标签:运行 概念 image nat 多个 framework 实例 lag 间接
1.定义
保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
2.适用性
1)当类只能有一个实例而客户可以从一个众所周知的访问点访问它时。
2)当这个唯一实例应该是通过子类化可扩展的,并且客户应该无需更改代码就能使用一个扩展的实例时。
3.结构
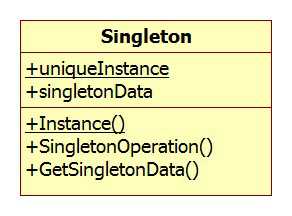
图1 单例模式类图
注:
Singleton:定义一个Instance操作,允许客户访问它的唯一实例。Instance是一个类操作(C#中为静态方法),Singleton负责创建它自己的唯一实例。
4.实现方法
1)经典模式
静态变量uniqueInstance存储唯一实例。公有静态方法GetInstance提供访问SingletonFirst的全局访问点,由于除了GetInstance方法外,类的成员均为私有的,所以GetInstance提供的为唯一访问方式。在GetInstance()方法中,对uniqueInstance是否为null做了判断,因此使得对象只能被实例化一次。
1 public class SingletonFirst 2 { 3 private static SingletonFirst uniqueInstance; 4 private SingletonFirst() { } 5 6 public static SingletonFirst GetInstance() 7 { 8 if(uniqueInstance==null) 9 { 10 uniqueInstance = new SingletonFirst(); 11 } 12 return uniqueInstance; 13 } 14 }
2)使用属性而不是方法
这种实现方式与第一种方式的区别在于客户通过属性获得对象实例。
1 public class SingletonSecond 2 { 3 private static SingletonSecond uniqueInstance; 4 private SingletonSecond() { } 5 public static SingletonSecond Instance 6 { 7 get 8 { 9 if (uniqueInstance == null) 10 { 11 uniqueInstance = new SingletonSecond(); 12 } 13 return uniqueInstance; 14 } 15 } 16 }
3)只能获得一次单例
这种单例模式的实现方式较之前几种有较大的差别,客户不能反复调用Instance属性获得实例;客户要将第一次获得的实例赋给一个变量,之后若要访问实例,则只能通过使用这一变量的间接方式。
1 public class SingletonThird 2 { 3 private static bool instanceFlag = false; 4 private SingletonThird() { } 5 6 public static SingletonThird Instance 7 { 8 get 9 { 10 if (!instanceFlag) 11 { 12 return new SingletonThird(); 13 } 14 else 15 { 16 return null; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 }
4)支持并发访问
这种单例模式的实现方式与第一种基本一致,只不过在声明uniqueInstanc的同时完成对象的实例化。优点是静态字段在类首次被使用前初始化,可以防止并发访问。
1 public class SingletonFourth 2 { 3 private static readonly SingletonFourth uniqueInstance = new SingletonFourth(); 4 private SingletonFourth() { } 5 6 public static SingletonFourth GetInstance() 7 { 8 return uniqueInstance; 9 } 10 }
5)使用私有静态构造器
这种方式使用了私有的静态构造器。静态构造器在类第一次被访问前由CLR自动调用,达到防止并发访问的目的。使用静态构造器而不是静态初始化器的好处是:可以在静态构造器中处理异常。
1 public class SingletonFifth 2 { 3 private static readonly SingletonFifth uniqueInstance; 4 static SingletonFifth() 5 { 6 uniqueInstance = new SingletonFifth(); 7 } 8 9 public static SingletonFifth GetInstance() 10 { 11 return uniqueInstance; 12 } 13 }
6)使用锁
这种方式采用加锁的办法来防止并发访问。缺点就是锁的开销比较大,如果用户对于性能比较关心,那么不建议采用这种方式。也可以考虑其他开销比较小的同步机制。
1 public class SingletonSixth 2 { 3 private static SingletonSixth uniqueInstance; 4 private static Object lockObj = new object(); 5 private SingletonSixth() { } 6 7 public static SingletonSixth GetInstance() 8 { 9 lock (lockObj) 10 { 11 if (uniqueInstance == null) 12 { 13 uniqueInstance = new SingletonSixth(); 14 } 15 return uniqueInstance; 16 } 17 } 18 }
7)延迟初始化
使用Lazy<T>达到延迟初始化的目的,但这种方式是非线程安全的。
1 public class SingletonSeventh 2 { 3 private static readonly Lazy<SingletonSeventh> lazy = 4 new Lazy<SingletonSeventh>(() => new SingletonSeventh()); 5 private SingletonSeventh(){} 6 7 public static SingletonSeventh Instance 8 { 9 get 10 { 11 return lazy.Value; 12 } 13 } 14 }
8)最简洁的方式
这种方法与标准的单例模式结构不符,但这种方式的确实现了单例模式, 符合单例模式的定义:只有一个实例且提供一个全局访问点uniqueInstance静态变量在声明时初始化,同时构造器可访问性为private,确保类不允许在外部实例化uniqueInstance变量的可访问性为public,所以全局的访问点就是uniqueInstance。
