标签:port enable linear products span char float oval horizon
变通实现微服务的per request以提高IO效率中提到的同一请求过程中对于同一个方法的多次读取只实际调用一次,其余的读取均从第一次读取的结果缓存中获取,以提高读取的效率。实现方案是引入了Context对象,可以理解成上下文的一个环境变量,业务方法在获取数据时先从Context中取,如果取不到从数据库中加载并将结果写入Context中,而Context是通过ThreadLocal来存储。但实现有点复杂需要寻找优化方案。
private ThreadLocal<CiaUserInfo> ciaUserInfoThreadLocal=new ThreadLocal<>();
public CiaUserInfo getTokenInfo(String token) throws Exception {
CiaUserInfo result = this.productContext.getCiaUserInfoFromCache(token);
if(null!=result){
return result;
}
else {
result=new CiaUserInfo();
}
//...get user from db
this.productContext.setCiaUserInfoToCache(result);
return result;
}
创建Context的目的无非就是将数据存储在ThreadLocal中充当请求级别的缓存,如果缓存是基于Spring Cache,那么上面的缺点就会不攻自破。
我找了下并没有找到基于ThreadLocal实现的缓存,大家如果有找到的可以发给我。
由于我们只关心存储(过期策略本文暂时还是延用上一篇的利用注解拦截形式去手工释放),所以实现难度并不大,因为我们完全可以参考Spring Cache的默认提供的内存级别的缓存ConcurrentMapCacheManager,整体效果如下图所示。
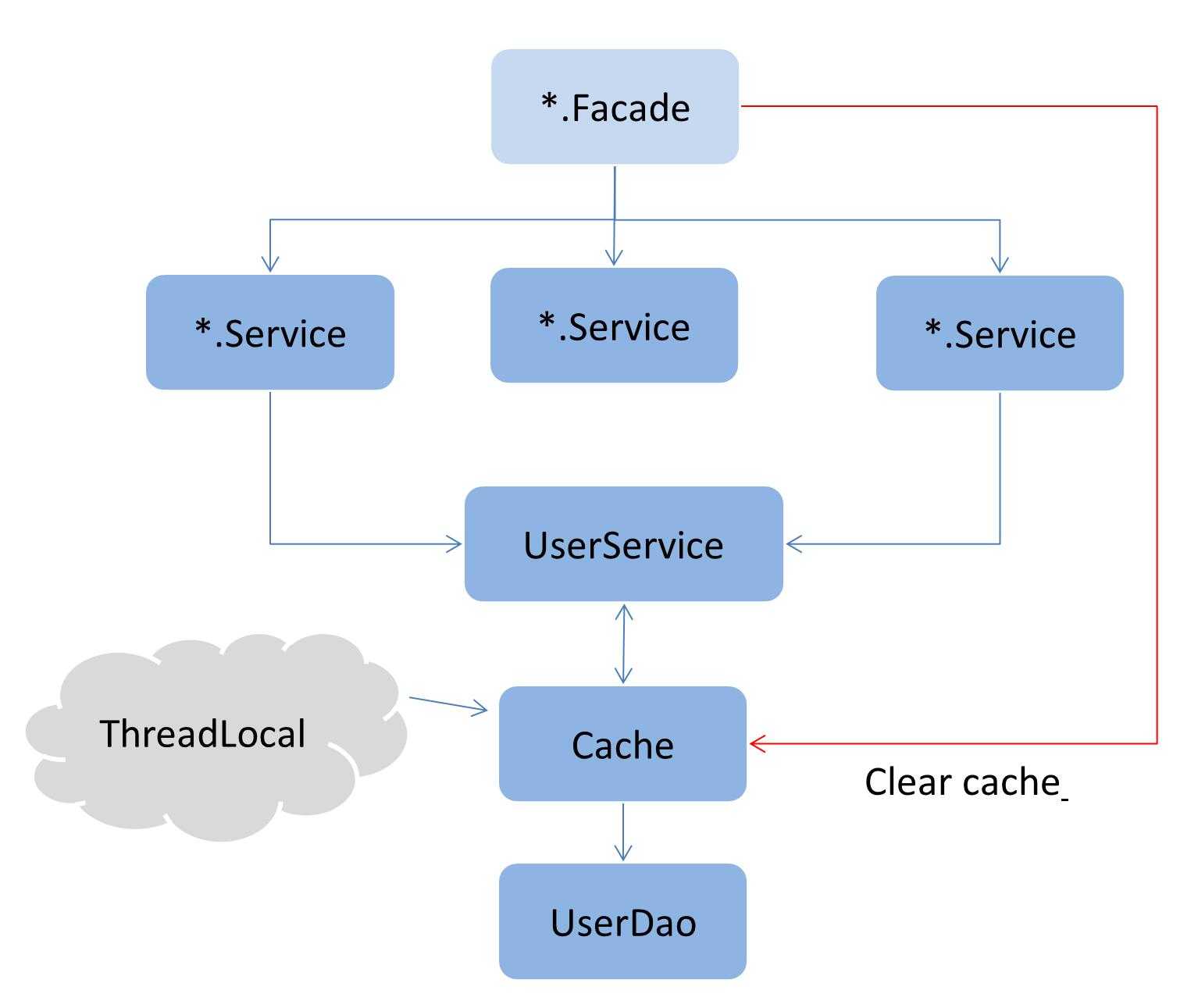
只需要实现CacheManager这个接口即可,所有的缓存都放在一个Map中管理。
这个方法中展现了并发情况下的操作,面试时这种题经常会被问到,看看Spring Cache的实现还是很有帮助的。
public class ThreadLocalCacheManager implements CacheManager {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Cache>(16);
public ThreadLocalCacheManager(){
}
public ThreadLocalCacheManager(String... cacheNames) {
setCacheNames(Arrays.asList(cacheNames));
}
protected Cache createConcurrentMapCache(String name) {
return new ThreadLocalCache(name);
}
public void setCacheNames(Collection<String> cacheNames) {
if (cacheNames != null) {
for (String name : cacheNames) {
this.cacheMap.put(name, createConcurrentMapCache(name));
}
}
}
@Override
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
@Override
public Collection<String> getCacheNames() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(this.cacheMap.keySet());
}
}
这个类是真正的缓存实现,继承AbstractValueAdaptingCache这个抽象类即可。相比内存缓存实现主要的区别就是存储的介质由ConcurrentMap变更为ThreadLocal,目的是每个线程单独一份缓存。
public class ThreadLocalCache extends AbstractValueAdaptingCache {
private final String name;
private final ThreadLocal<ConcurrentMap> storeThreaLocal=new ThreadLocal<>();
private void init(){
if(null==this.storeThreaLocal.get()){
this.storeThreaLocal.set(new ConcurrentHashMap());
}
}
public ThreadLocalCache(String name){
