标签:fast fail poi iss head games 理解 0.00 anti
The Parallel Challenge Ballgame
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 547 Accepted Submission(s): 26
Problem Description
Before the ACM/ICPC world final 2005, there is a competition called “The Parallel Challenge Ballgame”. The Parallel Challenge ballgame gives each team a chance to pit their programming skills against those of other teams in a fast-moving parallel-programming game of skill, treachery, and hazard avoidance. Each team will write a single C++ class named MyPlayer which defines the characteristics of a “player”. The MyPlayer class will be instantiated five times in the environment, making up a five-player team, which will then compete in a series of Parallel Challenge ballgames running on an IBM Power Architecture Blue Gene supercomputer – the world’s fastest computer.
A Parallel Challenge ballgame is played on a rectangular filed. The filed is surrounded by a wall; balls will bounce off the walls if they run into it. The rule of bouncing is the same as light (In figure 1,angle 1 equals angle 2). Near the edges of the fields are a number of goals where points can be scored. Goals are rectangular areas lying near the edges of the field but within the field boundaries. When the game starts there are a number of balls placed at random locations on the field. A player can move to a ball, pick it up, and throw (of course, it is not football, why not use hand?) it. At the start of each game there are also a number of “nets” distributed at various locations on the edges of the field. A player can move to and pick up one of these nets, and can then use them to “trap” players on other teams by throwing the net on top of them. Once a player is trapped beneath a net, that player cannot do anything more in the game until a teammate comes and lifts the net from the trapped player. A player may “tackle” another player, normally in an attempt to dislodge a ball being carried by the other player (although it is also legal to tackle a player who is not carrying a ball).
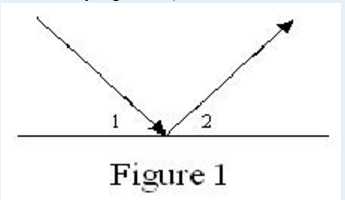
The objective of each team is to write their MyPlayer class so that their players (the five instances of the class) operate in a coordinated fashion, taking advantage of the various ways to score points while at the same time avoiding both hazards on the game filed and impediments thrown at them by players from other teams. The winner of a game is the team whose players score the largest total number of points.
There are many ways to score points:
(1) Successful Tackle (tackle not caught by Referees)
(2) Opponent’s Failed Tackle
(3) Throwing a net on one or more opponents
(4) Lifting a net off a teammate
And of course, the normal approach: (5) Carry or throw the balls into goals. This is also the easiest way to score points. In order to get more chance to make a ball into the goal, it is better to throw a ball to a goal once you get it. The ball may be blocked by other player, but the probability is low, because a thrown ball moves at the maximum speed allowed in the game, and the player can not catch up with it. So the only way it is blocked is that some player is just on the direction, which the ball moves. And because the ball will bounce off the wall when it hits the wall, it is not necessary to throw a ball straight to a goal (see figure 2). But the more times the ball bounces off the wall, the higher probability that other player will head off it. So we only consider the ball bounces off the wall no more than once.
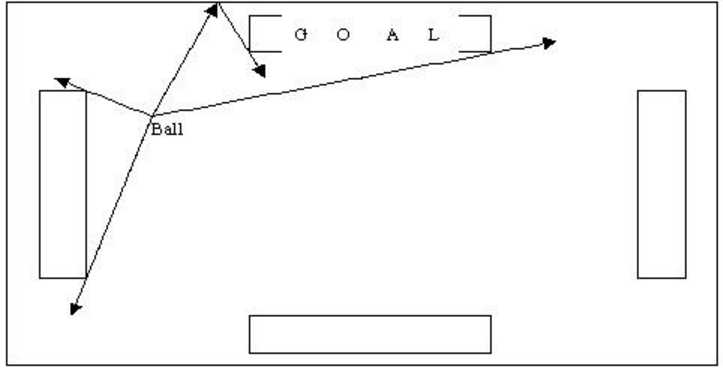
Here is our problem. Given the range of the field, the position of the ball and the goals, the size of the goals, your task is to calculate how many percents of the direction that the team can score points through method (5).
