标签:
React Native与传统的HybirdApp最大区别就是抛开WebView,使用JSC+原生组件的方式进行渲染,那么整个App启动/渲染流程又是怎样的呢?
首先从组件的角度来看下RN的启动流程:(Android为例)
setupReactContext初始化React上下文,调用JS端AppRegistry.runApplication(key,params),key为模块/组件名称,参数包含rootTag、initialPropsrenderApplication渲染整个应用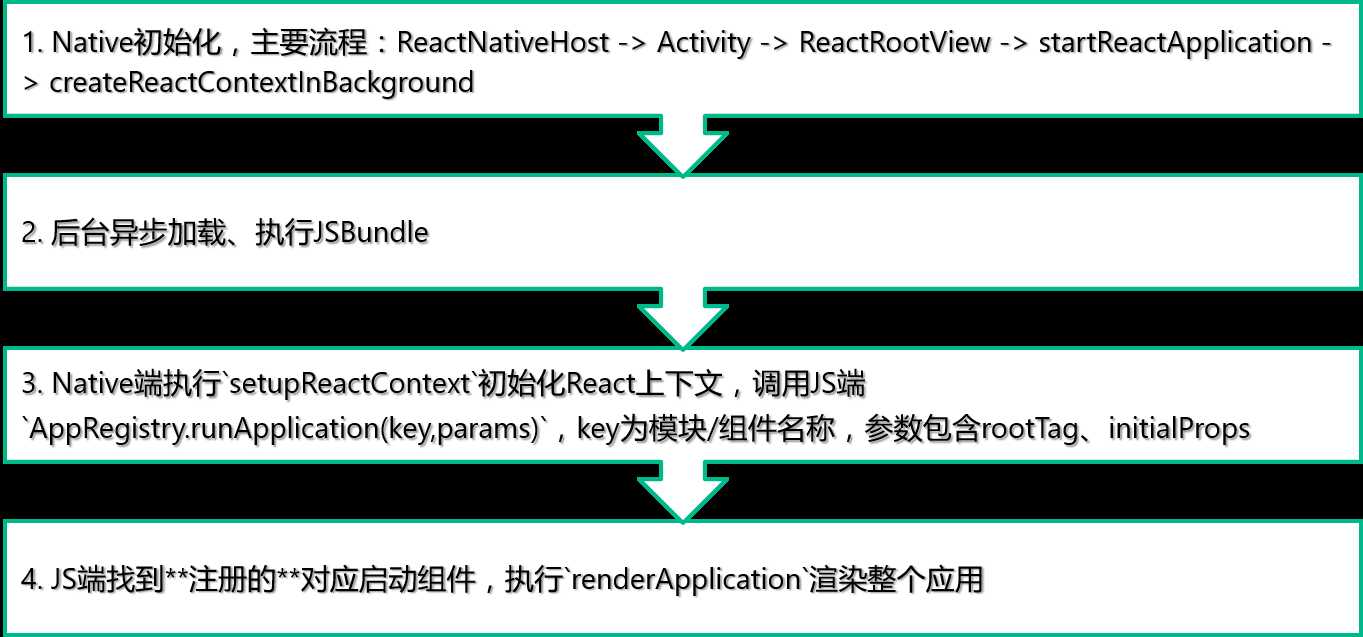
renderApplication函数中会执行:
ReactNative.render(
<AppContainer>
<RootComponent
{...initialProps}
rootTag={rootTag}
/>
</AppContainer>,
rootTag
);其中ReactNative是在React库中定义的,AppContainer是一个JS组件,使用View包裹了根组件,开发时工具Inspector、YellowBox都是在这个组件中加载,RootComponent是传入的根组件。
JS端注册组件:(在第2步执行JSBundle时)
AppRegistry.registerComponent(‘TiebaNext‘, rootComponent);*仅在JS端处理,记录在一个Map中。
Android端定义启动组件,Activity中,继承ReactActivity:(在第1步时调用)
@Override
protected String getMainComponentName() {
return "TiebaNext";
}iOS端定义启动组件:
self.rctRootView = [[RCTRootView alloc] initWithBundleURL:jsCodeLocation
moduleName:@"TiebaNext"
initialProperties:nil
launchOptions:nil];简单说就是Native初始化 -> 加载JS,JS端注册组件 -> 端上调用JS端run方法,传入入口组件名称 -> JS端启动渲染流程。
React的渲染都是以组件为单位,上面已经分析了,启动的最后阶段就是JS端开始渲染根组件。首先我们先看下React的组件是怎么编写的,以及他的生命周期:(熟悉React可略过)
一个例子,无网络提示组件:

(例子语言Typescript)
// 组件的属性定义
interface PropsDefine {
// 组件宽度
width: number
// 组件高度
height: number
// 点击刷新按钮回调,可选
onClickRefresh?: () => void
}
export class NoNetwork extends React.Component<PropsDefine, {}> { // 组件无状态,定义为空:{}
// 组件的默认属性定义,单例,实例间共享
static defaultProps = {
onClickRefresh: () => { }
}
render() {
let {width, height} = this.props
return (
<View style={[Styles.panel, {
width: width,
height: height,
}]}>
<View style={Styles.picBlock}>
<Image source={Styles.picUrl}/>
</View>
<View style={Styles.textBlock}>
<Text style={Styles.text}>你的网络好像不给力</Text>
<Text style={Styles.text}>点击按钮刷新</Text>
</View>
<TouchableOpacity style={Styles.button} onPress={this.props.onClickRefresh}>
<Text style={Styles.buttonText}>刷新</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
)
}
}跟端上组件开发一样,React组件也定义了组件的生命周期:
