标签:limit sources 监控 不能 -name arguments conf libvirt default
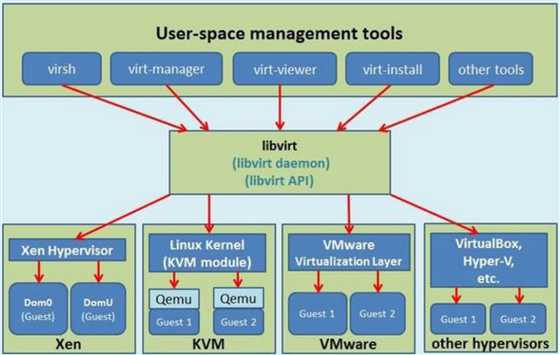
KVM 是 Kernel-based Virtual Machine 的简称,是 Linux 下 x86 硬件平台上的全功能虚拟化解决方案;
使用 KVM ,可允许运行多个虚拟机,包括 Linux 和 Windows操作系统。
KVM的虚拟化需要硬件支持(如Intel VT技术或者AMD V技术)。是基于硬件的完全虚拟化。
KVM 安装
在Windows 7系统中安装使用vmware,在vmware里安装linux系统,并在linux系统中安装使用kvm,虚拟化linux系统。
VMware: VMware? Workstation 10.0.0 build-1295980
Linux: CentOS-6.8-x86_64-minimal.iso
使用自定义方式安装CentOS
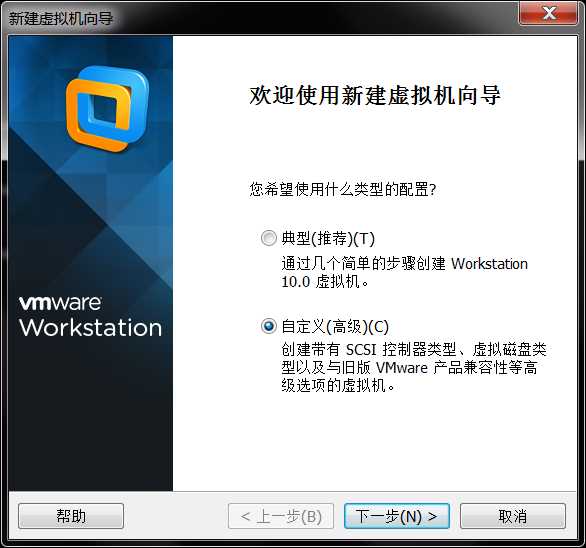
先创建虚拟机,然后再在光驱中指定iso镜像文件,再安装linux系统。
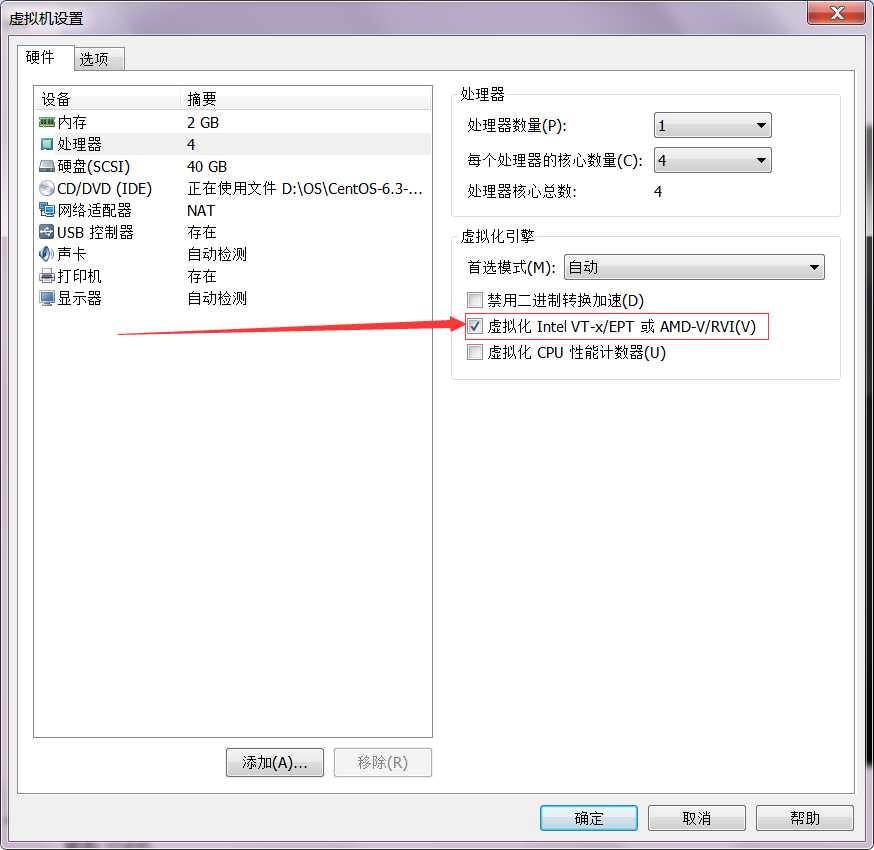
系统安装完成后,关闭操作系统,打开CentOS系统的虚拟机设置,点击处理器,选择“虚拟化..."