1 public class SingletonEighth 2 { 3 public static readonly SingletonEighth uniqueInstance = new SingletonEighth(); 4 private SingletonEighth() 5 { 6 //这里执行初始化工作或其他任务 7 } 8 }
5.扩展单例模式:使类可以有几个实例
1 public class SingletonExpansion 2 { 3 private static int count = 0; 4 private static SingletonExpansion uniqueInstance; 5 private SingletonExpansion(){} 6 7 public static SingletonExpansion Instance 8 { 9 get 10 { 11 if (count < 2) 12 { 13 uniqueInstance = new SingletonExpansion(); 14 count++; 15 return uniqueInstance; 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 return uniqueInstance; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }
6 概念辨析
1)使用静态成员与使用单例模式之间的比较:
相同点:
不同点:
2)一个类只有唯一的实例不一定就运用了单例模式
单例模式的两个要素:
上述两个条件缺一不可,否则就不是单例模式。
7 实现方式总结
1)实现了延迟初始化的为:SingletonFirst,SingletonSecond,SingletonThird,SingletonSeventh。
延迟初始化的好处:若对象占用资源(时间上创建时间比较长或空间上耗费内存较大)比较大,或程序的执行过程中从未使用到,那么延迟初始化可以避免耗费资源。如果对象并不占用较多的资源那么采用哪种方式都无所谓了。
2)线程安全的:SingletonFourth,SingletonFifth,SingletonSixth。
多线程编程中其他几种实现方法可能会有多个实例。
8 .NET Framework 中的单例模式
1) Microsoft.SqlServer.Server.SmiContextFactory
此方法实现方式与SingletonEighth的实现方式相同
源码概要
1 namespace Microsoft.SqlServer.Server { 2 3 using System; 4 5 using System.Data.Common; 6 7 using System.Data.SqlClient; 8 9 using System.Diagnostics; 10 11 sealed internal class SmiContextFactory 12 { 13 14 public static readonly SmiContextFactory Instance = new SmiContextFactory(); 15 //省略一些变量 16 private SmiContextFactory() { 17 18 //省略了具体实现} 19 20 //省略其他方法 21 22 } 23 }
2) sealed internal class SqlConnectionFactory
此方法实现方式与SingletonEighth的实现方式相同
源码概要
1 namespace System.Data.SqlClient 2 { 3 4 using System; 5 6 using System.Data.Common; 7 8 //省略其他using 9 10 using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server; 11 sealed internal class SqlConnectionFactory : DbConnectionFactory { 12 private SqlConnectionFactory() : 13 base(SqlPerformanceCounters.SingletonInstance) {} 14 15 public static readonly SqlConnectionFactory SingletonInstance = new SqlConnectionFactory(); 16 //省略以下其他代码 17 }
3) sealed internal class SqlPerformanceCounters
此方法实现方式与SingletonEighth的实现方式相同
源码概要
1 namespace System.Data.SqlClient 2 { 3 4 using System; 5 6 using System.Data.Common; 7 8 //省略其他using语句 9 10 using Microsoft.SqlServer.Server; 11 12 sealed internal class SqlPerformanceCounters : 13 DbConnectionPoolCounters { 14 15 private const string CategoryName = ".NET Data Provider for SqlServer"; 16 17 private const string CategoryHelp = "Counters for System.Data.SqlClient"; 18 19 20 public static readonly SqlPerformanceCounters SingletonInstance = new SqlPerformanceCounters(); 21 22 [System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterPermissionAttribute 23 (System.Security.Permissions.SecurityAction.Assert, PermissionAccess=PerformanceCounterPermissionAccess.Write, MachineName=".", CategoryName=CategoryName)] 24 25 private SqlPerformanceCounters() : base (CategoryName, CategoryHelp) { 26 } 27 28 } 29 }
标签:运行 概念 image nat 多个 framework 实例 lag 间接
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hdwgxz/p/6194110.html