getDefaultPropsgetInitialStatecomponentWillMountrendercomponentDidMountcomponentWillReceivePropsshouldComponentUpdatecomponentWillUpdaterendercomponentDidUpdatecomponentWillUnmount那么这个组件到底是怎么用原生组件渲染的呢?首先我们先来看看最主要的render做了什么。jsx不太直观,我们先翻译一下render:
render() {
let { width, height } = this.props;
return (React.createElement(View, { style: [Styles.panel, {
width: width,
height: height,
}] },
React.createElement(View, { style: Styles.picBlock },
React.createElement(Image, { source: Styles.picUrl })),
React.createElement(View, { style: Styles.textBlock },
React.createElement(Text, { style: Styles.text }, "\u4F60\u7684\u7F51\u7EDC\u597D\u50CF\u4E0D\u7ED9\u529B"),
React.createElement(Text, { style: Styles.text }, "\u70B9\u51FB\u6309\u94AE\u5237\u65B0")),
React.createElement(TouchableOpacity, { style: Styles.button, onPress: this.props.onClickRefresh },
React.createElement(Text, { style: Styles.buttonText }, "\u5237\u65B0"))));
}这下清晰多了吧?
React.createElement的方法签名:
ReactElement.createElement = function (type, config, children){ ... }ReactNative的UI组件通过requireNativeComponent -> createReactNativeComponentClass -> ReactNativeBaseComponent下mountComponent的调用关系,最终在mountComponent中调用UIManager组件创建View:UIManager.createView(tag, this.viewConfig.uiViewClassName, nativeTopRootTag, updatePayload);,在Native端,UIManager调用对应组件类型的ViewManager(单例,管理类)创建实例。
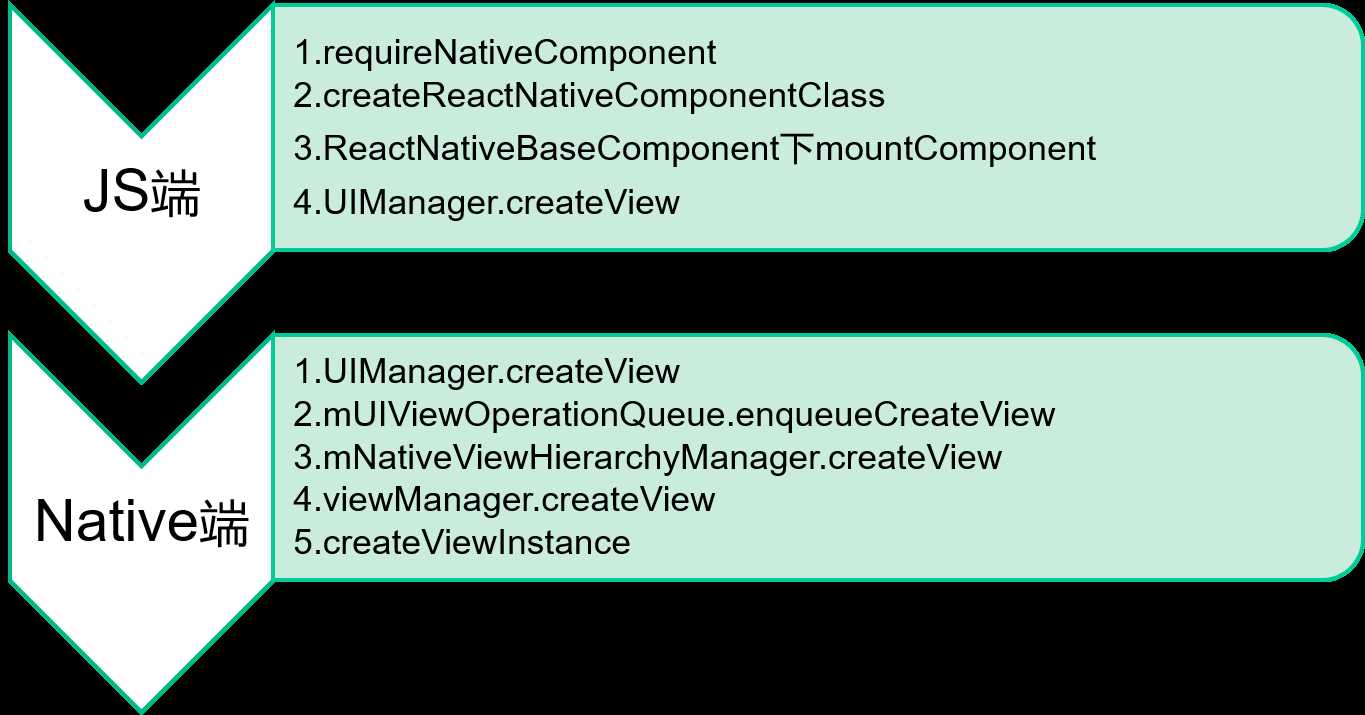
*UIManager是一个NativeModule,待下面分析
接下来我们来详细分析下原生组件的实现方法,以Image组件为例:
iOS和Android实现有一定差异,首先是Image组件JS端代码,都需要requireNativeComponent加载原生组件:
const RCTImageView = requireNativeComponent(‘RCTImageView‘, Image);Image的JS端实际上也是一个React JS组件,他也有render,返回的是:(iOS)
<RCTImageView
{...this.props}
style={style}
resizeMode={resizeMode}
tintColor={tintColor}
source={sources}
/>因为业务逻辑是写在JS端的,创建出了Native组件就需要进行控制,自然就涉及到属性传递、方法调用、事件回调这3个需求。
JS端组件跟Native真正实现的组件主要涉及三件事:
属性同步很简单,实际上是在组件重新render的时候调用ReactNativeBaseComponent下receiveComponent -> UIManager.updateView完成的。

