标签:any ams path amber orm href ref over term
原文:http://www.smartjava.org/content/render-geographic-information-3d-threejs-and-d3js
The last couple of days I‘ve been playing around with three.js and geo information. I wanted to be able to render map/geo data (e.g. in geojson format) inside the three.js scene. That way I have another dimension I could use to show a specific metric instead of just using the color in a 2D map. In this article I‘ll show you how you can do this. The example we‘ll create shows a 3D map of the Netherlands, rendered in Three.js, that uses a color to indicate the population density per municipality and the height of each municipality represents the actual number of residents.
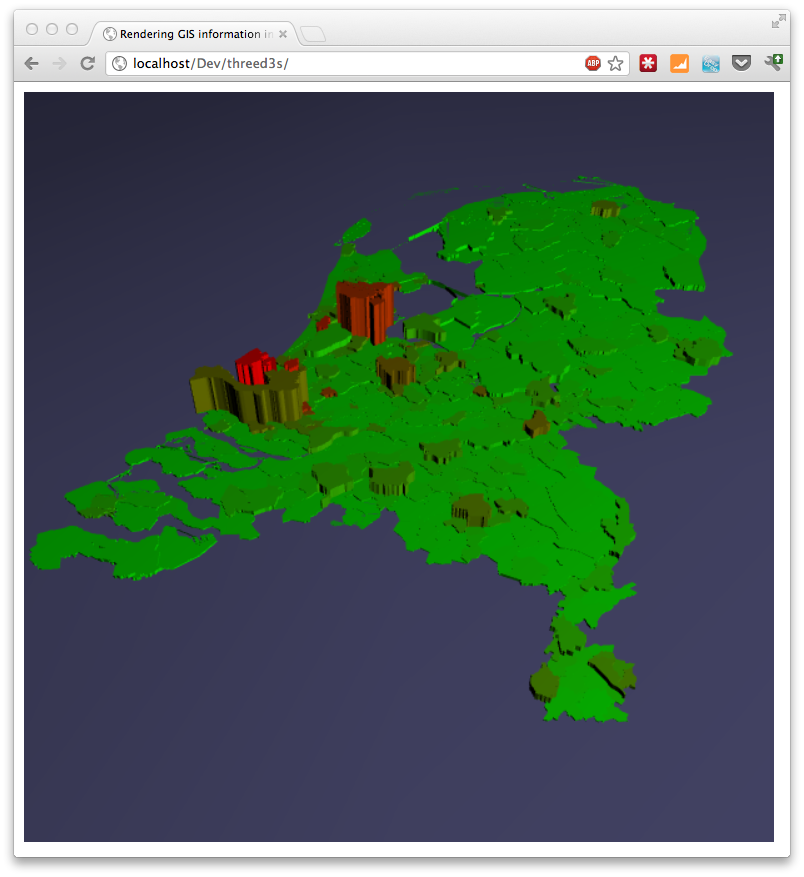
Or if you can look at aworking example.
This information is based on open data available from the Dutch government. If you look at the source from the example, you can see the json we use for this. For more information on geojson and how to parse it see the other articles I did on this subject:
To get this working we‘ll take the following steps:
Just a reminder to see everything working, just look at theexample.
D3.js has support to load json and directly transform it to an SVG path. Though this is a convenient way, I only needed the path data, not the complete SVG elements. So to load json I just used jquery‘s json support.
// get the data
jQuery.getJSON(‘data/cities.json‘, function(data, textStatus, jqXHR) {
..
});
This will load the data and pass it in the data object to the supplied function.
Before we do anything with the data lets first setup a basic Three.js scene.
// Set up the three.js scene. This is the most basic setup without
// any special stuff
function initScene() {
// set the scene size
var WIDTH = 600, HEIGHT = 600;
// set some camera attributes
var VIEW_ANGLE = 45, ASPECT = WIDTH / HEIGHT, NEAR = 0.1, FAR = 10000;
// create a WebGL renderer, camera, and a scene
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({antialias:true});
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(VIEW_ANGLE, ASPECT,
NEAR, FAR);
scene = new THREE.Scene();
// add and position the camera at a fixed position
scene.add(camera);
camera.position.z = 550;
camera.position.x = 0;
camera.position.y = 550;
camera.lookAt( scene.position );
// start the renderer, and black background
renderer.setSize(WIDTH, HEIGHT);
renderer.setClearColor(0x000);
// add the render target to the page
$("#chart").append(renderer.domElement);
// add a light at a specific position
var pointLight = new THREE.PointLight(0xFFFFFF);
scene.add(pointLight);
pointLight.position.x = 800;
pointLight.position.y = 800;
pointLight.position.z = 800;
// add a base plane on which we‘ll render our map
var planeGeo = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10000, 10000, 10, 10);
var planeMat = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color: 0x666699});
var plane = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeo, planeMat);
// rotate it to correct position
plane.rotation.x = -Math.PI/2;
scene.add(plane);
}
Nothing to special, the comments inline should nicely explain what we‘re doing here. Next it gets more interesting.
