标签:
package lis0924;
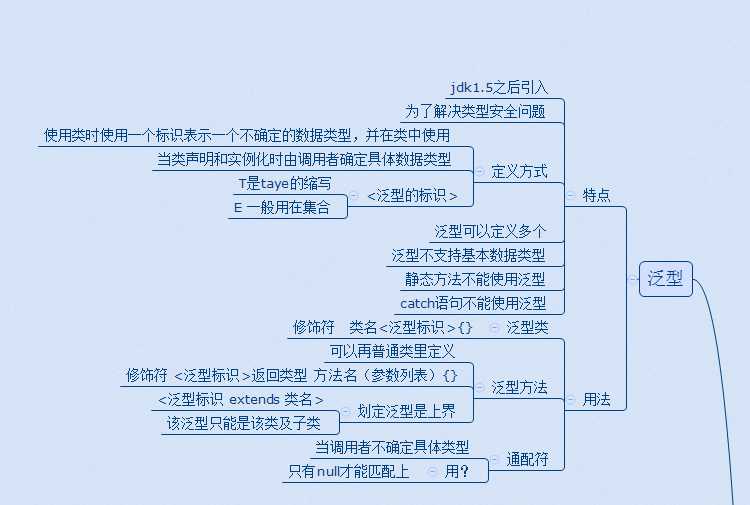
//泛型类
//在类名和大括号{之间用<泛型标识>
public class Tesxt06 <T>
{
//泛型方法
public <E> void test(E e)//修饰符 <泛型标识>返回类型 方法名(参数列表){}
{
}
//
public Object getObj(Object obj)
{
return obj;
}
//使用泛型
public T getT(T t)
{
return t;
}
// //使用泛型
// public M getM(M m)
// {
// return m;
// }
}
package lis0924;
//限定泛型的范围某个类及子类extends
public class TextGen <T extends Person>{
private T name;
public T getT()
{
T rtn =null;
return rtn;
}
public TextGen(T name)
{
this.name=name;
}
}
package lis0924;
public class TextGen2 {
public <T> T getT(T name)///修饰符 <泛型标识>返回类型 方法名(参数列表){}
{
T rtn=null;
return rtn;
}
// public void sexT(T name)
// {
//
// }
}
package lis0924;
public class Text07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tesxt06 t6=new Tesxt06();
Object obj=t6.getObj(new Person("G",20));
Person p=(Person)obj;
System.out.println(p);
//使用泛型类
Tesxt06 <Person> t1=new Tesxt06<>();
t1.getT(new Person("M",23));
Person p1=t1.getT(new Person("M",23));
System.out.println(p1);
//实例化泛型类
TextGen <Person> tp =new TextGen<>(new Person("A",30));//Student
TextGen2 t2=new TextGen2();
String srt =t2.getT("");
//通配符
//你只有null才能匹配
}
}
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liuyanzeng/p/5910249.html