Input
In the first line of input, there is an integer t, which is the number of test cases and followed by the data for the test cases. The first line of each test case contains four integers: x1, y1, x2, y2, and (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) (-1000 <= x1, y1, x2, y2 <= 1000) are the coordinates of the diagonally points of the field. In the next line, there are two integers x and y, and (x, y) is the coordinate of the ball. The third line of each test case contains an integer n (0 <= n <= 100), which is the number of the goals. In next n lines, each line contains four integers: xi1, yi1, xi2, yi2, and (xi1, yi1) and (xi2, yi2) are the coordinates of the diagonally points of the i-th goal. You may assume the goals and the ball are inside the field. And if a ball move into or on the boundaries of a goal, the team scores points.
Output
The output contains one line per test case containing a number, which is described above and followed a “%”. The number should be rounded up to two decimal digits. See the Sample Output to know the exact format.
Sample Input
1
100 100 -100 -100
0 0
1
10 10 -10 20
Sample Output
28.34%
当这道代表了我与ACM在四年里多次分分合合的题目终于被AC时,我的心情是激动而茫然的。
题意:一个长方形球场,其中有一些长方形区域,和一个球。把球从初始位置沿直线打出,在与球场边缘碰撞最多一次后若能经过某个长方形区域则可以得分。求可以得分的发射角度占总的角度2π的百分比,触壁反弹的规则同光反射。
首先,把每个小长方形根据球场4条边做轴对称,得到一共5个小长方形。这样操作后,完全可以假定不允许反弹。
然后对每个小长方形,算出可以打中的角度:
如果球就在小长方形里,可以不用计算,直接输出100%。
其他情况球和小长方形有8中位置关系和相应的角度范围:
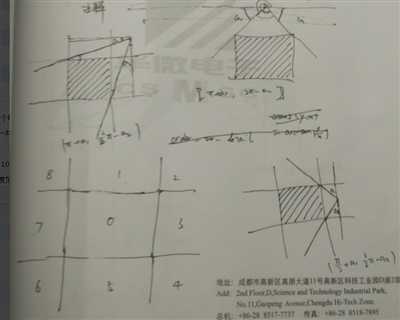
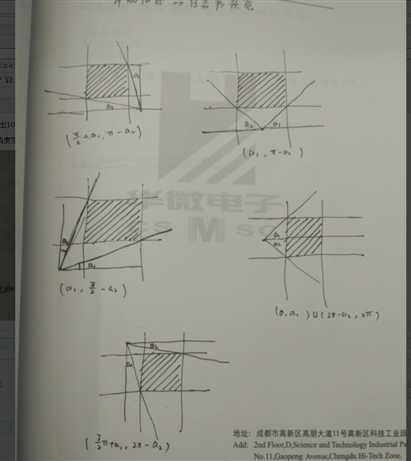
将5n个小长方形的角度全部算出来之后,求出它们的并的大小即可。
其实这道题真的不难,配不上这样的通过率。
理解题意点有困难。
然后主要就是精度问题吧。三角函数是肯定要用的,但是一定要少用,推荐这个atan2。对double类型进行任何逻辑判断都要用eps=1e-8来代替0。
真的不难,被这样一个纸老虎虐了,惭愧。

#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define eps (1e-8)
#define pi 3.1415926536
struct rectangle {
double x1, x2, y1, y2;
} b, g[800];
double x, y, l[1005], r[1005];
void adjust(rectangle & r) {
double t;
if (r.x1 - r.x2 > eps) {
t = r.x1;
r.x1 = r.x2;
r.x2 = t;
}
if (r.y1 - r.y2 > eps) {
t = r.y1;
r.y1 = r.y2;
r.y2 = t;
}
}
int pos(rectangle a) {
if ((a.x1 - x <= eps) && (x - a.x2 <= eps) && (a.y1 - y <= eps) && (y - a.y2 <= eps)) {
return 0;
}
if (x - a.x1 < eps) {
if (y > a.y2) {
return 8;
} else if (y - a.y1 < eps) {
return 6;
} else {
return 7;
}
} else if (x - a.x2 > eps) {
if (y > a.y2) {
return 2;
} else if (y - a.y1 < eps) {
return 4;
} else {
return 3;
}
} else {
if (y - a.y2 > eps) {
return 1;
} else {
return 5;
}
}
}
int main() {
int T, n;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &b.x1, &b.y1, &b.x2, &b.y2);
adjust(b);
scanf("%lf%lf%d", &x, &y, &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &g[i].x1, &g[i].y1, &g[i].x2, &g[i].y2);
adjust(g[i]);
g[i + n].x1 = g[i].x1;