重启系统
命令检查是否支持虚拟化,
egrep -c ‘(vmx|svm)‘ /proc/cpuinfo
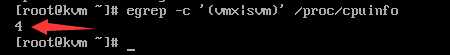
结果为支持虚拟化的核数
修改ip地址为静态ip
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0 TYPE=Ethernet ONBOOT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=192.168.126.200 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.126.2
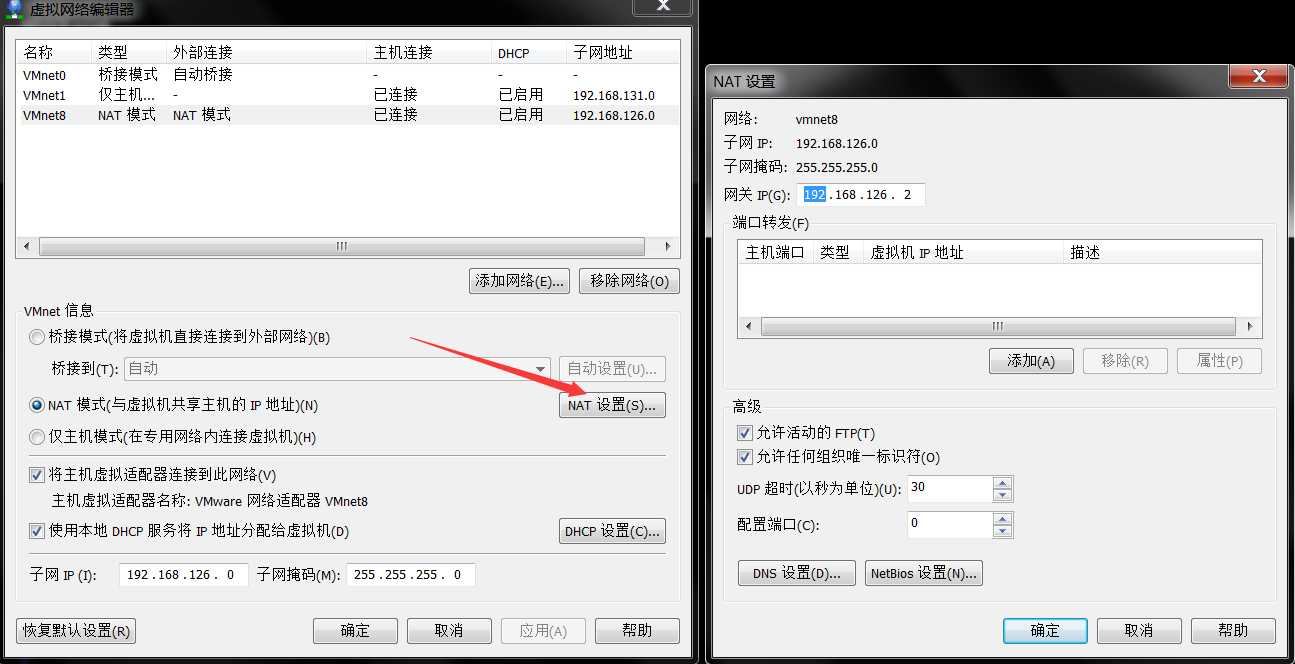
CentOS的网络链接方式是NAT模式,子网IP是192.168.126.0,设置IP地址为192.168.126.200
GATEWAY的设置为虚拟网络编辑器中的NAT设置中的网关地址
重启网络
service network
或重启主机
init 6
检查是否能够访问外网
ping www.baidu.com
安装kvm
yum -y install qemu-kvm
安装管理工具
yum -y install virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python python-virtinst bridge-utils
libvirt 是一套免费、开源的支持Linux下主流虚拟化工具的C函数库。提供一套方便、可靠的编程接口,支持与C,C++,Ruby,Python,Java等多种主流开发语言的绑定。
它支持各种虚拟机监控程序,包括 Xen 和 KVM,以及 QEMU 和用于其他操作系统的一些虚拟产品。
启动,并设置开机启动项
service libvirtd start
chkconfig libvirt don
如果不能安装或安装慢,可以换阿里开源镜像
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-6.repo
内核模块查看
查看已载入系统的模块
lsmod | grep kvm
[root@kvm ~]# lsmod| grep kvm
kvm_intel 55464 0
kvm 345038 1 kvm_intel
载入模块
modprobe kvm
modprobe kvm-intel
关闭防火墙
service iptables stop
关闭防火墙启动项
chkconfig iptables off
创建磁盘镜像文件
qemu-img 磁盘镜像工具
qemu-img --help 查看帮助
create [-f fmt] [-o options] filename [size]
fmt磁盘镜像文件格式,支持的格式有:raw cow qcow vdi vmdk cloop dmg bochs vpc vvfat qcow2 qed vhdx parallels nbd blkdebug null host_cdrom host_floppy host_device file gluster
执行脚本:
