标签:code ref 返回 集合 src bool array eth enum
Aggregate我用的最多的地方就是拼接字符串,打个比方来说,如果有数组,想要的结果是在他们之间插入一个","然后返回拼接以后的新字符串。
常规的做法是:
List<int> intList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", intList));
得到的结果是:
1,2,3,4,5
但是如果碰到想要的结果是‘1‘,‘2‘,‘3‘,‘4‘,‘5‘这样的字符串后,在用join这个方法就不好搞了。然而用for或者foreach一样可以很简单的 就实现效果了
List<string> strList = new List<string>() {"a","b","c","d","e" }; string tmp = string.Empty; foreach (string str in strList) { tmp += "‘" + str + "‘,"; } Console.WriteLine(tmp.Trim(‘,‘));
但是啊,这样写太土了。现在就可以用Aggregate方法来实现。
List<string> strList = new List<string>() { "a", "b", "c", "d", "e" }; tmp=strList.ToArray().Aggregate("",(c, i) => c + ("‘" + i + "‘,")).Trim(‘,‘); Console.WriteLine(tmp);
最后得到的结果就是:
‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘
Except是求集合之间的差集。直接上代码
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 4 List<string> strList1 = new List<string>() { "a", "b", "c", "d", "e" }; 5 6 List<string> strList2 = new List<string>() { "a", "b", "e", "f", "g" }; 7 string tmp = string.Empty; 8 9 10 tmp=strList1.Except(strList2).Aggregate("",(i,c)=>i+" "+c); 11 Console.WriteLine("实例方法调用Except查询strList1不存在strList2中的数据:{0}",tmp); 12 13 tmp = strList2.Except(strList1).Aggregate("", (i, c) => i + " " + c); 14 Console.WriteLine("实例方法调用Except查询strList2不存在strList1中的数据:{0}", tmp); 15 16 17 tmp = Enumerable.Except(strList1, strList2).Aggregate("", (i, c) => i + " " + c); 18 Console.WriteLine("Enumerable静态方法调用Except查询strList2不存在strList1中的数据:{0}", tmp); 19 }
直接结果:

那再来看看这个例子:
执行结果会是什么?张三?
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string tmp = string.Empty; List<Item> objList1 = new List<Item>() { }; objList1.Add(new Item { Key = "a", Name = "张三" }); objList1.Add(new Item { Key = "b", Name = "李四" }); objList1.Add(new Item { Key = "c", Name = "王五" }); List<Item> objList2 = new List<Item>() { }; objList2.Add(new Item { Key = "b", Name = "李四" }); objList2.Add(new Item { Key = "c", Name = "王五" }); objList2.Add(new Item { Key = "d", Name = "赵六" }); tmp = Enumerable.Except(objList1, objList2).Select(item => item.Name).Aggregate("", (i, c) => i + " " + c); Console.WriteLine("Enumerable静态方法调用Except查询objList1不存在objList2中的数据:{0}", tmp); } } public class Item { public string Key { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } }

出乎意料的是objList1集合里面的所有数据都显示出来了,这是为啥?原因很简单,因为Item是对象,对象之间的比较不想简单类型那样的“=”来判断的。
所以复杂对象之间的比较需要自定义一个比较器:
public class ItemComparer : IEqualityComparer<Item> { public bool Equals(Item x, Item y) { if (Object.ReferenceEquals(x, y)) return true; if (Object.ReferenceEquals(x, null) || Object.ReferenceEquals(y, null)) return false; //return x.Key == y.Key && x.Name == y.Name; return x.Key == y.Key; } public int GetHashCode(Item product) { if (Object.ReferenceEquals(product, null)) return 0; int hashProductName = product.Key == null ? 0 : product.Key.GetHashCode(); int hashProductCode = product.Name.GetHashCode(); return hashProductName ^ hashProductCode; } }
然后Main方法里面Enumerable.Except方法需要加入第三个参数new ItemComparer()
tmp = Enumerable.Except(objList1, objList2,new ItemComparer()).Select(item => item.Name).Aggregate("", (i, c) => i + " " + c);
再来看看执行结果:
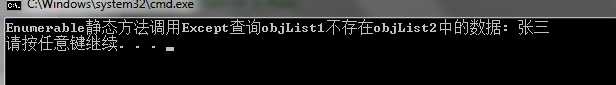
这样就对了!
未完....
标签:code ref 返回 集合 src bool array eth enum
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hc2016/p/6149308.html