你的朋友刚买了一台新电脑,他以前用过的最强大的计算工具是一台袖珍计算器。现在,看着自己的新电脑,他有点失望,因为他更喜欢计算器上的LC显示器。所以,你决定写一个LC显示风格的程序帮他在电脑上显示数字。
标签:input nts 自己 大小 include ima utc std script
你的朋友刚买了一台新电脑,他以前用过的最强大的计算工具是一台袖珍计算器。现在,看着自己的新电脑,他有点失望,因为他更喜欢计算器上的LC显示器。所以,你决定写一个LC显示风格的程序帮他在电脑上显示数字。
输入包括若干行,每一行有两个整数。输入为两个0表示结束,并且此行不被处理。
每行输入的两个整数s和n,满足1<=s<=10且0<=n<=99 999 999,其中n是要被现实的数字,s是n应该显示的大小(放大的倍数)。
输出的数字是LC显示风格的:使用s个“-”表示水平线和s个“|”竖直线,每个数字刚好占据s+2列和2s+3行,所有没有“-”和“|”的空白处请用空格填满。并且每两个数字之间要有一列空格。
每一行输入数字对应上述一组LC显示风格输出。任意两组数字的输出之间用一个空行分割。
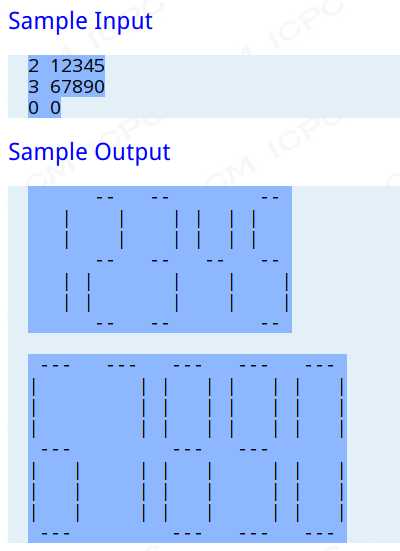
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 char a[12][10]= {"14041","03030","13121","13131","04130","12131","12141","13030","14141","14131"}; 3 void prints(char c,int n) 4 { 5 while(n--)putchar(c); 6 } 7 int main() 8 { 9 int k=2; 10 char s[20]; 11 int first=1; 12 while(scanf("%d%s",&k,s)==2&&(k||s[0]!=‘0‘)) 13 { 14 if(!first)printf("\n");else first=0; 15 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) 16 { 17 int t=1; 18 for(int j=0; j<k; j++) 19 { 20 for(int n=0; s[n]!=0; n++) 21 { 22 if(a[s[n]-‘0‘][i]==‘1‘) 23 { 24 if(j) t=0; 25 else{ 26 putchar(‘ ‘); 27 prints(‘-‘,k); 28 putchar(‘ ‘); 29 if(s[n+1]!=0)putchar(‘ ‘); 30 } 31 32 } 33 else if(a[s[n]-‘0‘][i]==‘0‘) 34 { 35 if(j) t=0; 36 else{ 37 prints(‘ ‘,k+2); 38 if(s[n+1]!=0)putchar(‘ ‘); 39 } 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 if(a[s[n]-‘0‘][i]==‘2‘) 44 { 45 putchar(‘|‘); 46 prints(‘ ‘,k+1); 47 } 48 else if(a[s[n]-‘0‘][i]==‘3‘) 49 { 50 prints(‘ ‘,k+1); 51 putchar(‘|‘); 52 } 53 else if(a[s[n]-‘0‘][i]==‘4‘) 54 { 55 putchar(‘|‘); 56 prints(‘ ‘,k); 57 putchar(‘|‘); 58 } 59 if(s[n+1]!=0)putchar(‘ ‘); 60 } 61 } 62 if(t)putchar(‘\n‘); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 return 0; 67 }
标签:input nts 自己 大小 include ima utc std script
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Wade-/p/6159276.html