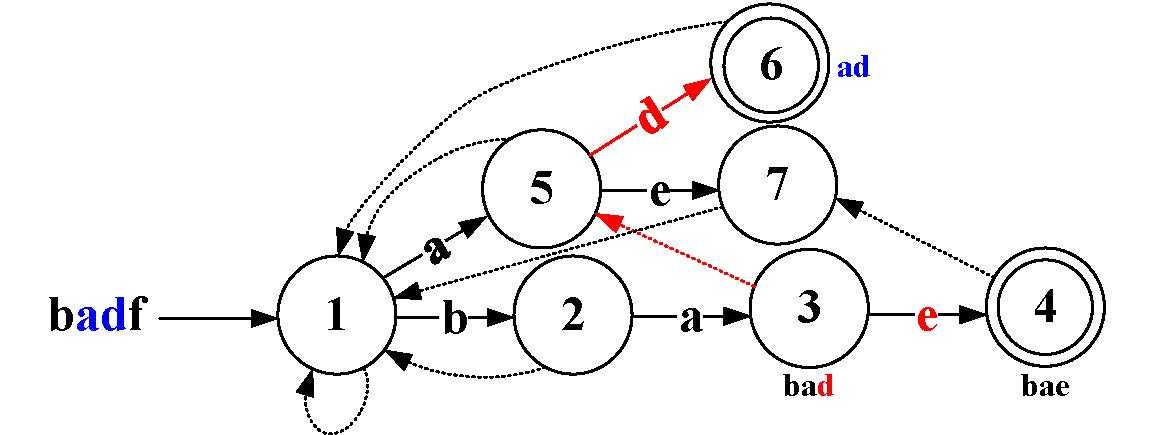
当匹配完成text的前面一部分时(即text‘),text‘有多个后缀串(不包含text的第一个字母的子串),trie树中可能包含多个text‘的后缀。当发生失配时,应该去往这些后缀中最长的一个。
1)最长后缀: text串匹配到3位置(babd)时发生失配(d和e),由3到5( ab-babd)
2)后缀指针:指向它的最长后缀的位置。在trie树中,为每个点添加后缀指针即可构成trie图
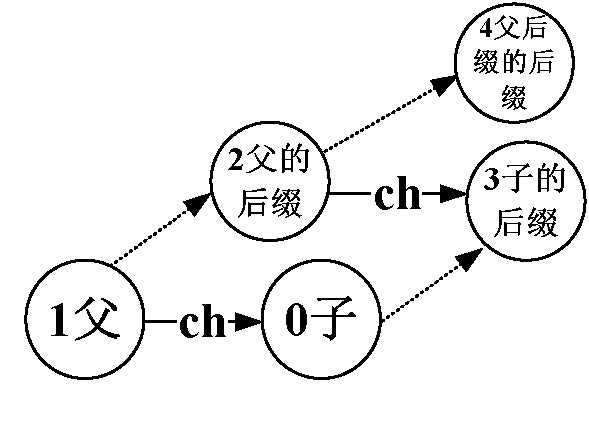
3)计算后缀指针:已知父节点的后缀节点,父节点经过字母ch到达子节点。那么子节点的后缀指针应该指向父节点的后缀节点经过当前字母到达的节点(按下图的顺序查找子节点后缀),直到根节点(根节点的后缀为自己)
例:虚线指向的是后缀。当前点为4,4的父节点为3(3-4间为e),3的后缀节点为5,5经过e到达7,所以3的后缀节点为7
源码
代码说明:
1. 节点的结构体中有next[26],表明经过26个字母分别可达的节点
2. 在为每个节点添加后缀指针时,有两种情况:
1)节点经过next[i]有可达位置(子节点):将子节点放入队列(需要计算后缀);计算子节点的后缀=当前点后缀的next[i];
2)节点经过next[i]无可达位置:当前点的next[i]=当前点后缀点的next[i] 避免计算过程中不断地回溯寻找后缀节点

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 static int nodeCnt = 0; 7 struct Node 8 { 9 Node() 10 { 11 post = 0; 12 for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) 13 next[i] = 0; 14 post = 0; 15 end = false; 16 } 17 int post;//后缀点的位置 18 int next[26];//经过26个字母的下一个可达的位置 19 bool end;//是否为终点 20 }nodes[1000000];//最多有1000000个点 21 22 //将str添加到trie图中 23 void build(string str) 24 { 25 int strLen = str.length(), i = 0, current = 0; 26 while(i < strLen) 27 { 28 if(nodes[current].next[str[i]-‘a‘] == 0)//若当前点经过str[i]可达的位置未设置 29 nodes[current].next[str[i]-‘a‘] = ++nodeCnt; 30 current = nodes[current].next[str[i]-‘a‘]; 31 i++; 32 } 33 nodes[current].end = true; 34 } 35 //为trie图中的每个点添加它指向的后缀点位置 36 void addPost() 37 { 38 queue<int> _int_nodes; 39 _int_nodes.push(0); 40 int current; 41 while(!_int_nodes.empty()) 42 { 43 current = _int_nodes.front(); 44 _int_nodes.pop(); 45 for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) 46 { 47 if(nodes[current].next[i] != 0) 48 { 49 _int_nodes.push(nodes[current].next[i]); 50 if(current != 0)//不是根结点,需要设置当前点的子节点的后缀=父结点的后缀经过i到达的点 51 nodes[nodes[current].next[i]].post = nodes[nodes[current].post].next[i]; 52 } 53 else //nodes[current].next[i] == -1当前点经过i没有可达的 54 nodes[current].next[i] = nodes[nodes[current].post].next[i]; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 //查找str 60 bool search(string str) 61 { 62 int strLen = str.length(), i = 0, current = 0; 63 while( i < strLen) 64 { 65 if(nodes[nodes[current].next[str[i]-‘a‘]].end) 66 return true; 67 current = nodes[current].next[str[i]-‘a‘]; 68 i++; 69 } 70 return false; 71 } 72 int main() 73 { 74 int cnt; 75 string str; 76 cin>>cnt; 77 while(cnt-- > 0) 78 { 79 cin>>str; 80 build(str); 81 } 82 addPost(); 83 cin>>str; 84 cout<<(search(str)?"YES":"NO")<<endl; 85 return 0; 86 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/coolqiyu/p/5712530.html