标签:
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/archive/2013/04/07/3006334.html
一、自适应直方图均衡化(Adaptive histgram equalization/AHE)
1.简述
自适应直方图均衡化(AHE)用来提升图像的对比度的一种计算机图像处理技术。和普通的直方图均衡算法不同,AHE算法通过计算图像的局部直方图,然后重新分布亮度来来改变图像对比度。因此,该算法更适合于改进图像的局部对比度以及获得更多的图像细节。
不过,AHE有过度放大图像中相同区域的噪音的问题,另外一种自适应的直方图均衡算法即限制对比度直方图均衡(CLAHE)算法能有限的限制这种不利的放大。
2. 算法的解释
普通的直方图均衡算法对于整幅图像的像素使用相同的直方图变换,对于那些像素值分布比较均衡的图像来说,算法的效果很好。然后,如果图像中包括明显比图像其它区域暗或者亮的部分,在这些部分的对比度将得不到有效的增强。
AHE算法通过对局部区域执行响应的直方图均衡来改变上述问题。该算法首先被开发出来适用于改进航天器驾驶舱的显示效果。其最简单的形式,就是每个像素通过其周边一个矩形范围内的像素的直方图进行均衡化。均衡的方式则完全同普通的均衡化算法:变换函数同像素周边的累积直方图函数(CDF)成比例。
图像边缘的像素需要特殊处理,因为边缘像素的领域不完全在图像内部。这个通过镜像图像边缘的行像素或列像素来解决。直接复制边缘的像素进行扩充是不合适的。因为这会导致带有剑锋的领域直方图。
3. AHE的属性
二、限制对比度自适应直方图均衡(Contrast Limited Adaptive histgram equalization/CLAHE)
1.简述
CLAHE同普通的自适应直方图均衡不同的地方主要是其对比度限幅。这个特性也可以应用到全局直方图均衡化中,即构成所谓的限制对比度直方图均衡(CLHE),但这在实际中很少使用。在CLAHE中,对于每个小区域都必须使用对比度限幅。CLAHE主要是用来克服AHE的过度放大噪音的问题。
这主要是通过限制AHE算法的对比提高程度来达到的。在指定的像素值周边的对比度放大主要是由变换函数的斜度决定的。这个斜度和领域的累积直方图的斜度成比例。CLAHE通过在计算CDF前用预先定义的阈值来裁剪直方图以达到限制放大幅度的目的。这限制了CDF的斜度因此,也限制了变换函数的斜度。直方图被裁剪的值,也就是所谓的裁剪限幅,取决于直方图的分布因此也取决于领域大小的取值。
通常,直接忽略掉那些超出直方图裁剪限幅的部分是不好的,而应该将这些裁剪掉的部分均匀的分布到直方图的其他部分。如下图所示。
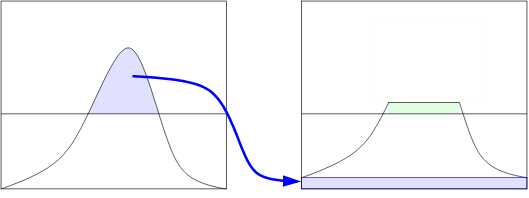
这个重分布的过程可能会导致那些倍裁剪掉的部分由重新超过了裁剪值(如上图的绿色部分所示)。如果这不是所希望的,可以不带使用重复不的过程指导这个超出的部分已经变得微不足道了。
2. 通过插值加快计算速度
如上所述的直接的自适应直方图,不管是否带有对比度限制,都需要对图像中的每个像素计算器领域直方图以及对应的变换函数,这使得算法及其耗时。
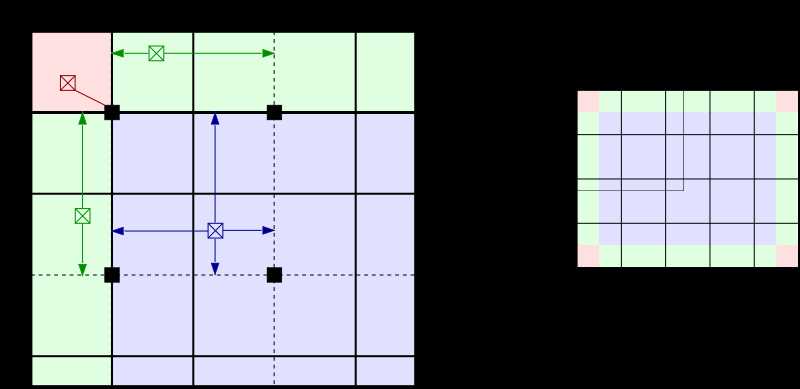
而插值使得上述算法效率上有极大的提升,并且质量上没有下降。首先,将图像均匀分成等份矩形大小,如下图的右侧部分所示(8行8列64个块是常用的选择)。然后计算个块的直方图、CDF以及对应的变换函数。这个变换函数对于块的中心像素(下图左侧部分的黑色小方块)是完全符合原始定义的。而其他的像素通过哪些于其临近的四个块的变换函数插值获取。位于图中蓝色阴影部分的像素采用双线性查插值,而位于便于边缘的(绿色阴影)部分采用线性插值,角点处(红色阴影处)直接使用块所在的变换函数。
CLAHE算法的源代码参考:

/* * ANSI C code from the article * "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization" * by Karel Zuiderveld, karel@cv.ruu.nl * in "Graphics Gems IV", Academic Press, 1994 * * * These functions implement Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization. * The main routine (CLAHE) expects an input image that is stored contiguously in * memory; the CLAHE output image overwrites the original input image and has the * same minimum and maximum values (which must be provided by the user). * This implementation assumes that the X- and Y image resolutions are an integer * multiple of the X- and Y sizes of the contextual regions. A check on various other * error conditions is performed. * * #define the symbol BYTE_IMAGE to make this implementation suitable for * 8-bit images. The maximum number of contextual regions can be redefined * by changing uiMAX_REG_X and/or uiMAX_REG_Y; the use of more than 256 * contextual regions is not recommended. * * The code is ANSI-C and is also C++ compliant. * * Author: Karel Zuiderveld, Computer Vision Research Group, * Utrecht, The Netherlands (karel@cv.ruu.nl) */ #ifdef BYTE_IMAGE typedef unsigned char kz_pixel_t; /* for 8 bit-per-pixel images */ #define uiNR_OF_GREY (256) #else typedef unsigned short kz_pixel_t; /* for 12 bit-per-pixel images (default) */ # define uiNR_OF_GREY (4096) #endif /******** Prototype of CLAHE function. Put this in a separate include file. *****/ int CLAHE(kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY, unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit); /*********************** Local prototypes ************************/ static void ClipHistogram (unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned long); static void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t*, unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned long*, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*); static void MapHistogram (unsigned long*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t, unsigned int, unsigned long); static void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t, unsigned int); static void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t*, int, unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*); /************** Start of actual code **************/ #include <stdlib.h> /* To get prototypes of malloc() and free() */ const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_X = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in x-direction */ const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_Y = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in y-direction */ /************************** main function CLAHE ******************/ int CLAHE (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY, unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit) /* pImage - Pointer to the input/output image * uiXRes - Image resolution in the X direction * uiYRes - Image resolution in the Y direction * Min - Minimum greyvalue of input image (also becomes minimum of output image) * Max - Maximum greyvalue of input image (also becomes maximum of output image) * uiNrX - Number of contextial regions in the X direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_X) * uiNrY - Number of contextial regions in the Y direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_Y) * uiNrBins - Number of greybins for histogram ("dynamic range") * float fCliplimit - Normalized cliplimit (higher values give more contrast) * The number of "effective" greylevels in the output image is set by uiNrBins; selecting * a small value (eg. 128) speeds up processing and still produce an output image of * good quality. The output image will have the same minimum and maximum value as the input * image. A clip limit smaller than 1 results in standard (non-contrast limited) AHE. */ { unsigned int uiX, uiY; /* counters */ unsigned int uiXSize, uiYSize, uiSubX, uiSubY; /* size of context. reg. and subimages */ unsigned int uiXL, uiXR, uiYU, uiYB; /* auxiliary variables interpolation routine */ unsigned long ulClipLimit, ulNrPixels;/* clip limit and region pixel count */ kz_pixel_t* pImPointer; /* pointer to image */ kz_pixel_t aLUT[uiNR_OF_GREY]; /* lookup table used for scaling of input image */ unsigned long* pulHist, *pulMapArray; /* pointer to histogram and mappings*/ unsigned long* pulLU, *pulLB, *pulRU, *pulRB; /* auxiliary pointers interpolation */ if (uiNrX > uiMAX_REG_X) return -1; /* # of regions x-direction too large */ if (uiNrY > uiMAX_REG_Y) return -2; /* # of regions y-direction too large */ if (uiXRes % uiNrX) return -3; /* x-resolution no multiple of uiNrX */ if (uiYRes & uiNrY) return -4; /* y-resolution no multiple of uiNrY */ if (Max >= uiNR_OF_GREY) return -5; /* maximum too large */ if (Min >= Max) return -6; /* minimum equal or larger than maximum */ if (uiNrX < 2 || uiNrY < 2) return -7;/* at least 4 contextual regions required */ if (fCliplimit == 1.0) return 0; /* is OK, immediately returns original image. */ if (uiNrBins == 0) uiNrBins = 128; /* default value when not specified */ pulMapArray=(unsigned long *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned long)*uiNrX*uiNrY*uiNrBins); if (pulMapArray == 0) return -8; /* Not enough memory! (try reducing uiNrBins) */ uiXSize = uiXRes/uiNrX; uiYSize = uiYRes/uiNrY; /* Actual size of contextual regions */ ulNrPixels = (unsigned long)uiXSize * (unsigned long)uiYSize; if(fCliplimit > 0.0) { /* Calculate actual cliplimit */ ulClipLimit = (unsigned long) (fCliplimit * (uiXSize * uiYSize) / uiNrBins); ulClipLimit = (ulClipLimit < 1UL) ? 1UL : ulClipLimit; } else ulClipLimit = 1UL<<14; /* Large value, do not clip (AHE) */ MakeLut(aLUT, Min, Max, uiNrBins); /* Make lookup table for mapping of greyvalues */ /* Calculate greylevel mappings for each contextual region */ for (uiY = 0, pImPointer = pImage; uiY < uiNrY; uiY++) { for (uiX = 0; uiX < uiNrX; uiX++, pImPointer += uiXSize) { pulHist = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiY * uiNrX + uiX)]; MakeHistogram(pImPointer,uiXRes,uiXSize,uiYSize,pulHist,uiNrBins,aLUT); ClipHistogram(pulHist, uiNrBins, ulClipLimit); MapHistogram(pulHist, Min, Max, uiNrBins, ulNrPixels); } pImPointer += (uiYSize - 1) * uiXRes; /* skip lines, set pointer */ } /* Interpolate greylevel mappings to get CLAHE image */ for (pImPointer = pImage, uiY = 0; uiY <= uiNrY; uiY++) { if (uiY == 0) { /* special case: top row */ uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = 0; uiYB = 0; } else { if (uiY == uiNrY) { /* special case: bottom row */ uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = uiNrY-1; uiYB = uiYU; } else { /* default values */ uiSubY = uiYSize; uiYU = uiY - 1; uiYB = uiYU + 1; } } for (uiX = 0; uiX <= uiNrX; uiX++) { if (uiX == 0) { /* special case: left column */ uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = 0; uiXR = 0; } else { if (uiX == uiNrX) { /* special case: right column */ uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = uiNrX - 1; uiXR = uiXL; } else { /* default values */ uiSubX = uiXSize; uiXL = uiX - 1; uiXR = uiXL + 1; } } pulLU = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYU * uiNrX + uiXL)]; pulRU = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYU * uiNrX + uiXR)]; pulLB = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYB * uiNrX + uiXL)]; pulRB = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYB * uiNrX + uiXR)]; Interpolate(pImPointer,uiXRes,pulLU,pulRU,pulLB,pulRB,uiSubX,uiSubY,aLUT); pImPointer += uiSubX; /* set pointer on next matrix */ } pImPointer += (uiSubY - 1) * uiXRes; } free(pulMapArray); /* free space for histograms */ return 0; /* return status OK */ } void ClipHistogram (unsigned long* pulHistogram, unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, unsigned long ulClipLimit) /* This function performs clipping of the histogram and redistribution of bins. * The histogram is clipped and the number of excess pixels is counted. Afterwards * the excess pixels are equally redistributed across the