What we need to do next is convert our geojson input format to a THREE.Path that we can use in our scene. Three.js itself doesn‘t support geojson or SVG for that matter. Luckily though someone already started work on integrating d3.js with three.js. This project is called "d3-threeD" (sources can be found on github here ). With this extension you can automagically render SVG elements in 3D directly from D3.js. Cool stuff, but it didn‘t allow me any control over how the elements were rendered. It does however contain a function we can use for our scenario. If you look through the source code of this project you‘ll find a method called "transformSVGPath". This method converts an SVG path string to a Three.Shape element. Unfortunately this method isn‘t exposed, but that‘s quickly solved by adding this to the d3-threeD.js file:
// at the top
var transformSVGPathExposed;
...
// within the d3threeD(exports) function
transformSVGPathExposed = transformSVGPath;
</javscript>
This way we can call this method separately. Now that we have a way to transform an SVG path to a Three.js shape, we only need to convert the geojson to an SVG string and pass it to this function. We can use the geo functionaly from D3.js for this:
<javascript>
geons.geoConfig = function() {
this.TRANSLATE_0 = appConstants.TRANSLATE_0;
this.TRANSLATE_1 = appConstants.TRANSLATE_1;
this.SCALE = appConstants.SCALE;
this.mercator = d3.geo.mercator();
this.path = d3.geo.path().projection(this.mercator);
this.setupGeo = function() {
var translate = this.mercator.translate();
translate[0] = this.TRANSLATE_0;
translate[1] = this.TRANSLATE_1;
this.mercator.translate(translate);
this.mercator.scale(this.SCALE);
}
}
The path variable from the previous piece of code can now be used like this:
var feature = geo.path(geoFeature);
To convert a geojson element to an SVG path. So how does this look combined?
// add the loaded gis object (in geojson format) to the map
function addGeoObject() {
// keep track of rendered objects
var meshes = [];
...
// convert to mesh and calculate values
for (var i = 0 ; i < data.features.length ; i++) {
var geoFeature = data.features[i]
var feature = geo.path(geoFeature);
// we only need to convert it to a three.js path
var mesh = transformSVGPathExposed(feature);
// add to array
meshes.push(mesh);
...
}
As you can see we iterate over the data.features list (this contains all the geojson representations of the municipalities). Each municipality is converted to an svg string, and each svg string is converted to a mesh. This mesh is a Three.js object that we can render on the scene.
Now we just need to set the height and the color of the Three.js shape and add it to the scene. The extended addGeoObject method now looks like this:
// add the loaded gis object (in geojson format) to the map
function addGeoObject() {
// keep track of rendered objects
var meshes = [];
var averageValues = [];
var totalValues = [];
// keep track of min and max, used to color the objects
var maxValueAverage = 0;
var minValueAverage = -1;
// keep track of max and min of total value
var maxValueTotal = 0;
var minValueTotal = -1;
// convert to mesh and calculate values
for (var i = 0 ; i < data.features.length ; i++) {
var geoFeature = data.features[i]
var feature = geo.path(geoFeature);
// we only need to convert it to a three.js path
var mesh = transformSVGPathExposed(feature);
// add to array
meshes.push(mesh);
// we get a property from the json object and use it
// to determine the color later on
var value = parseInt(geoFeature.properties.bev_dichth);
if (value > maxValueAverage) maxValueAverage = value;
if (value < minValueAverage || minValueAverage == -1) minValueAverage = value;
averageValues.push(value);
// and we get the max values to determine height later on.
value = parseInt(geoFeature.properties.aant_inw);
if (value > maxValueTotal) maxValueTotal = value;
if (value < minValueTotal || minValueTotal == -1) minValueTotal = value;
totalValues.push(value);
}
// we‘ve got our paths now extrude them to a height and add a color
for (var i = 0 ; i < averageValues.length ; i++) {
// create material color based on average
var scale = ((averageValues[i] - minValueAverage) / (maxValueAverage - minValueAverage)) * 255;
var mathColor = gradient(Math.round(scale),255);
var material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: mathColor
});
// create extrude based on total
var extrude = ((totalValues[i] - minValueTotal) / (maxValueTotal - minValueTotal)) * 100;
var shape3d = meshes[i].extrude({amount: Math.round(extrude), bevelEnabled: false});
// create a mesh based on material and extruded shape
var toAdd = new THREE.Mesh(shape3d, material);
// rotate and position the elements nicely in the center
toAdd.rotation.x = Math.PI/2;
toAdd.translateX(-490);
toAdd.translateZ(50);
toAdd.translateY(extrude/2);
// add to scene
scene.add(toAdd);
}
}
// simple gradient function
function gradient(length, maxLength) {
var i = (length * 255 / maxLength);
var r = i;
var g = 255-(i);
var b = 0;
var rgb = b | (g << 8) | (r << 16);
return rgb;
}
A big piece of code, but not that complex. What we do here is we keep track of two values for each municipality: the population density and the total population. These values are used to respectively calculate the color (using the gradient function) and the height. The height is used in the Three.js extrude function which converts our 2D Three.Js path to a 3D shape. The color is used to define a material. This shape and material is used to create the Mesh that we add to the scene.
All that is left is to render everything. For this example we‘re not interested in animations or anything so we can make a single call to the renderer:
renderer.render( scene, camera );
And the result is as you saw in the beginning. The following image shows a different example. This time we once again show the population density, but now the height represents the land area of the municipality.

I‘m currently creating a new set of geojson data, but this time for the whole of Europe. So in the next couple of weeks expect some articles using maps of Europe.
标签:any ams path amber orm href ref over term
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shenwenkai/p/6113080.html