标签:rgs 大数 范围 表达 random 相同 循环 博客 读取
1 阅读并运行示例PassArray.java,观察并分析程序输出的结果,小结,然后与下页幻灯片所讲的内容进行对照。
程序源代码:
// PassArray.java
// Passing arrays and individual array elements to methods
public class PassArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
String output = "The values of the original array are:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
output += " " + a[i];
output += "\n\nEffects of passing array " + "element call-by-value:\n"
+ "a[3] before modifyElement: " + a[3];
modifyElement(a[3]);
output += "\na[3] after modifyElement: " + a[3];
output += "\n Effects of passing entire array by reference";
modifyArray(a); // array a passed call-by-reference
output += "\n\nThe values of the modified array are:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
output += " " + a[i];
System.out.println(output);
}
public static void modifyArray(int b[]) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++)
b[j] *= 2;
}
public static void modifyElement(int e) {
e *= 2;
}
}
截图分析:

分析:
按引用传递与按值传送数组类型方法参数的最大关键在于:
使用前者时,如果方法中有代码更改了数组元素的值,实际上是直接修改了原始的数组元素,。
使用后者则没有这个问题,方法体中修改的仅是原始数组元素的一个拷贝。
2 阅读QiPan.java示例程序了解如何利用二维数组和循环语句绘制五子棋盘。
源程序:
import java.io.*;
public class Test3
{
//定义一个二维数组来充当棋盘
private String[][] board;
//定义棋盘的大小
private static int BOARD_SIZE = 15;
public void initBoard()
{
//初始化棋盘数组
board = new String[BOARD_SIZE][BOARD_SIZE];
//把每个元素赋为"╋",用于在控制台画出棋盘
for (int i = 0 ; i < BOARD_SIZE ; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j < BOARD_SIZE ; j++)
{
board[i][j] = "╋";
}
}
}
//在控制台输出棋盘的方法
public void printBoard()
{
//打印每个数组元素
for (int i = 0 ; i < BOARD_SIZE ; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j < BOARD_SIZE ; j++)
{
//打印数组元素后不换行
System.out.print(board[i][j]);
}
//每打印完一行数组元素后输出一个换行符
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
Test3 gb = new Test3();
gb.initBoard();
gb.printBoard();
//这是用于获取键盘输入的方法
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String inputStr = null;
System.out.println("请输入您下棋的座标,应以x y的格式:");
//br.readLine():每当在键盘上输入一行内容按回车,刚输入的内容将被br读取到。
while ((inputStr = br.readLine()) != null)
{
//将用户输入的字符串以空格( )作为分隔符,分隔成2个字符串
String[] posStrArr = inputStr.split(" ");
//将2个字符串转换成用户下棋的座标
int xPos = Integer.parseInt(posStrArr[0]);
int yPos = Integer.parseInt(posStrArr[1]);
//把对应的数组元素赋为"●"。
gb.board[xPos - 1][yPos - 1] = "●";
//电脑下棋的位置
xPos=(int)(Math.random()*15);
yPos=(int)(Math.random()*15);
gb.board[xPos - 1][yPos - 1] = "?";
/*
电脑随机生成2个整数,作为电脑下棋的座标,赋给board数组。
还涉及
1.座标的有效性,只能是数字,不能超出棋盘范围
2.如果下的棋的点,不能重复下棋。
3.每次下棋后,需要扫描谁赢了
*/
gb.printBoard();
System.out.println("请输入您下棋的座标,应以x,y的格式:");
}
}
}
程序分析:
先建立二维字符串数组存储╋, 然后使用遍历描绘出棋盘,然后将输入的坐标点赋值为电脑和人各自的符号。在进行输赢判断。
3 编写一个程序将一个整数转换为汉字读法字符串。比如“1123”转换为“一千一百二十三”。 更进一步,能否将数字表示的金额改为“汉字表达? 比如将“¥123.52”转换为“壹佰贰拾叁元伍角贰分”。
程序源代码:
package dongshou;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class one {
private static final String[] CN_UPPER_NUMBER = { "零", "壹", "贰", "叁", "肆",
"伍", "陆", "柒", "捌", "玖" };
/**
* 汉语中货币单位大写,这样的设计类似于占位符
*/
private static final String[] CN_UPPER_MONETRAY_UNIT = { "分", "角", "元",
"拾", "佰", "仟", "万", "拾", "佰", "仟", "亿", "拾", "佰", "仟", "兆", "拾",
"佰", "仟" };
/**
* 特殊字符:整
*/
private static final String CN_FULL = "整";
/**
* 特殊字符:负
*/
private static final String CN_NEGATIVE = "负";
/**
* 金额的精度,默认值为2
*/
private static final int MONEY_PRECISION = 2;
/**
* 特殊字符:零元整
*/
private static final String CN_ZEOR_FULL = "零元" + CN_FULL;
/**
* 把输入的金额转换为汉语中人民币的大写
*
* @param numberOfMoney
* 输入的金额
* @return 对应的汉语大写
*/
public static String number2CNMontrayUnit(BigDecimal numberOfMoney) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
// -1, 0, or 1 as the value of this BigDecimal is negative, zero, or
// positive.