whole histogram (providing * the bin count is smaller than the cliplimit). */ { unsigned long* pulBinPointer, *pulEndPointer, *pulHisto; unsigned long ulNrExcess, ulUpper, ulBinIncr, ulStepSize, i; long lBinExcess; ulNrExcess = 0; pulBinPointer = pulHistogram; for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) { /* calculate total number of excess pixels */ lBinExcess = (long) pulBinPointer[i] - (long) ulClipLimit; if (lBinExcess > 0) ulNrExcess += lBinExcess; /* excess in current bin */ }; /* Second part: clip histogram and redistribute excess pixels in each bin */ ulBinIncr = ulNrExcess / uiNrGreylevels; /* average binincrement */ ulUpper = ulClipLimit - ulBinIncr; /* Bins larger than ulUpper set to cliplimit */ for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) { if (pulHistogram[i] > ulClipLimit) pulHistogram[i] = ulClipLimit; /* clip bin */ else { if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper) { /* high bin count */ ulNrExcess -= pulHistogram[i] - ulUpper; pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit; } else { /* low bin count */ ulNrExcess -= ulBinIncr; pulHistogram[i] += ulBinIncr; } } } while (ulNrExcess) { /* Redistribute remaining excess */ pulEndPointer = &pulHistogram[uiNrGreylevels]; pulHisto = pulHistogram; while (ulNrExcess && pulHisto < pulEndPointer) { ulStepSize = uiNrGreylevels / ulNrExcess; if (ulStepSize < 1) ulStepSize = 1; /* stepsize at least 1 */ for (pulBinPointer=pulHisto; pulBinPointer < pulEndPointer && ulNrExcess; pulBinPointer += ulStepSize) { if (*pulBinPointer < ulClipLimit) { (*pulBinPointer)++; ulNrExcess--; /* reduce excess */ } } pulHisto++; /* restart redistributing on other bin location */ } } } void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiSizeX, unsigned int uiSizeY, unsigned long* pulHistogram, unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, kz_pixel_t* pLookupTable) /* This function classifies the greylevels present in the array image into * a greylevel histogram. The pLookupTable specifies the relationship * between the greyvalue of the pixel (typically between 0 and 4095) and * the corresponding bin in the histogram (usually containing only 128 bins). */ { kz_pixel_t* pImagePointer; unsigned int i; for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) pulHistogram[i] = 0L; /* clear histogram */ for (i = 0; i < uiSizeY; i++) { pImagePointer = &pImage[uiSizeX]; while (pImage < pImagePointer) pulHistogram[pLookupTable[*pImage++]]++; pImagePointer += uiXRes; pImage = &pImagePointer[-uiSizeX]; } } void MapHistogram (unsigned long* pulHistogram, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, unsigned long ulNrOfPixels) /* This function calculates the equalized lookup table (mapping) by * cumulating the input histogram. Note: lookup table is rescaled in range [Min..Max]. */ { unsigned int i; unsigned long ulSum = 0; const float fScale = ((float)(Max - Min)) / ulNrOfPixels; const unsigned long ulMin = (unsigned long) Min; for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) { ulSum += pulHistogram[i]; pulHistogram[i]=(unsigned long)(ulMin+ulSum*fScale); if (pulHistogram[i] > Max) pulHistogram[i] = Max; } } void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t * pLUT, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrBins) /* To speed up histogram clipping, the input image [Min,Max] is scaled down to * [0,uiNrBins-1]. This function calculates the LUT. */ { int i; const kz_pixel_t BinSize = (kz_pixel_t) (1 + (Max - Min) / uiNrBins); for (i = Min; i <= Max; i++) pLUT[i] = (i - Min) / BinSize; } void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t * pImage, int uiXRes, unsigned long * pulMapLU, unsigned long * pulMapRU, unsigned long * pulMapLB, unsigned long * pulMapRB, unsigned int uiXSize, unsigned int uiYSize, kz_pixel_t * pLUT) /* pImage - pointer to input/output image * uiXRes - resolution of image in x-direction * pulMap* - mappings of greylevels from histograms * uiXSize - uiXSize of image submatrix * uiYSize - uiYSize of image submatrix * pLUT - lookup table containing mapping greyvalues to bins * This function calculates the new greylevel assignments of pixels within a submatrix * of the image with size uiXSize and uiYSize. This is done by a bilinear interpolation * between four different mappings in order to eliminate boundary artifacts. * It uses a division; since division is often an expensive operation, I added code to * perform a logical shift instead when feasible. */ { const unsigned int uiIncr = uiXRes-uiXSize; /* Pointer increment after processing row */ kz_pixel_t GreyValue; unsigned int uiNum = uiXSize*uiYSize; /* Normalization factor */ unsigned int uiXCoef, uiYCoef, uiXInvCoef, uiYInvCoef, uiShift = 0; if (uiNum & (uiNum - 1)) /* If uiNum is not a power of two, use division */ for (uiYCoef = 0, uiYInvCoef = uiYSize; uiYCoef < uiYSize; uiYCoef++, uiYInvCoef--,pImage+=uiIncr) { for (uiXCoef = 0, uiXInvCoef = uiXSize; uiXCoef < uiXSize; uiXCoef++, uiXInvCoef--) { GreyValue = pLUT[*pImage]; /* get histogram bin value */ *pImage++ = (kz_pixel_t ) ((uiYInvCoef * (uiXInvCoef*pulMapLU[GreyValue] + uiXCoef * pulMapRU[GreyValue]) + uiYCoef * (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLB[GreyValue] + uiXCoef * pulMapRB[GreyValue])) / uiNum); } } else { /* avoid the division and use a right shift instead */ while (uiNum >>= 1) uiShift++; /* Calculate 2log of uiNum */ for (uiYCoef = 0, uiYInvCoef = uiYSize; uiYCoef < uiYSize; uiYCoef++, uiYInvCoef--,pImage+=uiIncr) { for (uiXCoef = 0, uiXInvCoef = uiXSize; uiXCoef < uiXSize; uiXCoef++, uiXInvCoef--) { GreyValue = pLUT[*pImage]; /* get histogram bin value */ *pImage++ = (kz_pixel_t)((uiYInvCoef* (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLU[GreyValue] + uiXCoef * pulMapRU[GreyValue]) + uiYCoef * (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLB[GreyValue] + uiXCoef * pulMapRB[GreyValue])) >> uiShift); } } } }
上面的代码中对于各块之间的插值部分的编码技巧很值得学习和参考。
以上描述均翻译自:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CLAHE#Contrast_Limited_AHE
Karel Zuiderveld提供的代码:
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper)
{ /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= (pulHistogram[i] - ulUpper); pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
应该修正为:

1 if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper) 2 { /* high bin count */ 3 ulNrExcess -= (ulClipLimit -pulHistogram[i]); pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit; 4 }
同时,各位也可以参考下matlab的adapthisteq.m文件,该文件的代码基本是严格按照 Karel Zuiderveld作者的原文写的,贴出如下:

1 function out = adapthisteq(varargin) 2 %ADAPTHISTEQ Contrast-limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE). 3 % ADAPTHISTEQ enhances the contrast of images by transforming the 4 % values in the intensity image I. Unlike HISTEQ, it operates on small 5 % data regions (tiles), rather than the entire image. Each tile‘s 6 % contrast is enhanced, so that the histogram of the output region 7 % approximately matches the specified histogram. The neighboring tiles 8 % are then combined using bilinear interpolation in order to eliminate 9 % artificially induced boundaries. The contrast, especially 10 % in homogeneous areas, can be limited in order to avoid amplifying the 11 % noise which might be present in the image. 12 % 13 % J = ADAPTHISTEQ(I) Performs CLAHE on the intensity image I. 14 % 15 % J = ADAPTHISTEQ(I,PARAM1,VAL1,PARAM2,VAL2...) sets various parameters. 16 % Parameter names can be abbreviated, and case does not matter. Each 17 % string parameter is followed by a value as indicated below: 18 % 19 % ‘NumTiles‘ Two-element vector of positive integers: [M N]. 20 % [M N] specifies the number of tile rows and 21 % columns. Both M and N must be at least 2. 22 % The total number of image tiles is equal to M*N. 23 % 24 % Default: [8 8]. 25 % 26 % ‘ClipLimit‘ Real scalar from 0 to 1. 27 % ‘ClipLimit‘ limits contrast enhancement. Higher numbers 28 % result in more contrast. 29 % 30 % Default: 0.01. 31 % 32 % ‘NBins‘ Positive integer scalar. 33 % Sets number of bins for the histogram used in building a 34 % contrast enhancing transformation. Higher values result 35 % in greater dynamic range at the cost of slower processing 36 % speed. 37 % 38 % Default: 256. 39 % 40 % ‘Range‘ One of the strings: ‘original‘ or ‘full‘. 41 % Controls the range of the output image data. If ‘Range‘ 42 % is set to ‘original‘, the range is limited to 43 % [min(I(:)) max(I(:))]. Otherwise, by default, or when 44 % ‘Range‘ is set to ‘full‘, the full range of the output 45 % image class is used (e.g. [0 255] for uint8). 46 % 47 % Default: ‘full‘. 48 % 49 % ‘Distribution‘ Distribution can be one of three strings: ‘uniform‘, 50 % ‘rayleigh‘, ‘exponential‘. 51 % Sets desired histogram shape for the image tiles, by 52 % specifying a distribution type. 53 % 54 % Default: ‘uniform‘. 55 % 56 % ‘Alpha‘ Nonnegative real scalar. 57 % ‘Alpha‘ is a distribution parameter, which can be supplied 58 % when ‘Dist‘ is set to either ‘rayleigh‘ or ‘exponential‘. 59 % 60 % Default: 0.4. 61 % 62 % Notes 63 % ----- 64 % - ‘NumTiles‘ specify the number of rectangular contextual regions (tiles) 65 % into which the image is divided. The contrast transform function is 66 % calculated for each of these regions individually. The optimal number of 67 % tiles depends on the type of the input image, and it is best determined 68 % through experimentation. 69 % 70 % - The ‘ClipLimit‘ is a contrast factor that prevents over-saturation of the 71 % image specifically in homogeneous areas. These areas are characterized 72 % by a high peak in the histogram of the particular image tile due to many 73 % pixels falling inside the same gray level range. Without the clip limit, 74 % the adaptive histogram equalization technique could produce results that, 75 % in some cases, are worse than the original image. 