[root@kvm ~]# mkdir /kvmImg [root@kvm ~]# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /kvmImg/centos-6.8.qcow2 5G Formatting ‘/kvmImg/centos-6.8.qcow2‘, fmt=qcow2 size=5368709120 encryption=off cluster_size=65536
安装虚拟机
虚拟机安装的系统为:CentOS-6.8-x86_64-minimal.iso
先将镜像文件上传至主机的/kvmImg目录下
virt-install 工具
virt-install --help 查看帮助
脚本命令:
virt-install --virt-type kvm --name centos-6.8 --ram 1024 --vcpus 1 --cdrom=/kvmImg/CentOS-6.8-x86_64-minimal.iso --disk /kvmImg/centos-6.8.qcow2,format=qcow2 --network network=default --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole --os-type=linux --os-variant=rhel6
[root@kvm kvmImg]# virt-install --virt-type kvm --name centos-6.8 --ram 1024 > --vcpus 1 > --cdrom=/kvmImg/CentOS-6.8-x86_64-minimal.iso > --disk /kvmImg/centos-6.8.qcow2,format=qcow2 > --network network=default > --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole > --os-type=linux --os-variant=rhel6 Starting install... Creating domain... | 0 B 00:00 Domain installation still in progress. You can reconnect to the console to complete the installation process.
由于在创建脚本中指定了来宾的图形化工具为VNC --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0,然后通过VNC进入虚拟机,在创建时可指定端口(参考帮助),由于没有指定端口,需要查询一下端口号。
查看qemu-kvm虚拟机的端口号为 5900
[root@kvm kvmImg]# netstat -antp|grep kvm tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2749/qemu-kvm
通过VNC进入虚拟机
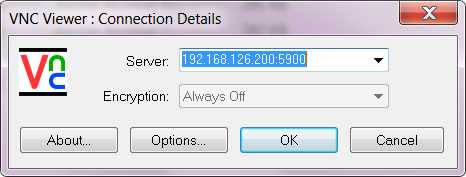
点击ok,进入系统
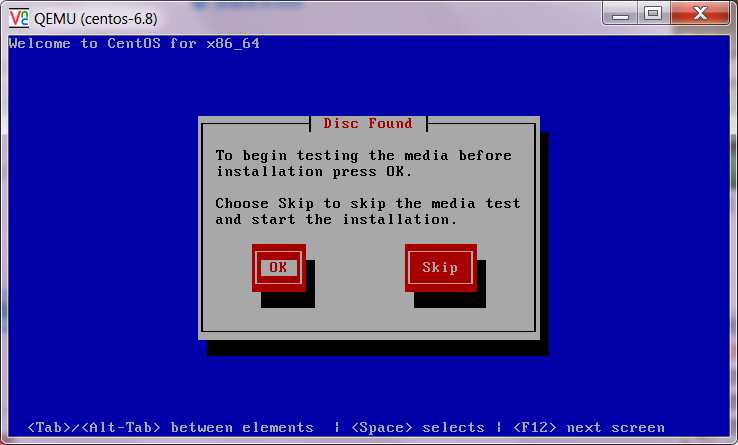
然后就可以通过vnc对系统进行安装设置,安装完成后,需要重启虚拟机,点击重启
虚拟机没了,找找虚拟机哪里去了
查看端口查找不到
[root@kvm kvmImg]# netstat -antp|grep kvm
那虚拟机应该是关闭了,怎么查看虚拟机的状态,怎么把它启动起来哪?