g[i + n].y1 = 2 * b.y1 - g[i].y1;
g[i + n].x2 = g[i].x2;
g[i + n].y2 = 2 * b.y1 - g[i].y2;
adjust(g[i + n]);
g[i + 2 * n].x1 = g[i].x1;
g[i + 2 * n].y1 = 2 * b.y2 - g[i].y1;
g[i + 2 * n].x2 = g[i].x2;
g[i + 2 * n].y2 = 2 * b.y2 - g[i].y2;
adjust(g[i + 2 * n]);
g[i + 3 * n].x1 = 2 * b.x1 - g[i].x1;
g[i + 3 * n].y1 = g[i].y1;
g[i + 3 * n].x2 = 2 * b.x1 - g[i].x2;
g[i + 3 * n].y2 = g[i].y2;
adjust(g[i + 3 * n]);
g[i + 4 * n].x1 = 2 * b.x2 - g[i].x1;
g[i + 4 * n].y1 = g[i].y1;
g[i + 4 * n].x2 = 2 * b.x2 - g[i].x2;
g[i + 4 * n].y2 = g[i].y2;
adjust(g[i + 4 * n]);
}
n *= 5;
int m = 0;
bool flag = false;
double a1, a2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int tmp = pos(g[i]);
if (tmp == 0) {
flag = true;
break;
} else if (tmp == 1) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(y - g[i].y2, x - g[i].x1);
a2 = atan2(y - g[i].y2, g[i].x2 - x);
l[m] = pi + a1;
r[m] = 2 * pi - a2;
} else if (tmp == 2) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(y - g[i].y2, x - g[i].x1);
a2 = atan2(x - g[i].x2, y - g[i].y1);
l[m] = pi + a1;
r[m] = 1.5 * pi - a2;
} else if (tmp == 3) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(x - g[i].x2, g[i].y2 - y);
a2 = atan2(x - g[i].x2, y - g[i].y1);
l[m] = 0.5 * pi + a1;
r[m] = 1.5 * pi - a2;
} else if (tmp == 4) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(x - g[i].x2, g[i].y2 - y);
a2 = atan2(g[i].y1 - y, x - g[i].x1);
l[m] = 0.5 * pi + a1;
r[m] = pi - a2;
} else if (tmp == 5) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(g[i].y1 - y, g[i].x2 - x);
a2 = atan2(g[i].y1 - y, x - g[i].x1);
l[m] = a1;
r[m] = pi - a2;
} else if (tmp == 6) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(g[i].y1 - y, g[i].x2 - x);
a2 = atan2(g[i].x1 - x, g[i].y2 - y);
l[m] = a1;
r[m] = 0.5 * pi - a2;
} else if (tmp == 7) {
m++;
a1 = atan2(g[i].y2 - y, g[i].x1 - x);
l[m] = 0;
r[m] = a1;
m++;
a2 = atan2(y - g[i].y1, g[i].x1 - x);
l[m] = 2 * pi - a2;
r[m] = 2 * pi;
} else {
m++;
a1 = atan2(g[i].x1 - x, y - g[i].y1);
a2 = atan2(y - g[i].y2, g[i].x2 - x);
l[m] = 1.5 * pi + a1;
r[m] = 2 * pi - a2;
}
}
if (flag) {
printf("100.00%%\n");
} else {
double tot = 0, t, ll, rr;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (l[i] - l[j] > eps) {
t = l[i];
l[i] = l[j];
l[j] = t;
t = r[i];
r[i] = r[j];
r[j] = t;
}
}
}
ll = l[1];
rr = r[1];
m++;
l[m] = 361;
r[m] = 461;
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
if (l[i] - rr <= eps) {
if (rr - r[i] < eps) {
rr = r[i];
}
} else {
tot += (rr - ll);
ll = l[i];
rr = r[i];
}
}
printf("%.2lf%%\n", tot * 50 / pi);
}
}
return 0;
}
The Parallel Challenge Ballgame[HDU1101]
标签:fast fail poi iss head games 理解 0.00 anti
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dramstadt/p/6122527.html