int signum = numberOfMoney.signum();
if (signum == 0) {
return CN_ZEOR_FULL;
}
long number = numberOfMoney.movePointRight(MONEY_PRECISION)
.setScale(0, 4).abs().longValue();
long scale = number % 100;
int numUnit = 0;
int numIndex = 0;
boolean getZero = false;
if (!(scale > 0)) {
numIndex = 2;
number = number / 100;
getZero = true;
}
if ((scale > 0) && (!(scale % 10 > 0))) {
numIndex = 1;
number = number / 10;
getZero = true;
}
int zeroSize = 0;
while (true) {
if (number <= 0) {
break;
}
numUnit = (int) (number % 10);
if (numUnit > 0) {
if ((numIndex == 9) && (zeroSize >= 3)) {
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_MONETRAY_UNIT[6]);
}
if ((numIndex == 13) && (zeroSize >= 3)) {
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_MONETRAY_UNIT[10]);
}
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_MONETRAY_UNIT[numIndex]);
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_NUMBER[numUnit]);
getZero = false;
zeroSize = 0;
} else {
++zeroSize;
if (!(getZero)) {
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_NUMBER[numUnit]);
}
if (numIndex == 2) {
if (number > 0) {
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_MONETRAY_UNIT[numIndex]);
}
} else if (((numIndex - 2) % 4 == 0) && (number % 1000 > 0)) {
sb.insert(0, CN_UPPER_MONETRAY_UNIT[numIndex]);
}
getZero = true;
}
// 让number每次都去掉最后一个数
number = number / 10;
++numIndex;
}
if (signum == -1) {
sb.insert(0, CN_NEGATIVE);
}
if (!(scale > 0)) {
sb.append(CN_FULL);
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
double money;
Scanner scanner= new Scanner(System.in);//扫描控制台输入
money=scanner.nextDouble();
BigDecimal numberOfMoney = new BigDecimal(money);
String s = number2CNMontrayUnit(numberOfMoney);
System.out.println("你输入的金额为:"+ money +" 大写金额为 " +s.toString());
}
}
4 前面几讲介绍过JDK所提供的BigInteger能完成大数计算,如果不用它,直接使用数组表达大数,你能实现相同的功能吗?
要求:
(1)用你的大数类实现加和减两个功能
(2)阅读BigInteger类源码,弄清楚它是使用什么算法实现加减乘除四种运算的?
(3)通过互联网查找大数运算的相关资料,给你的大数类添加乘、除、求阶乘等其它功能。
程序源代码:
import java.io.*;
public class BigNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BigNumber a;
System.out.println("输入一个正整数:");
a = inputInteger();
System.out.println("输入另一个正整数:");
int b[] = inputArray();
System.out.println("两个数的和是:");
display(a.add(b));
}
public static int[] inputArray()throws IOException{
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(reader);
String number = input.readLine();
char temp[] = number.toCharArray();
int array[] = new int[temp.length];
for(int i=0; i<temp.length; i++){
if(temp[i] < ‘0‘ || temp[i] > ‘9‘){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(1);
}
array[i] = temp[i]-‘0‘;
}
return array;
}
public static BigNumber inputInteger()throws IOException{
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(reader);
String number = input.readLine();
char temp[] = number.toCharArray();
int array[] = new int[temp.length];
for(int i=0; i<temp.length; i++){
if(temp[i] < ‘0‘ || temp[i] > ‘9‘){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(1);
}
array[i] = temp[i]-‘0‘;
}
BigNumber a = new BigNumber(array);
return a;
}
public static void display(int[] a){
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
System.out.print(a[i]);
System.out.println();
}
public BigNumber(){}
public BigNumber(int[] array){
for(int i=0;i < array.length && i < this.array.length;i++){
this.array[i] = array[i];
len++;
}
}
public void display(){
for(int i = 0; i < len;i++){
System.out.print(array[i]);
}
}
public void setIneger(int[] array){
len=0;
for(int i=0; i < this.array.length && i < array.length; i++){
this.array[i] = array[i];
len++;
}
}
public int[] getInteger(){return this.array;}
public int getLength(){return this.len;}
public int[] add(int[] addend){
int firstlen = len;
int secondlen = (int) addend.length;
int gap = Math.abs(firstlen-secondlen);
int thirdlen = firstlen > secondlen? firstlen:secondlen;
int result[] = new int[thirdlen+1];
int temp=0;
for(int i = thirdlen-1; i >=gap;i--){
if(firstlen < secondlen){
result[i+1] = (array[i-gap]+addend[i])%10 +temp;
temp = (array[i-gap]+addend[i])/10;
}else{
result[i+1] = (array[i]+addend[i-gap])%10 +temp;
temp = (array[i]+addend[i-gap])/10;
}
}
int j = 1;
do{
if(firstlen < secondlen){
result[j] = addend[j-1];
}else if(firstlen > secondlen){
result[j] = array[j-1];
}j++;
}while(j < gap);
if(temp != 0){
result[0] = temp;
}else{
int s[] = new int[thirdlen];
for(int i=0; i < thirdlen; i++)
s[i] = result[i+1];
return s;
}
return result;
}
private int array[] = new int[20];
private int len = 0;
}
5 随机生成10个数,填充一个数组,然后用消息框显示数组内容,接着计算数组元素的和,将结果也显示在消息框中。
要求将设计思路、程序流程图、源程序代码、结果截图、编程总结等发表到博客园,并备份到课堂派
程序设计思想:
建立数组对每一个数赋值随机数,并相加输出结果即可。
程序流程图:
程序源代码:
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class RandomNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a[]= new int [10];
int sum=0;
int i=0;
String output=new String();
Random r=new Random();
for(int x:a){
x=r.nextInt();
sum+=x;
output+=i+1+"\t "+x +"\n";
i++;
}
output+="The results is ";
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(
null,output + sum , "Results",
JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE );
}
}
截图:
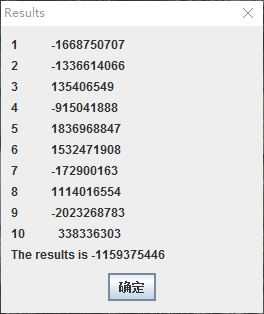
编程总结:for语句的特殊使用方法。消息框的使用,等等。
标签:rgs 大数 范围 表达 random 相同 循环 博客 读取
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/anjiu/p/6036269.html