标签:complete one oppo 技术 example rod 分享 math href
These are two vectors:
They can be multiplied using the "Cross Product"
(also see Dot Product)
The Cross Product a × b of two vectors is another vector that is at right angles to both:
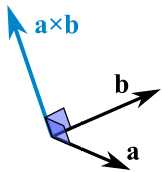
And it all happens in 3 dimensions!
a × b = |a| |b| sin(θ) n
So the length is: the length of a times the length of b times the sine of the angle between a and b,
Then we multiply by the vector n to make sure it heads in the right direction (at right angles to both a and b).
When a and b start at the origin point (0,0,0), the Cross Product will end at:
Answer: a × b = (?3,6,?3)
The cross product could point in the completely opposite direction and still be at right angles to the two other vectors, so we have the:
"Right Hand Rule"
With your right-hand, point your index finger along vector a, and point your middle finger along vector b: the cross product goes in the direction of your thumb.
The Cross Product gives a vector answer, and is sometimes called the vector product.
But there is also the Dot Product which gives a scalar (ordinary number) answer, and is sometimes called the scalar product.
Question: What do you get when you cross an elephant with a banana?
Answer: |elephant| |banana| sin(θ) n
标签:complete one oppo 技术 example rod 分享 math href
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/McKean/p/6087672.html