76 % 77 % - ADAPTHISTEQ can use Uniform, Rayleigh, or Exponential distribution as 78 % the basis for creating the contrast transform function. The distribution 79 % that should be used depends on the type of the input image. 80 % For example, underwater imagery appears to look more natural when the 81 % Rayleigh distribution is used. 82 % 83 % Class Support 84 % ------------- 85 % Intensity image I can be uint8, uint16, int16, double, or single. 86 % The output image J has the same class as I. 87 % 88 % Example 1 89 % --------- 90 % Apply Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to an 91 % image and display the results. 92 % 93 % I = imread(‘tire.tif‘); 94 % A = adapthisteq(I,‘clipLimit‘,0.02,‘Distribution‘,‘rayleigh‘); 95 % figure, imshow(I); 96 % figure, imshow(A); 97 % 98 % Example 2 99 % --------- 100 % 101 % Apply Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to a color 102 % photograph. 103 % 104 % [X MAP] = imread(‘shadow.tif‘); 105 % RGB = ind2rgb(X,MAP); % convert indexed image to truecolor format 106 % cform2lab = makecform(‘srgb2lab‘); 107 % LAB = applycform(RGB, cform2lab); %convert image to L*a*b color space 108 % L = LAB(:,:,1)/100; % scale the values to range from 0 to 1 109 % LAB(:,:,1) = adapthisteq(L,‘NumTiles‘,[8 8],‘ClipLimit‘,0.005)*100; 110 % cform2srgb = makecform(‘lab2srgb‘); 111 % J = applycform(LAB, cform2srgb); %convert back to RGB 112 % figure, imshow(RGB); %display the results 113 % figure, imshow(J); 114 % 115 % See also HISTEQ. 116 117 % Copyright 1993-2010 The MathWorks, Inc. 118 % $Revision: 1.1.6.12 $ $Date: 2011/08/09 17:48:54 $ 119 120 % References: 121 % Karel Zuiderveld, "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization", 122 % Graphics Gems IV, p. 474-485, code: p. 479-484 123 % 124 % Hanumant Singh, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, personal 125 % communication 126 127 %--------------------------- The algorithm ---------------------------------- 128 % 129 % 1. Obtain all the inputs: 130 % * image 131 % * number of regions in row and column directions 132 % * number of bins for the histograms used in building image transform 133 % function (dynamic range) 134 % * clip limit for contrast limiting (normalized from 0 to 1) 135 % * other miscellaneous options 136 % 2. Pre-process the inputs: 137 % * determine real clip limit from the normalized value 138 % * if necessary, pad the image before splitting it into regions 139 % 3. Process each contextual region (tile) thus producing gray level mappings 140 % * extract a single image region 141 % * make a histogram for this region using the specified number of bins 142 % * clip the histogram using clip limit 143 % * create a mapping (transformation function) for this region 144 % 4. Interpolate gray level mappings in order to assemble final CLAHE image 145 % * extract cluster of four neighboring mapping functions 146 % * process image region partly overlapping each of the mapping tiles 147 % * extract a single pixel, apply four mappings to that pixel, and 148 % interpolate between the results to obtain the output pixel; repeat 149 % over the entire image 150 % 151 % See code for further details. 152 % 153 %----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 154 155 [I, selectedRange, fullRange, numTiles, dimTile, clipLimit, numBins, ... 156 noPadRect, distribution, alpha, int16ClassChange] = parseInputs(varargin{:}); 157 158 tileMappings = makeTileMappings(I, numTiles, dimTile, numBins, clipLimit, ... 159 selectedRange, fullRange, distribution, alpha); 160 161 %Synthesize the output image based on the individual tile mappings. 162 out = makeClaheImage(I, tileMappings, numTiles, selectedRange, numBins,... 163 dimTile); 164 165 if int16ClassChange 166 % Change uint16 back to int16 so output has same class as input. 167 out = uint16toint16(out); 168 end 169 170 if ~isempty(noPadRect) %do we need to remove padding? 171 out = out(noPadRect.ulRow:noPadRect.lrRow, ... 172 noPadRect.ulCol:noPadRect.lrCol); 173 end 174 175 %----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 176 177 function tileMappings = ... 178 makeTileMappings(I, numTiles, dimTile, numBins, clipLimit,... 179 selectedRange, fullRange, distribution, alpha) 180 181 numPixInTile = prod(dimTile); 182 183 tileMappings = cell(numTiles); 184 185 % extract and process each tile 186 imgCol = 1; 187 for col=1:numTiles(2), 188 imgRow = 1; 189 for row=1:numTiles(1), 190 191 tile = I(imgRow:imgRow+dimTile(1)-1,imgCol:imgCol+dimTile(2)-1); 192 193 % for speed, call MEX file directly thus avoiding costly 194 % input parsing of imhist 195 tileHist = imhistc(tile, numBins, 1, fullRange(2)); 196 197 tileHist = clipHistogram(tileHist, clipLimit, numBins); 198 199 tileMapping = makeMapping(tileHist, selectedRange, fullRange, ... 