两种方法,一种是调用NativeModules(后面有简单分析),如果想直接调用一个具体View的方法,那就需要使用UIManager模块:
Android端UIManager中的定义:
@ReactMethod
public void dispatchViewManagerCommand(int reactTag, int commandId, ReadableArray commandArgs) {
mUIImplementation.dispatchViewManagerCommand(reactTag, commandId, commandArgs);
}iOS端UIManager中的定义:
RCT_EXPORT_METHOD(dispatchViewManagerCommand:(nonnull NSNumber *)reactTag
commandID:(NSInteger)commandID
commandArgs:(NSArray<id> *)commandArgs)
{
RCTShadowView *shadowView = _shadowViewRegistry[reactTag];
RCTComponentData *componentData = _componentDataByName[shadowView.viewName];
Class managerClass = componentData.managerClass;
RCTModuleData *moduleData = [_bridge moduleDataForName:RCTBridgeModuleNameForClass(managerClass)];
id<RCTBridgeMethod> method = moduleData.methods[commandID];
NSArray *args = [@[reactTag] arrayByAddingObjectsFromArray:commandArgs];
[method invokeWithBridge:_bridge module:componentData.manager arguments:args];
}这个方法是从端上映射到JS的,所以在JS端可以这样调用:
UIManager.dispatchViewManagerCommand(
findNodeHandle(this), // 找到与NativeUI组件对应的JS组件实例
UIManager.[UI组件名].Commands.[方法],
[] // 参数
)findNodeHandle方法是在React中定义,可以找到组件实例的reactTag(执行在JS端),UIManager可以把调用命令分发到Native端对应的组件类型的ViewManager,再通过ViewManager调用View组件实例的对应方法。
Android端使用的是类似JS端调用Native的方式,使用了事件机制,不过事件的接收者是从JS端映射过来的,React下ReactNativeEventEmitter.receiveEvent(tag, topLevelType, nativeEventParam),所以需要先实现一个Event:(Switch的onValueChange事件)
class ReactSwitchEvent extends Event<ReactSwitchEvent> {
public static final String EVENT_NAME = "topChange"; // topChange会被映射成onChange,具体映射关系参见 UIManagerModuleConstants.java
public ReactSwitchEvent(int viewId, boolean isChecked) {
super(viewId);
mIsChecked = isChecked;
}
public boolean getIsChecked() {
return mIsChecked;
}
@Override
public String getEventName() {
return EVENT_NAME;
}
@Override
public short getCoalescingKey() {
// All switch events for a given view can be coalesced.
return 0;
}
@Override
public void dispatch(RCTEventEmitter rctEventEmitter) {
