标签:return rip rom port end lib turn atp axis
利用python实现简单的线性回归对房屋面积进行预测
1 # -*-coding:utf-8 -*- 2 ‘‘‘ 3 Created on 2016年12月15日 4 5 @author: lpworkdstudy 6 ‘‘‘ 7 import numpy as np 8 from numpy.core.multiarray import dtype 9 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 10 11 filename = "ex1data1.txt" 12 alpha = 0.01 13 14 f = open(filename,"r") 15 data = [] 16 y = [] 17 for item in f: 18 item = item.rstrip().split(",") 19 data.append(item[:-1]) 20 y.append(item[-1:]) 21 Data = np.array(data,dtype= "float64") 22 Y = np.array(y,dtype = "float64") 23 Y = (Y-Y.mean())/(Y.max()-Y.min()) 24 One = np.ones(Data.shape[0],dtype = "float64") 25 Data = np.insert(Data, 0, values=One, axis=1) 26 for i in range(1,Data.shape[1]): 27 Data[:,i] = (Data[:,i]-Data[:,i].mean())/(Data[:,i].max()-Data[:,i].min()) 28 theta = np.zeros((1,Data.shape[1]),dtype= "float64") 29 30 def CostFunction(Data,Y,theta): 31 h = np.dot(Data,theta.T) 32 cost = 1/float((2*Data.shape[0]))*np.sum((h-Y)**2) 33 return cost 34 def GradientDescent(Data,Y,theta,alpha): 35 costList = [] 36 for i in range(10000): 37 theta = theta- (alpha/Data.shape[0]*np.dot(Data.T,(np.dot(Data,theta.T)-Y))).T 38 cost = CostFunction(Data, Y, theta) 39 costList.append(cost) 40 41 plt.plot(range(10000),costList) 42 plt.xlabel("the no. of iterations") 43 plt.ylabel("cost Error") 44 plt.title("LinearRegression") 45 plt.show() 46 return theta 47 if __name__ == "__main__": 48 weight = GradientDescent(Data,Y,theta,alpha) 49 print weight 50 cost = CostFunction(Data, Y, weight) 51 print cost
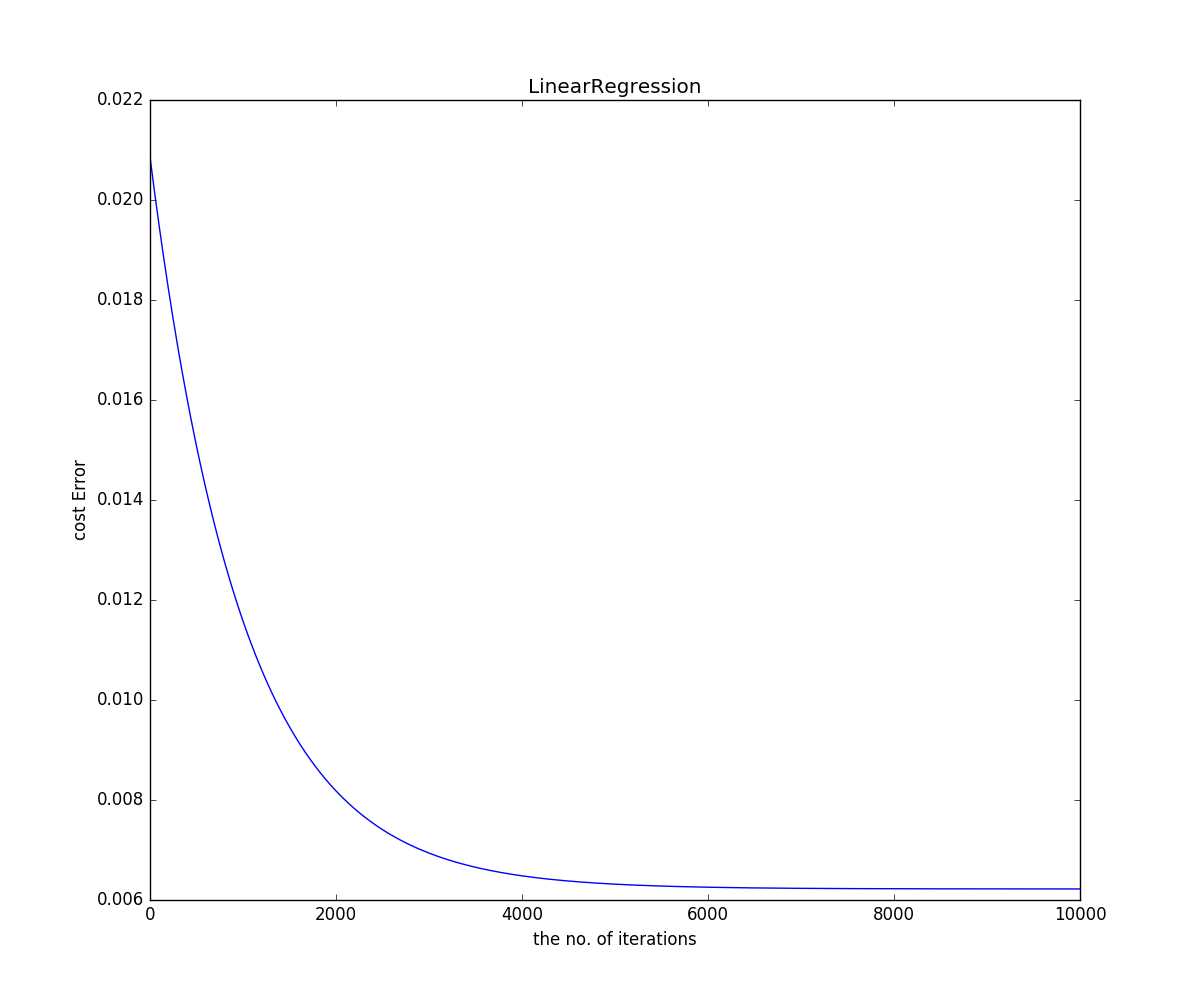
上图是Loss Error 随 迭代次数变化的曲线,显然,在迭代4000次左右后随着迭代次数增加,loss下降缓慢。
注:在这里只是简单的利用LMS Loss Function 和 GD对Linear Regression进行了编写,并没有预测
标签:return rip rom port end lib turn atp axis
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lpworkstudyspace1992/p/6184442.html