标签:main typedef sea vol goto word 字符串 while 实验
一、 实验目的
通过设计一个词法分析程序,对词法进行分析,加强对词法的理解,掌握对程序设计语言的分解和理解。
二、 实验内容和要求
在原程序中输入源代码
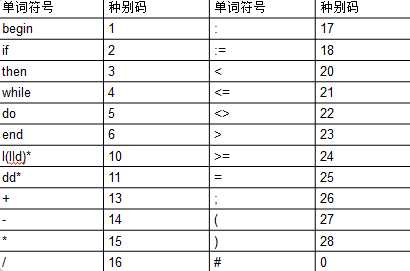
在源程序中,自动识别单词,把单词分为五种,并输出对应的单词种别码。
各种单词符号对应的种别码。
输出形式:
– (单词种别,单词自身的值)
– 整数码
– 标识符token、常数sum
– 关键字、运算符、界符token
三、 实验方法、步骤及结果测试
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <malloc.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define NULL 0 FILE *fp; char cbuffer; char *key[32]={"if","else","for","break","continue","int","float","double","auto","case","char","const","default","do","enum","long","extern","goto","register","return","short","signed","sizeof","static","struct","switch","typedef","union","unsigned","void","volatile","while"}; char *border[8]={",",";","{","}","(",")","[","]"}; char *arithmetic[4]={"+","-","*","/"}; char *relation[6]={"<","<=","=",">",">=","<>"}; char *consts[20]; char *label[20]; int constnum=0,labelnum=0; int search(char searchchar[],int wordtype) { int i=0; switch(wordtype) { case 1:for(i=0;i<=31;i++) { if (strcmp(key[i],searchchar)==0) return(i+1); } return 0; case 2: { for (i=0;i<=7;i++) { if (strcmp(border[i],searchchar)==0) return(i+1); } return(0); } case 3: { for (i=0;i<=3;i++) { if (strcmp(arithmetic[i],searchchar)==0) { return(i+1); } } return(0); } case 4: { for (i=0;i<=5;i++) if (strcmp(relation[i],searchchar)==0) return(i+1); return(0); } case 5: { for (i=0;i<=constnum;i++) { if(consts[i] && (strcmp(consts[i],searchchar)==0)) return(i+1); } consts[i-1]=(char *)malloc(sizeof(searchchar)); strcpy(consts[i-1],searchchar); constnum++; return(i); } case 6: { for(i=0;i<=labelnum;i++) if(label[i] && (strcmp(label[i],searchchar)==0)) return(i+1); label[i-1]=(char *)malloc(sizeof(searchchar)); strcpy(label[i-1],searchchar); labelnum++; return(i); } default: return 0; } } char alphaprocess(char buffer) { // int atype; int i=-1; char alphatp[20]; while((isalpha(buffer))||(isdigit(buffer))) { alphatp[++i]=buffer; buffer=fgetc(fp); } alphatp[i+1]=‘\0‘; if (/*atype=*/search(alphatp,1)) // printf("%s (1,%d)\n",alphatp,atype-1); printf("(1, \"%s\")\n",alphatp); else { search(alphatp,6); // printf("%s (6,%d)\n",alphatp,atype-1); printf("(2, \"%s\")\n",alphatp); } return(buffer); } char digitprocess(char buffer) { int i=-1; char digittp[20]; // int dtype; while ((isdigit(buffer))) { digittp[++i]=buffer; buffer=fgetc(fp); } digittp[i+1]=‘\0‘; search(digittp,5); // printf("%s (5,%d)\n",digittp,dtype-1); printf("(3, \"%s\")\n",digittp); return(buffer); } char otherprocess(char buffer) { int i=-1; char othertp[20]; // int otype,otypetp; othertp[0]=buffer; othertp[1]=‘\0‘; if (/*otype=*/search(othertp,3)) { // printf("%s (3,%d)\n",othertp,otype-1); printf("(4, \"%s\")\n",othertp); buffer=fgetc(fp); goto out; } if (/*otype=*/search(othertp,4)) { buffer=fgetc(fp); othertp[1]=buffer; othertp[2]=‘\0‘; if (/*otypetp=*/search(othertp,4)) { // printf("%s (4,%d)\n",othertp,otypetp-1); printf("(4, \"%s\")\n",othertp); goto out; } else othertp[1]=‘\0‘; // printf("%s (4,%d)\n",othertp,otype-1); printf("(4, \"%s\")\n",othertp); goto out; } if (buffer==‘:‘) { buffer=fgetc(fp); if (buffer==‘=‘) printf(":= (2,2)\n"); buffer=fgetc(fp); goto out; } else { if (/*otype=*/search(othertp,2)) { // printf("%s (2,%d)\n",othertp,otype-1); printf("(5, \"%s\")\n",othertp); buffer=fgetc(fp); goto out; } } if ((buffer!=‘\n‘)&&(buffer!=‘ ‘)) printf("%c error,not a word\n",buffer); buffer=fgetc(fp); out: return(buffer); } void main() { int i; for (i=0;i<=20;i++) { label[i]=NULL; consts[i]=NULL; } if ((fp=fopen("example.c","r"))==NULL) printf("error"); else { cbuffer = fgetc(fp); while (cbuffer!=EOF) { if (isalpha(cbuffer)) cbuffer=alphaprocess(cbuffer); else if(isdigit(cbuffer)) cbuffer=digitprocess(cbuffer); else cbuffer=otherprocess(cbuffer); } printf("over\n"); getchar(); } }
#inlclude<stdio.h> int main() { int d,a,c; a=10; c=a+b; printf("%d%d",a,b);; return 0; }
四.运行结果及分析
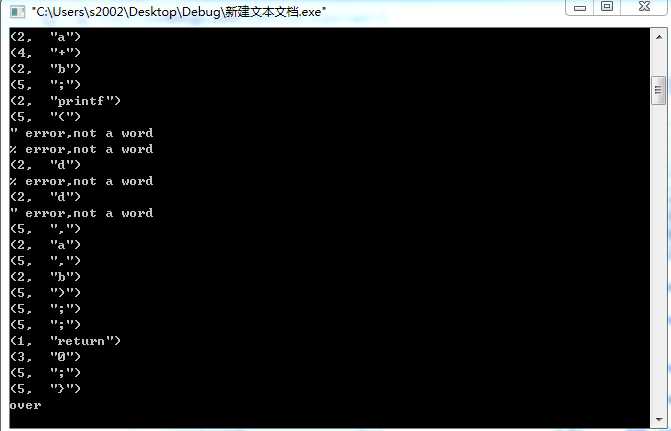
标签:main typedef sea vol goto word 字符串 while 实验
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sewhen/p/5985505.html