200 numPixInTile, distribution, alpha); 201 202 % assemble individual tile mappings by storing them in a cell array; 203 tileMappings{row,col} = tileMapping; 204 205 imgRow = imgRow + dimTile(1); 206 end 207 imgCol = imgCol + dimTile(2); % move to the next column of tiles 208 end 209 210 %----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 211 % Calculate the equalized lookup table (mapping) based on cumulating the input 212 % histogram. Note: lookup table is rescaled in the selectedRange [Min..Max]. 213 214 function mapping = makeMapping(imgHist, selectedRange, fullRange, ... 215 numPixInTile, distribution, alpha) 216 217 histSum = cumsum(imgHist); 218 valSpread = selectedRange(2) - selectedRange(1); 219 220 switch distribution 221 case ‘uniform‘, 222 scale = valSpread/numPixInTile; 223 mapping = min(selectedRange(1) + histSum*scale,... 224 selectedRange(2)); %limit to max 225 226 case ‘rayleigh‘, % suitable for underwater imagery 227 % pdf = (t./alpha^2).*exp(-t.^2/(2*alpha^2))*U(t) 228 % cdf = 1-exp(-t.^2./(2*alpha^2)) 229 hconst = 2*alpha^2; 230 vmax = 1 - exp(-1/hconst); 231 val = vmax*(histSum/numPixInTile); 232 val(val>=1) = 1-eps; % avoid log(0) 233 temp = sqrt(-hconst*log(1-val)); 234 mapping = min(selectedRange(1)+temp*valSpread,... 235 selectedRange(2)); %limit to max 236 237 case ‘exponential‘, 238 % pdf = alpha*exp(-alpha*t)*U(t) 239 % cdf = 1-exp(-alpha*t) 240 vmax = 1 - exp(-alpha); 241 val = (vmax*histSum/numPixInTile); 242 val(val>=1) = 1-eps; 243 temp = -1/alpha*log(1-val); 244 mapping = min(selectedRange(1)+temp*valSpread,selectedRange(2)); 245 246 otherwise, 247 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:distributionType‘)) %should never get here 248 249 end 250 251 %rescale the result to be between 0 and 1 for later use by the GRAYXFORM 252 %private mex function 253 mapping = mapping/fullRange(2); 254 255 %----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 256 % This function clips the histogram according to the clipLimit and 257 % redistributes clipped pixels across bins below the clipLimit 258 259 function imgHist = clipHistogram(imgHist, clipLimit, numBins) 260 261 % total number of pixels overflowing clip limit in each bin 262 totalExcess = sum(max(imgHist - clipLimit,0)); 263 264 % clip the histogram and redistribute the excess pixels in each bin 265 avgBinIncr = floor(totalExcess/numBins); 266 upperLimit = clipLimit - avgBinIncr; % bins larger than this will be 267 % set to clipLimit 268 269 % this loop should speed up the operation by putting multiple pixels 270 % into the "obvious" places first 271 for k=1:numBins 272 if imgHist(k) > clipLimit 273 imgHist(k) = clipLimit; 274 else 275 if imgHist(k) > upperLimit % high bin count 276 totalExcess = totalExcess - (clipLimit - imgHist(k)); 277 imgHist(k) = clipLimit; 278 else 279 totalExcess = totalExcess - avgBinIncr; 280 imgHist(k) = imgHist(k) + avgBinIncr; 281 end 282 end 283 end 284 285 % this loops redistributes the remaining pixels, one pixel at a time 286 k = 1; 287 while (totalExcess ~= 0) 288 %keep increasing the step as fewer and fewer pixels remain for 289 %the redistribution (spread them evenly) 290 stepSize = max(floor(numBins/totalExcess),1); 291 for m=k:stepSize:numBins 292 if imgHist(m) < clipLimit 293 imgHist(m) = imgHist(m)+1; 294 totalExcess = totalExcess - 1; %reduce excess 295 if totalExcess == 0 296 break; 297 end 298 end 299 end 300 301 k = k+1; %prevent from always placing the pixels in bin #1 302 if k > numBins % start over if numBins was reached 303 k = 1; 304 end 305 end 306 307 %----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 308 % This function interpolates between neighboring tile mappings to produce a 309 % new mapping in order to remove artificially induced tile borders. 310 % Otherwise, these borders would become quite visible. The resulting 311 % mapping is applied to the input image thus producing a CLAHE processed 312 % image. 313 314 function claheI = makeClaheImage(I, tileMappings, numTiles, selectedRange,... 315 numBins, dimTile) 316 317 %initialize the output image to zeros (preserve the class of the input image) 318 claheI = I; 319 claheI(:) = 0; 320 321 %compute the LUT for looking up original image values in the tile mappings, 322 %which we created earlier 323 if ~(isa(I,‘double‘) || isa(I,‘single‘)) 324 k = selectedRange(1)+1 : selectedRange(2)+1; 325 aLut = zeros(length(k),1); 326 aLut(k) = (k-1)-selectedRange(1); 327 aLut = aLut/(selectedRange(2)-selectedRange(1)); 328 else 329 % remap from 0..1 to 0..numBins-1 330 if numBins ~= 1 331 binStep = 1/(numBins-1); 332 start = ceil(selectedRange(1)/binStep); 333 stop = floor(selectedRange(2)/binStep); 334 k = start+1:stop+1; 335 aLut(k) = 0:1/(length(k)-1):1; 336 else 337 aLut(1) = 