标签:
目录:
数学函数
统计函数
x <- c(2,4,6,8,10,11) mean(x,trim = 0.2) #6*0.2=1.2(取整),除去最大最小值11、2 ,实际计算 4 6 8 10的平均 --> 7 mean(x) # 41/6 --> 6.833
> x <- c(2,4,6,9,10,11) > median(x) [1] 7.5 > x <- c(2,4,9,10,11) > median(x) [1] 9
> x <- c(1,2,3,5,7,8) > mad(x) [1] 3.7065 > #分解mad(x)计算过程 > y <- abs(x - median(x));y [1] 3 2 1 1 3 4 > z <- median(y);z [1] 2.5 > 1.4826 * z [1] 3.7065
> x <- c(1,2,3,5,7,8) > y <- range(x);y [1] 1 8 > diff(y) #滞后差分 [1] 7
 , ,
, ,> x <- c(1,2,3,4) > sd(x) [1] 1.290994 > m <- mean(x); > y <- sum((x - m)^2)/(length(x) -1) > sqrt(y) [1] 1.290994
scale(x): 为数据对象x按列进行中心化或标准化,语法:scale(x, center = TRUE, scale = TRUE)
> data <- c(1, 2, 3, 6, 3) > scale(data) [,1] [1,] -1.0690450 [2,] -0.5345225 [3,] 0.0000000 [4,] 1.6035675 [5,] 0.0000000 attr(,"scaled:center") [1] 3 attr(,"scaled:scale") [1] 1.870829
> m <- c(1:20) > quantile(m,probs = c(0.25,0.75,1)); 25% 75% 100% 5.75 15.25 20.00 > (20 -1)*0.25 + 1 [1] 5.75
应用示例
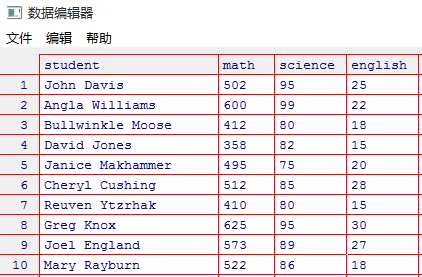
> setwd("E:\\R") > load(file = "roster.rda") > options(digits = 2) #小数点后保留2位 > z <- scale(roster[,2:4]) > z math science english 1 0.013 1.078 0.587 2 1.143 1.591 0.037 3 -1.026 -0.847 -0.697 4 -1.649 -0.590 -1.247 5 -0.068 -1.489 -0.330 6 0.128 -0.205 1.137 7 -1.049 -0.847 -1.247 8 1.432 1.078 1.504 9 0.832 0.308 0.954 10 0.243 -0.077 -0.697
第二步:计算每行的平均得分获得综合得分,合并到花名册,如下:
> score <- apply(z,MARGIN = 1,FUN = mean);
> score
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0.56 0.92 -0.86 -1.16 -0.63 0.35 -1.05 1.34 0.70 -0.18
> roster <- cbind(roster,score);roster
student math science english score
1 John Davis 502 95 25 0.56
2 Angla Williams 600 99 22 0.92
3 Bullwinkle Moose 412 80 18 -0.86
4 David Jones 358 82 15 -1.16
5 Janice Makhammer 495 75 20 -0.63
6 Cheryl Cushing 512 85 28 0.35
7 Reuven Ytzrhak 410 80 15 -1.05
8 Greg Knox 625 95 30 1.34
9 Joel England 573 89 27 0.70
10 Mary Rayburn 522 86 18 -0.18
第三步:按百分位数进行等级划分,如下:
> y <- quantile(roster$score,probs = c(0.8,0.6,0.4,0.2))
> y
80% 60% 40% 20%
0.74 0.44 -0.36 -0.89
> roster <- within(roster,{
+ grader <- NA
+ grader[score >= y[1]] <- "A"
+ grader[score < y[1] & score >= y[2]] <- "B"
+ grader[score < y[2] & score >= y[3]] <- "C"
+ grader[score < y[3] & score >= y[4]] <- "D"
+ grader[score < y[4]] <- "E"
+ })
> roster
student math science english score grader
1 John Davis 502 95 25 0.56 B
2 Angla Williams 600 99 22 0.92 A
3 Bullwinkle Moose 412 80 18 -0.86 D
4 David Jones 358 82 15 -1.16 E
5 Janice Makhammer 495 75 20 -0.63 D
6 Cheryl Cushing 512 85 28 0.35 C
7 Reuven Ytzrhak 410 80 15 -1.05 E
8 Greg Knox 625 95 30 1.34 A
9 Joel England 573 89 27 0.70 B
10 Mary Rayburn 522 86 18 -0.18 C
第四步: 将student变量拆分为firstname 和 lastname ,并按姓氏和名称排序,将结果保存为本地文件 studentGrade.rda
> name <- strsplit(roster$student," ")
Error in strsplit(roster$student, " ") : non-character argument
> class(roster$student) #查看student类型,是因子,必须转化成字符
[1] "factor"
正确代码如下:
> name <- strsplit(as.character(roster$student)," ") > firstname <- sapply(name,"[",1) # "[" 是一个可以提取某个对象一部分的函数,在这里用来提取列表中name各成份中的第一或二个元素 > lastname <- sapply(name,"[",2) > sGrade <- cbind(firstname,lastname,roster[,-1]) > sGrade[order(sGrade$lastname),] firstname lastname math science english score grader 6 Cheryl Cushing 512 85 28 0.3532485 C 1 John Davis 502 95 25 0.5592028 B 9 Joel England 573 89 27 0.6978361 B 4 David Jones 358 82 15 -1.1620473 E 8 Greg Knox 625 95 30 1.3378934 A 5 Janice Makhammer 495 75 20 -0.6289776 D 3 Bullwinkle Moose 412 80 18 -0.8565414 D 10 Mary Rayburn 522 86 18 -0.1768163 C 2 Angla Williams 600 99 22 0.9238259 A 7 Reuven Ytzrhak 410 80 15 -1.0476242 E > save(sGrade,file = "studentGrade.rda")
控制流
i<-10 while (i>0) { print("hello") i <- i-1 }
x <- switch( 3, "first", "second", "third", "fourth" ) x
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tgzhu/p/5951651.html