标签:uniq 构建 nbsp 过拟合 char 文本 reg 问题 detection
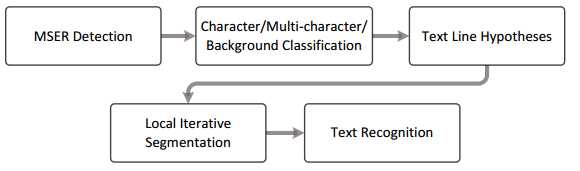
Fig. 2. Overview of the method. Initial text hypotheses efficiently generated
by a MSER detector are further refined using a local text model, unique to
each text line
一、 候选字符提取
1. MSER提取,二值化
2. 算出Distance Map
3. 求出所有SSP(以每个像素为中心的3*3窗口内,若中心点是最大值,则表示是SSP点)
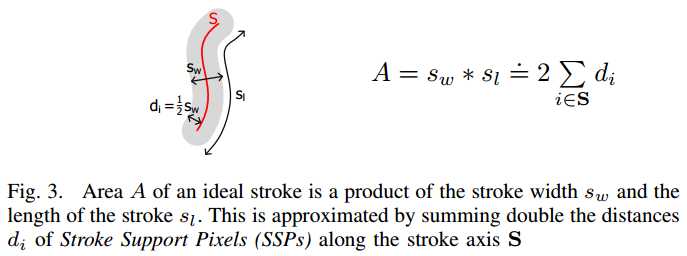
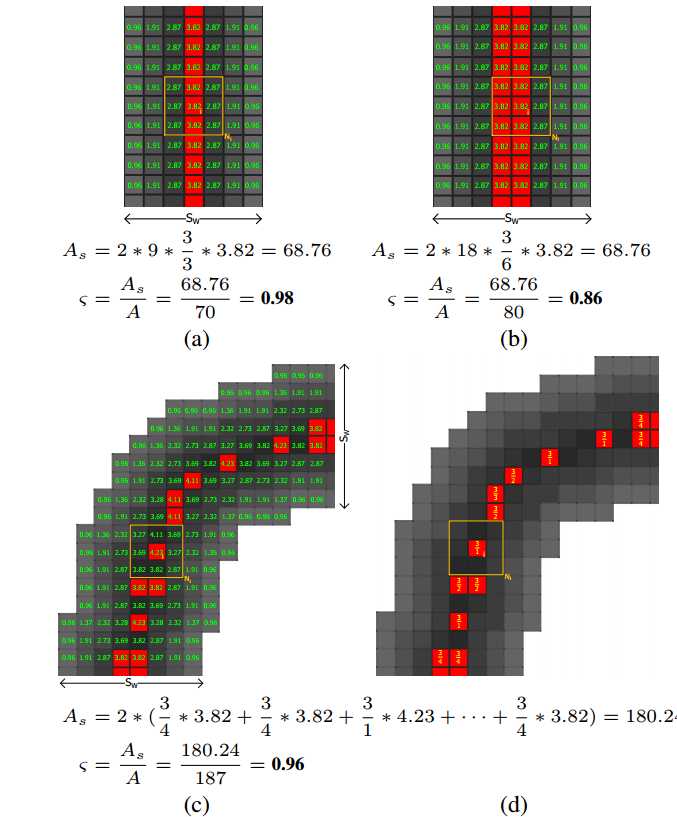

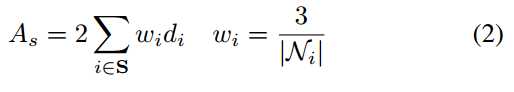
4. 对每个连通分量,计算5维特征

5. 用4中学到的5维特征训练SVM分类器(三类,单字符,多字符,背景)
二、 文本线形成
1. 每三个字符拟合一条直线(三个,拟合误差小)
2. 所有直线进行聚类
3. 对每类的文本线投票选出最终的文本线
三、 字符调整
1. 算法目标:补全每个文本框里的字符
2. 算法初始值:Pf为MSER像素值,B为其他像素值,DF为空
3. 算法步骤:
(1) 边界扩展:计算PF的外接矩形,并进行边界扩展(水平取字符平均宽度,高度取高度的1/3)
(2) 更新DF:计算PF点中的SSP点,加入到DF中
(3) 训练GMM:使用DF点作为前景,B点作为背景,学习GMM的参数
(4) 构建图模型:加入源点(source)和汇点(sink),边权重如下:
1) 第一类:源点与DF、PF相连,汇点与B相连。这些边的权重即为公式中的U,由算法步骤(3)中的GMM模型给出;
2) 第二类:相邻像素点相连。边权重即为公式中的V,通过计算像素点在RGB空间的欧式距离得到;
(5) 求最小割模型:利用GrabCut算法求最小割,割分成的两个集合一个为PF,一个为B。
(6) 重新迭代(1)~(5),直到收敛(PF和B不再变化)
4. 算法输出:一个稳定的PF集合(属于字符的像素点)和B集合(属于背景的像素点)。
5. 算法的后处理:
(1) 计算PF的连通分量,得到候选图;
(2) 如果PF或B为空,则表示只有前景或背景点,说明是噪声块
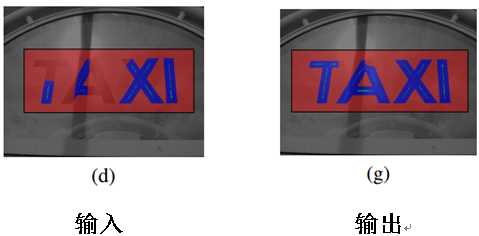
6. 算法的示例图如下:




Fig. 1. The method pipeline. Source image (a). Initial MSER detection and classification (b) - character MSERs denoted green, multi-character MSERs blue and background MSERs denoted red. Text lines formation (c) - bottom line estimate in red. Local text refinement for the first text line - initialization (d), first iteration (e), second iteration (f), the last iteration (g), definitive foreground pixels in green, probable foreground pixels in blue, background pixels in red, ignored pixels in yellow. Final segmentation and text recognition (h)
标签:uniq 构建 nbsp 过拟合 char 文本 reg 问题 detection
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lillylin/p/6103242.html