接下来需要用到virsh工具
Virsh:基于libvirt的命令行工具(CLI)
[root@kvm ~]# virsh Welcome to virsh, the virtualization interactive terminal. Type: ‘help‘ for help with commands ‘quit‘ to quit
virsh的帮助
virsh # help Grouped commands: Domain Management (help keyword ‘domain‘): attach-device attach device from an XML file attach-disk attach disk device attach-interface attach network interface autostart autostart a domain blkdeviotune Set or query a block device I/O tuning parameters. blkiotune Get or set blkio parameters blockcommit Start a block commit operation. blockcopy Start a block copy operation. blockjob Manage active block operations blockpull Populate a disk from its backing image. blockresize Resize block device of domain. change-media Change media of CD or floppy drive console connect to the guest console cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU cpu-compare compare host CPU with a CPU described by an XML file cpu-stats show domain cpu statistics create create a domain from an XML file define define (but don‘t start) a domain from an XML file desc show or set domain‘s description or title destroy destroy (stop) a domain detach-device detach device from an XML file detach-disk detach disk device detach-interface detach network interface domdisplay domain display connection URI domhostname print the domain‘s hostname domid convert a domain name or UUID to domain id domif-setlink set link state of a virtual interface domiftune get/set parameters of a virtual interface domjobabort abort active domain job domjobinfo domain job information domname convert a domain id or UUID to domain name dompmsuspend suspend a domain gracefully using power management functions dompmwakeup wakeup a domain from pmsuspended state domuuid convert a domain name or id to domain UUID domxml-from-native Convert native config to domain XML domxml-to-native Convert domain XML to native config dump dump the core of a domain to a file for analysis dumpxml domain information in XML edit edit XML configuration for a domain inject-nmi Inject NMI to the guest send-key Send keycodes to the guest managedsave managed save of a domain state managedsave-remove Remove managed save of a domain maxvcpus connection vcpu maximum memtune Get or set memory parameters migrate migrate domain to another host migrate-setmaxdowntime set maximum tolerable downtime migrate-setspeed Set the maximum migration bandwidth migrate-getspeed Get the maximum migration bandwidth numatune Get or set numa parameters reboot reboot a domain reset reset a domain restore restore a domain from a saved state in a file resume resume a domain save save a domain state to a file save-image-define redefine the XML for a domain‘s saved state file save-image-dumpxml saved state domain information in XML save-image-edit edit XML for a domain‘s saved state file schedinfo show/set scheduler parameters screenshot take a screenshot of a current domain console and store it into a file setmaxmem change maximum memory limit setmem change memory allocation setvcpus change number of virtual CPUs shutdown gracefully shutdown a domain start start a (previously defined) inactive domain suspend suspend a domain ttyconsole tty console undefine undefine a domain update-device update device from an XML file vcpucount domain vcpu counts vcpuinfo detailed domain vcpu information vcpupin control or query domain vcpu affinity emulatorpin control or query domain emulator affinity vncdisplay vnc display Domain Monitoring (help keyword ‘monitor‘): domblkerror Show errors on block devices domblkinfo domain block device size information domblklist list all domain blocks domblkstat get device block stats for a domain domcontrol domain control interface state domif-getlink get link state of a virtual interface domiflist list all domain virtual interfaces domifstat get network interface stats for a domain dominfo domain information dommemstat get memory statistics for a domain domstate domain state list list domains Host and Hypervisor (help keyword ‘host‘): capabilities capabilities freecell NUMA free memory hostname print the hypervisor hostname node-memory-tune Get or set node memory parameters nodecpustats Prints cpu stats of the node. nodeinfo node information nodememstats Prints memory stats of the node. nodesuspend suspend the host node for a given time duration qemu-attach QEMU Attach qemu-monitor-command QEMU Monitor Command qemu-agent-command QEMU Guest Agent Command sysinfo print the hypervisor sysinfo uri print the hypervisor canonical URI version show version Interface (help keyword ‘interface‘): iface-begin create a snapshot of current interfaces settings, which can be later committed (iface-commit) or restored (iface-rollback) iface-bridge create a bridge device and attach an existing network device to it iface-commit commit changes made since iface-begin and free restore point iface-define define (but don‘t start) a physical host interface from an XML file iface-destroy destroy a