标签:
狼人过河问题:有三个人和三只狼要过河,河里有一只船同时能容纳最多两个生物
假设狼和人都会划船,但如果岸边(不包括船上)狼的数量比人多 ,狼就要吃人
问:怎么把三只狼和三个人安全运输到对岸
1 // mytest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 2 // 3 4 #include "stdafx.h" 5 #include <windows.h> 6 #include <iostream> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <map> 10 #include <vector> 11 using namespace std; 12 13 //打印结果相关函数 14 void printState(char state); 15 void printStates(const vector<char>& vecStates); 16 //根据当前状态,获取下一步可能的所有状态函数 17 void getNextStates(char currState, vector<char>& vecNextStates); 18 19 //检查状态是否符合要求的函数 20 #define RET_IF_NOT_OK(cnt) do { if(cnt < 0 || cnt > 3) return false; } while(0) 21 bool isStateOk(int leftPeopleCnt, int leftWolfCnt, int rightPeopleCnt, int rightWolfCnt) 22 { 23 RET_IF_NOT_OK(leftPeopleCnt); 24 RET_IF_NOT_OK(leftWolfCnt); 25 RET_IF_NOT_OK(rightPeopleCnt); 26 RET_IF_NOT_OK(rightWolfCnt); 27 28 //岸边有人,且人的数量少于狼的数量 29 if (leftPeopleCnt > 0 && leftPeopleCnt < leftWolfCnt) return false; 30 if (rightPeopleCnt > 0 && rightPeopleCnt < rightWolfCnt) return false; 31 32 return true; 33 } 34 35 //根据下一步船所在岸边和岸边狼/人数量生成下一步状态字节 36 //这个函数与getNextStates紧密结合 详细用法请参考该函数调用逻辑 37 char makeState(int leftPeopleCnt, int leftWolfCnt, bool bLeft) 38 { 39 //用一个字节第一位(左数,下同 )表示船在左边(0)还是在右边(1) 40 //用第3、4代表人的数量,第7、8位代表狼的数量(00 ~ 11) 41 //举例:0b00110011 表示左岸有三个人三只狼 船在左边 42 // 0b10100001 表示左岸有三个人一只狼 船在右边 43 char state = 0; 44 45 46 //下一步船在左边 47 if (bLeft) 48 { 49 //传进来的其实是下一步右边岸上人和狼的数量 50 //需要推导出下一步左边岸上的人和儿狼的数量 51 state = state | ((3 - leftPeopleCnt) << 4) | (3 - leftWolfCnt); 52 } 53 else 54 { 55 //下一步船要在右边了 56 state = state | 0x80; 57 state = state | (leftPeopleCnt << 4) | leftWolfCnt; 58 } 59 60 61 return state; 62 } 63 64 //根据当前状态,获取下一步可能的所有状态函数 65 void getNextStates(char state, vector<char>& vecNextStates) 66 { 67 bool bLeft = (state & 0x80) == 0; 68 int leftPepleCnt = (state & 0x30) >> 4, rihgtPeopleCnt = 3 - leftPepleCnt; 69 int leftWolfCnt = (state & 0x03), rightWolfCnt = 3 - leftWolfCnt; 70 if (!isStateOk(leftPepleCnt, leftWolfCnt, rihgtPeopleCnt, rightWolfCnt)) return; 71 72 //定义指针指向当前船所在的岸边和对岸的人和狼数量 73 //这样做的原因是左岸和右岸状态变化逻辑是一样的 可以减少逻辑重复的代码 74 int *pShipPeopleCnt, *pNotShipPeopleCnt, *pShipWolfCnt, *pNotShipWolfCnt; 75 76 if (bLeft) 77 { 78 pShipPeopleCnt = &leftPepleCnt; 79 pShipWolfCnt = &leftWolfCnt; 80 pNotShipPeopleCnt = &rihgtPeopleCnt; 81 pNotShipWolfCnt = &rightWolfCnt; 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 pShipPeopleCnt = &rihgtPeopleCnt; 86 pShipWolfCnt = &rightWolfCnt; 87 pNotShipPeopleCnt = &leftPepleCnt; 88 pNotShipWolfCnt = &leftWolfCnt; 89 } 90 91 //可能变化有五种,一个人/狼单独过河 两个人/狼过河 一只狼和一个人一起过河 92 //根据人的思维,尽量先处理两个生物过河的状态,不行再处理单个生物过河的 93 //两个人/狼过河 94 if ( isStateOk(*pShipPeopleCnt - 2, *pShipWolfCnt, *pNotShipPeopleCnt + 2, *pNotShipWolfCnt) ) 95 { 96 vecNextStates.push_back( makeState(*pShipPeopleCnt - 2, *pShipWolfCnt, !bLeft) ); 97 } 98 99 if ( isStateOk(*pShipPeopleCnt, *pShipWolfCnt - 2, *pNotShipPeopleCnt, *pNotShipWolfCnt + 2) ) 100 { 101 vecNextStates.push_back( makeState(*pShipPeopleCnt, *pShipWolfCnt - 2, !bLeft) ); 102 } 103 104 //一只狼和一个人一起过河 105 if ( isStateOk(*pShipPeopleCnt - 1, *pShipWolfCnt - 1, *pNotShipPeopleCnt + 1, *pNotShipWolfCnt + 1) ) 106 { 107 vecNextStates.push_back( makeState(*pShipPeopleCnt - 1, *pShipWolfCnt - 1, !bLeft) ); 108 } 109 110 //一个人/狼单独过河 111 if ( isStateOk(*pShipPeopleCnt - 1, *pShipWolfCnt, *pNotShipPeopleCnt + 1, *pNotShipWolfCnt) ) 112 { 113 vecNextStates.push_back( makeState(*pShipPeopleCnt - 1, *pShipWolfCnt, !bLeft) ); 114 } 115 116 if ( isStateOk(*pShipPeopleCnt, *pShipWolfCnt - 1, *pNotShipPeopleCnt, *pNotShipWolfCnt + 1) ) 117 { 118 vecNextStates.push_back( makeState(*pShipPeopleCnt, *pShipWolfCnt - 1, !bLeft) ); 119 } 120 121 //如果要避免一些看起来比较愚蠢的走法,可以在这里加上对状态优先级排序的逻辑 122 } 123 124 //狼人过河问题:有三个人和三只狼要过河,河里有一只船同时能容纳最多两个生物 125 //假设狼和人都会划船,但如果岸边(不包括船上)狼的数量比人多 ,狼就要吃人 126 //问:怎么把三只狼和三个人安全运输到对岸 127 int dualLangRenOnce(char currState, vector<char>& vecStates, set<char> closeTab) 128 { 129 //如果当前状态是目标状态,则退出递归 130 if ((currState & 0x33) == 0) return 0; 131 132 vector<char> vecNextState; 133 //获取下个状态,即考虑怎么安排狼和人过河 134 getNextStates(currState, vecNextState); 135 for (size_t i = 0; i < vecNextState.size(); i++) 136 { 137 if ( closeTab.find(vecNextState[i]) == closeTab.end() ) 138 { 139 closeTab.insert(vecNextState[i]); 140 vecStates.push_back(vecNextState[i]); 141 //如果打算找全部可能解 这里就不需要return了 142 if (dualLangRenOnce(vecNextState[i], vecStates, closeTab) == 0) return 0; 143 vecStates.pop_back(); 144 } 145 } 146 147 return 1; 148 } 149 150 void dualLangRen() 151 { 152 //用一个字节第一位(左数,下同 )表示船在左边还是在右边 153 //用第3、4代表人的数量,第7、8位代表狼的数量(00 ~ 11) 154 //举例:0b00110011 表示左岸有三个人三只狼 船在左边 155 // 0b10100001 表示左岸有三个人一只狼 船在右边 156 char state = 0x33; 157 //vector记录状态变化过程 158 vector<char> vecStates; 159 //set记录已经历过的状态,以免重复尝试造成无尽递归 160 set<char> closeTab; 161 162 vecStates.push_back(state); 163 closeTab.insert(state); 164 if (dualLangRenOnce(state, vecStates, closeTab) == 0) 165 { 166 printStates(vecStates); 167 } 168 else 169 { 170 cout << "问题无解!" << endl; 171 } 172 173 return; 174 } 175 176 void printState(char state) 177 { 178 bool bLeft = (state & 0x80) == 0; 179 int leftPepleCnt = (state & 0x30) >> 4; 180 int leftWolfCnt = (state & 0x03); 181 182 printf("人%d 狼%d %s 人%d 狼%d", leftPepleCnt, leftWolfCnt, (bLeft ? "左": "右"), 3 -leftPepleCnt, 3 - leftWolfCnt); 183 } 184 185 void printStates(const vector<char>& vecStates) 186 { 187 for(vector<char>::const_iterator it = vecStates.begin(); it != vecStates.end(); it++) 188 { 189 printState(*it); 190 printf("\n"); 191 } 192 } 193 194 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) 195 { 196 double start = GetTickCount(); 197 dualLangRen(); 198 199 //我自己机在win7 vs2008环境 debug模式是16毫秒 release不到1毫秒 200 printf("总共耗时 %f 毫秒\n", GetTickCount() - start); 201 202 //挂屏 203 system("pause"); 204 return 0; 205 }
运行结果:
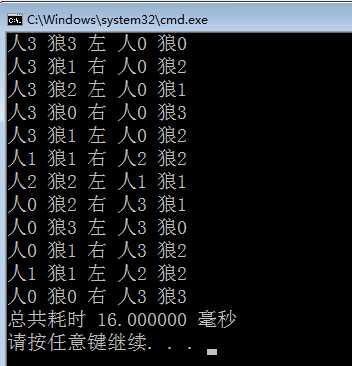
这是最近第二次写了,复习一遍数据结构之后的作品
之前没有复习前写过另一版,逻辑比较混乱,有空再贴上来对比
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kingstarer/p/5931569.html