rctEventEmitter.receiveEvent(getViewTag(), getEventName(), serializeEventData());
}
private WritableMap serializeEventData() {
WritableMap eventData = Arguments.createMap();
eventData.putInt("target", getViewTag());
eventData.putBoolean("value", getIsChecked());
return eventData;
}
}然后在ViewManager或View中进行事件派发:
ReactContext reactContext = (ReactContext) buttonView.getContext();
reactContext.getNativeModule(UIManagerModule.class).getEventDispatcher().dispatchEvent(
new ReactSwitchEvent(
buttonView.getId(),
isChecked));iOS端实现有所区别,iOS端将JS函数直接映射到Native,所以可以直接调用(可多次调用):(View为RCTSwitch)
// ViewManager中声明事件为RCTBubblingEventBlock或RCTDirectEventBlock
RCT_EXPORT_VIEW_PROPERTY(onChange, RCTBubblingEventBlock);
// View中声明
@property (nonatomic, copy) RCTBubblingEventBlock onChange;
// view实例化时监听onChange
- (void)onChange:(RCTSwitch *)sender
{
if (sender.wasOn != sender.on) {
if (sender.onChange) {
sender.onChange(@{ @"value": @(sender.on) });
}
sender.wasOn = sender.on;
}
}这样就可以从JS端创建NativeUI组件了,可以看到UI组件的Native和JS端是通过reactTag进行的关联,通过UIManager模块,在Native端的DOM和React的DOM进行同步操作,保持结构一致。
模块数据结构,JS端可访问:
UIManager.[UI组件名].[Constants(静态值)/Commands(命令/方法)]
从端上映射的方法:(部分)
createView(int tag, String className, int rootViewTag, ReadableMap props)updateView(int tag, String className, ReadableMap props)manageChildren(int viewTag, Array moveFrom, Array moveTo, Array addChildTags, Array addAtIndices, Array removeFrom)measure(int reactTag, Callback callback)measureInWindow(int reactTag, Callback callback)dispatchViewManagerCommand(int reactTag, int commandId, ReadableArray commandArgs)这个模块是NativeModule方式定义的,在RN的JS端启动时,端上会通过JSC把收集到的模块信息(名称)打到JS端全局变量global.__fbBatchedBridgeConfig中,并采用延迟加载策略:设置NativeModules.[模块名]的getter,延迟通过JSC读取模块详细信息(方法、命令号等信息)。在调用的时候会放到MessageQueue的队列里,批量提交,两次批量提交限制的最小间隔为5ms。
关于React Native通讯更详尽的分析参见:React Native通讯原理
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Leo_wl/p/5983060.html