physical host interface (disable it / "if-down") iface-dumpxml interface information in XML iface-edit edit XML configuration for a physical host interface iface-list list physical host interfaces iface-mac convert an interface name to interface MAC address iface-name convert an interface MAC address to interface name iface-rollback rollback to previous saved configuration created via iface-begin iface-start start a physical host interface (enable it / "if-up") iface-unbridge undefine a bridge device after detaching its slave device iface-undefine undefine a physical host interface (remove it from configuration) Network Filter (help keyword ‘filter‘): nwfilter-define define or update a network filter from an XML file nwfilter-dumpxml network filter information in XML nwfilter-edit edit XML configuration for a network filter nwfilter-list list network filters nwfilter-undefine undefine a network filter Networking (help keyword ‘network‘): net-autostart autostart a network net-create create a network from an XML file net-define define (but don‘t start) a network from an XML file net-destroy destroy (stop) a network net-dumpxml network information in XML net-edit edit XML configuration for a network net-info network information net-list list networks net-name convert a network UUID to network name net-start start a (previously defined) inactive network net-undefine undefine an inactive network net-update update parts of an existing network‘s configuration net-uuid convert a network name to network UUID Node Device (help keyword ‘nodedev‘): nodedev-create create a device defined by an XML file on the node nodedev-destroy destroy (stop) a device on the node nodedev-detach detach node device from its device driver nodedev-dumpxml node device details in XML nodedev-list enumerate devices on this host nodedev-reattach reattach node device to its device driver nodedev-reset reset node device Secret (help keyword ‘secret‘): secret-define define or modify a secret from an XML file secret-dumpxml secret attributes in XML secret-get-value Output a secret value secret-list list secrets secret-set-value set a secret value secret-undefine undefine a secret Snapshot (help keyword ‘snapshot‘): snapshot-create Create a snapshot from XML snapshot-create-as Create a snapshot from a set of args snapshot-current Get or set the current snapshot snapshot-delete Delete a domain snapshot snapshot-dumpxml Dump XML for a domain snapshot snapshot-edit edit XML for a snapshot snapshot-info snapshot information snapshot-list List snapshots for a domain snapshot-parent Get the name of the parent of a snapshot snapshot-revert Revert a domain to a snapshot Storage Pool (help keyword ‘pool‘): find-storage-pool-sources-as find potential storage pool sources find-storage-pool-sources discover potential storage pool sources pool-autostart autostart a pool pool-build build a pool pool-create-as create a pool from a set of args pool-create create a pool from an XML file pool-define-as define a pool from a set of args pool-define define (but don‘t start) a pool from an XML file pool-delete delete a pool pool-destroy destroy (stop) a pool pool-dumpxml pool information in XML pool-edit edit XML configuration for a storage pool pool-info storage pool information pool-list list pools pool-name convert a pool UUID to pool name pool-refresh refresh a pool pool-start start a (previously defined) inactive pool pool-undefine undefine an inactive pool pool-uuid convert a pool name to pool UUID Storage Volume (help keyword ‘volume‘): vol-clone clone a volume. vol-create-as create a volume from a set of args vol-create create a vol from an XML file vol-create-from create a vol, using another volume as input vol-delete delete a vol vol-download download volume contents to a file vol-dumpxml vol information in XML vol-info storage vol information vol-key returns the volume key for a given volume name or path vol-list list vols vol-name returns the volume name for a given volume key or path vol-path returns the volume path for a given volume name or key vol-pool returns the storage pool for a given volume key or path vol-resize resize a vol vol-upload upload file contents to a volume vol-wipe wipe a vol Virsh itself (help keyword ‘virsh‘): cd change the current directory connect (re)connect to hypervisor echo echo arguments exit quit this interactive terminal help print help pwd print the current directory quit quit this interactive terminal
查看帮助,使用list命令
virsh # list Id Name State ---------------------------------------------------- virsh # list --all Id Name State ---------------------------------------------------- - centos-6.8 shut off
使用 list --al列出所有,查看centos-6.8状态是shut off,那接下里想办法把他启动起来
查看帮助,使用start命令
virsh # start centos-6.8 Domain centos-6.8 started
start命令后面参数是虚拟机名称,提示已经启动起来,然后通过vnc链接测试,可以登录系统,一个虚拟机完成简单安装。
标签:limit sources 监控 不能 -name arguments conf libvirt default
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/one--way/p/6012300.html