0; %in case someone specifies numBins = 1, which is just silly 338 end 339 end 340 341 imgTileRow=1; 342 for k=1:numTiles(1)+1 343 if k == 1 %special case: top row 344 imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1)/2; %always divisible by 2 because of padding 345 mapTileRows = [1 1]; 346 else 347 if k == numTiles(1)+1 %special case: bottom row 348 imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1)/2; 349 mapTileRows = [numTiles(1) numTiles(1)]; 350 else %default values 351 imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1); 352 mapTileRows = [k-1, k]; %[upperRow lowerRow] 353 end 354 end 355 356 % loop over columns of the tileMappings cell array 357 imgTileCol=1; 358 for l=1:numTiles(2)+1 359 if l == 1 %special case: left column 360 imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2)/2; 361 mapTileCols = [1, 1]; 362 else 363 if l == numTiles(2)+1 % special case: right column 364 imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2)/2; 365 mapTileCols = [numTiles(2), numTiles(2)]; 366 else %default values 367 imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2); 368 mapTileCols = [l-1, l]; % right left 369 end 370 end 371 372 % Extract four tile mappings 373 ulMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(1), mapTileCols(1)}; 374 urMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(1), mapTileCols(2)}; 375 blMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(2), mapTileCols(1)}; 376 brMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(2), mapTileCols(2)}; 377 378 % Calculate the new greylevel assignments of pixels 379 % within a submatrix of the image specified by imgTileIdx. This 380 % is done by a bilinear interpolation between four different mappings 381 % in order to eliminate boundary artifacts. 382 383 normFactor = imgTileNumRows*imgTileNumCols; %normalization factor 384 imgTileIdx = {imgTileRow:imgTileRow+imgTileNumRows-1, ... 385 imgTileCol:imgTileCol+imgTileNumCols-1}; 386 387 imgPixVals = grayxform(I(imgTileIdx{1},imgTileIdx{2}), aLut); 388 389 % calculate the weights used for linear interpolation between the 390 % four mappings 391 rowW = repmat((0:imgTileNumRows-1)‘,1,imgTileNumCols); 392 colW = repmat(0:imgTileNumCols-1,imgTileNumRows,1); 393 rowRevW = repmat((imgTileNumRows:-1:1)‘,1,imgTileNumCols); 394 colRevW = repmat(imgTileNumCols:-1:1,imgTileNumRows,1); 395 396 claheI(imgTileIdx{1}, imgTileIdx{2}) = ... 397 (rowRevW .* (colRevW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,ulMapTile)) + ... 398 colW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,urMapTile)))+ ... 399 rowW .* (colRevW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,blMapTile)) + ... 400 colW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,brMapTile))))... 401 /normFactor; 402 403 imgTileCol = imgTileCol + imgTileNumCols; 404 end %over tile cols 405 imgTileRow = imgTileRow + imgTileNumRows; 406 end %over tile rows 407 408 %----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 409 410 function [I, selectedRange, fullRange, numTiles, dimTile, clipLimit,... 411 numBins, noPadRect, distribution, alpha, ... 412 int16ClassChange] = parseInputs(varargin) 413 414 narginchk(1,13); 415 416 I = varargin{1}; 417 validateattributes(I, {‘uint8‘, ‘uint16‘, ‘double‘, ‘int16‘, ‘single‘}, ... 418 {‘real‘, ‘2d‘, ‘nonsparse‘, ‘nonempty‘}, ... 419 mfilename, ‘I‘, 1); 420 421 % convert int16 to uint16 422 if isa(I,‘int16‘) 423 I = int16touint16(I); 424 int16ClassChange = true; 425 else 426 int16ClassChange = false; 427 end 428 429 if any(size(I) < 2) 430 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:inputImageTooSmall‘)) 431 end 432 433 %Other options 434 %%%%%%%%%%%%%% 435 436 %Set the defaults 437 distribution = ‘uniform‘; 438 alpha = 0.4; 439 440 if isa(I, ‘double‘) || isa(I,‘single‘) 441 fullRange = [0 1]; 442 else 443 fullRange(1) = I(1); %copy class of the input image 444 fullRange(1:2) = [-Inf Inf]; %will be clipped to min and max 445 fullRange = double(fullRange); 446 end 447 448 selectedRange = fullRange; 449 450 %Set the default to 256 bins regardless of the data type; 451 %the user can override this value at any time 452 numBins = 256; 453 normClipLimit = 0.01; 454 numTiles = [8 8]; 455 456 checkAlpha = false; 457 458 validStrings = {‘NumTiles‘,‘ClipLimit‘,‘NBins‘,‘Distribution‘,... 459 ‘Alpha‘,‘Range‘}; 460 461 if nargin > 1 462 done = false; 463 464 idx = 2; 465 while ~done 466 input = varargin{idx}; 467 inputStr = validatestring(input, validStrings,mfilename,‘PARAM‘,idx); 468 469 idx = idx+1; %advance index to point to the VAL portion of the input 470 471 if idx > nargin 472 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:missingValue‘, inputStr)) 473 end 474 475 switch inputStr 476 477 case ‘NumTiles‘ 478 numTiles = varargin{idx}; 479 validateattributes(numTiles, {‘double‘}, {‘real‘, ‘vector‘, ... 