this(name,true);
}
protected ThreadLocalCache(String name,boolean allowNullValues) {
super(allowNullValues);
this.name=name;
this.init();
}
@Override
protected Object lookup(Object key) {
return this.storeThreaLocal.get().get(key);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public Object getNativeCache() {
return this.storeThreaLocal.get();
}
@Override
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
this.storeThreaLocal.get().put(key,value);
}
@Override
public ValueWrapper putIfAbsent(Object key, Object value) {
Object existing = this.storeThreaLocal.get().putIfAbsent(key, toStoreValue(value));
return toValueWrapper(existing);
}
@Override
public void evict(Object key) {
this.storeThreaLocal.get().remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
this.storeThreaLocal.get().clear();
}
}
配置非常简单,启动缓存注解,指定缓存容器。
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager"/>
<bean id="cacheManager" class="core.cache.ThreadLocalCacheManager">
</bean>
增加@Cacheable注解,指定缓存名称以及缓存容器名称即可。相比Context方案就解决了缓存代码侵入性的问题,而且可以利用SpringCache的众多优点,比如缓存条件,缓存KEY的生成规则等等。
@Cacheable(value = "CiaService.getCiaUserInfo",cacheManager = "cacheManager")
@Override
public CiaUserInfo getCiaUserInfo(String token) {
//...
}
由于有线程池的存在,所以如果不手动清除存储于ThreadLocal中的缓存数据,那么会影响我们最初的需求:请求级缓存。暂时还是通过特殊的注解来完成。通过cacheManager获取所有的缓存,然后依次执行释放操作。
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
@After("pointCut()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws ProductServiceException {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method targetMethod = methodSignature.getMethod();
LocalCacheContext localCacheContext= targetMethod.getAnnotation(LocalCacheContext.class);
if(null!=localCacheContext){
Collection<String> cacheNames= this.cacheManager.getCacheNames();
if(null!=cacheNames) {
for(String cacheName :cacheNames) {
this.cacheManager.getCache(cacheName).clear();
}
}
}
}

上面的缓存释放是通过注解来完成的,这个注解只能加在入口函数上,是有一定限制的,如果加错了缓存就有可能在请求的中途被错误的清除。像Web容器就有非常多的方案,比如HandleInterceptor是请求级别的,可以非常方便的在请求前请求后增加一些自定义的功能。由于我这边的微服务是dubbo实现,所以可以在dubbo提供的方案中找一找,也许会有收获。
标签:port enable linear products span char float oval horizon
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ASPNET2008/p/6107034.html