480 ‘integer‘, ‘finite‘,‘positive‘},... 481 mfilename, inputStr, idx); 482 483 if (any(size(numTiles) ~= [1,2])) 484 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:invalidNumTilesVector‘, inputStr)) 485 end 486 487 if any(numTiles < 2) 488 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:invalidNumTilesValue‘, inputStr)) 489 end 490 491 case ‘ClipLimit‘ 492 normClipLimit = varargin{idx}; 493 validateattributes(normClipLimit, {‘double‘}, ... 494 {‘scalar‘,‘real‘,‘nonnegative‘},... 495 mfilename, inputStr, idx); 496 497 if normClipLimit > 1 498 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:invalidClipLimit‘, inputStr)) 499 end 500 501 case ‘NBins‘ 502 numBins = varargin{idx}; 503 validateattributes(numBins, {‘double‘}, {‘scalar‘,‘real‘,‘integer‘,... 504 ‘positive‘}, mfilename, ‘NBins‘, idx); 505 506 case ‘Distribution‘ 507 validDist = {‘rayleigh‘,‘exponential‘,‘uniform‘}; 508 distribution = validatestring(varargin{idx}, validDist, mfilename,... 509 ‘Distribution‘, idx); 510 511 case ‘Alpha‘ 512 alpha = varargin{idx}; 513 validateattributes(alpha, {‘double‘},{‘scalar‘,‘real‘,... 514 ‘nonnan‘,‘positive‘,‘finite‘},... 515 mfilename, ‘Alpha‘,idx); 516 checkAlpha = true; 517 518 case ‘Range‘ 519 validRangeStrings = {‘original‘,‘full‘}; 520 rangeStr = validatestring(varargin{idx}, validRangeStrings,mfilename,... 521 ‘Range‘,idx); 522 523 if strmatch(rangeStr,‘original‘) 524 selectedRange = double([min(I(:)), max(I(:))]); 525 end 526 527 otherwise 528 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:inputString‘)) %should never get here 529 end 530 531 if idx >= nargin 532 done = true; 533 end 534 535 idx=idx+1; 536 end 537 end 538 539 540 %% Pre-process the inputs 541 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 542 543 dimI = size(I); 544 dimTile = dimI ./ numTiles; 545 546 %check if tile size is reasonable 547 if any(dimTile < 1) 548 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:inputImageTooSmallToSplit‘, num2str( numTiles ))) 549 end 550 551 if checkAlpha 552 if strcmp(distribution,‘uniform‘) 553 error(message(‘images:adapthisteq:alphaShouldNotBeSpecified‘, distribution)) 554 end 555 end 556 557 %check if the image needs to be padded; pad if necessary; 558 %padding occurs if any dimension of a single tile is an odd number 559 %and/or when image dimensions are not divisible by the selected 560 %number of tiles 561 rowDiv = mod(dimI(1),numTiles(1)) == 0; 562 colDiv = mod(dimI(2),numTiles(2)) == 0; 563 564 if rowDiv && colDiv 565 rowEven = mod(dimTile(1),2) == 0; 566 colEven = mod(dimTile(2),2) == 0; 567 end 568 569 noPadRect = []; 570 if ~(rowDiv && colDiv && rowEven && colEven) 571 padRow = 0; 572 padCol = 0; 573 574 if ~rowDiv 575 rowTileDim = floor(dimI(1)/numTiles(1)) + 1; 576 padRow = rowTileDim*numTiles(1) - dimI(1); 577 else 578 rowTileDim = dimI(1)/numTiles(1); 579 end 580 581 if ~colDiv 582 colTileDim = floor(dimI(2)/numTiles(2)) + 1; 583 padCol = colTileDim*numTiles(2) - dimI(2); 584 else 585 colTileDim = dimI(2)/numTiles(2); 586 end 587 588 %check if tile dimensions are even numbers 589 rowEven = mod(rowTileDim,2) == 0; 590 colEven = mod(colTileDim,2) == 0; 591 592 if ~rowEven 593 padRow = padRow+numTiles(1); 594 end 595 596 if ~colEven 597 padCol = padCol+numTiles(2); 598 end 599 600 padRowPre = floor(padRow/2); 601 padRowPost = ceil(padRow/2); 602 padColPre = floor(padCol/2); 603 padColPost = ceil(padCol/2); 604 605 I = padarray(I,[padRowPre padColPre ],‘symmetric‘,‘pre‘); 606 I = padarray(I,[padRowPost padColPost],‘symmetric‘,‘post‘); 607 608 %UL corner (Row, Col), LR corner (Row, Col) 609 noPadRect.ulRow = padRowPre+1; 610 noPadRect.ulCol = padColPre+1; 611 noPadRect.lrRow = padRowPre+dimI(1); 612 noPadRect.lrCol = padColPre+dimI(2); 613 end 614 615 %redefine this variable to include the padding 616 dimI = size(I); 617 618 %size of the single tile 619 dimTile = dimI ./ numTiles; 620 621 %compute actual clip limit from the normalized value entered by the user 622 %maximum value of normClipLimit=1 results in standard AHE, i.e. no clipping; 623 %the minimum value minClipLimit would uniformly distribute the image pixels 624 %across the entire histogram, which would result in the lowest possible 625 %contrast value 626 numPixInTile = prod(dimTile); 627 minClipLimit = ceil(numPixInTile/numBins); 628 clipLimit = minClipLimit + round(normClipLimit*(numPixInTile-minClipLimit)); 629 630 %-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
参考上述代码,作者分别用VB和C#实现了该算法,提供个编译好的文件给有兴趣研究该算法的朋友看看效果(不提供源代码的):
http://files.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/CLAHE.rar
C#示例代码下载:http://files.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/AdaptHistEqualizeTest.rar
感谢作者!
限制对比度自适应直方图均衡(Contrast Limited Adaptive histgram equalization/CLAHE)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Allen-rg/p/5948323.html