标签:ges color pac 初始化 student 多个 遍历 线性 free
一,线性表的概念以及数学定义
1.线性表的概念
零个或多个数据元素的有限序列。首先说明这是一个序列,也就是说数据元素之间是有顺序的,若元素存在多个,则第一个元素无前驱,最后一个元素无后继,其他每个元素都有且仅有一个前驱和后继。
2.数学定义
若将线性表记为(a1...ai-1,ai,ai+1....an),则线性表中,ai-1领先于ai,ai领先于ai+1,则称ai-1是ai的直接前驱元素,ai+1是ai的直接后继元素,当i=1,2....n-1的时候,ai有且仅有一个直接后继元素,当i=2,3...n的时候,ai有且仅有一个直接前驱元素。
二,线性表的顺序存储结构
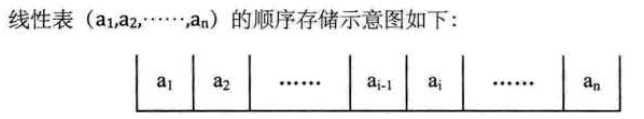
1.顺序存储结构的概念
线性表的顺序存储结构,指的是利用一段地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素。
2.顺序存储方式的实现
我们利用数组这个数据类型,来表示一段地址连续的存储单元。
三,线性表之顺序存储结构的的实现
1.线性表基本功能:
1.创建线性表 ==> List * createList(int capacity);
2.销毁线性表 ==> void destoryList(List * list);
3.清空线性表 ==> void clearList(List * list);
4.获取线性表长度 ==> int length(List * list);
5.获取线性表容量 ==> int capacity(List * list);
6.线性表的插入 ==> void insert(List * list,int pos,Node * node);
7.线性表的删除 ==> Node * delete(List * list,int pos);
8.线性表的修改 ==> Node * update(List * list,int pos,Node * node);
9.线性表的获取 ==> Node * get(List * list,int pos);
2.线性表基本功能的代码实现:
# include<stdio.h> # include<stdlib.h> # include<string.h> typedef void Node; typedef struct SeqList { int capacity; int length; int * array; }List; /* 创建指定容量大小的线性表 */ List * createList(int capacity) { // 在堆上分配线性表对象 List * list = (List *)malloc(sizeof(List)); // 初始化线性表对象的容量 list->capacity = capacity; // 初始化线性表当前长度 list->length = 0; // 初始化线性表的数组 list->array = malloc(capacity*sizeof(void *)); // 返回线性表 return list; } /* 销毁线性表 */ void destoryList(List * list) { if (list != NULL) { if (list->array != NULL) { // 释放线性表中的数组 free(list->array); list->array = NULL; } // 释放线性表对象 free(list); list = NULL; } } /* 清空线性表 */ void clearList(List * list) { if (list != NULL) { // 线性表的数组清空 memset(list->array, 0, sizeof(list->array)/list->capacity); // 线性表的长度清空 list->length = 0; } } /* 线性表的长度 */ int length(List * list) { return list->length; } /* 线性表的容量 */ int capacity(List * list) { return list->capacity; } /* 线性表的插入 */ void insert(List * list, int pos, Node * node) { if (list == NULL) { printf("线性表为NULL\n"); return; } if (pos > list->capacity) { printf("插入位置超过线性表的容量\n"); return; } if (list->length > list->capacity) { printf("线性表容量已满,无法插入\n"); return; } // 容错机制 6个长度,容量20,插入10,则自动插入到7这个位置 if (pos>list->length) { list->array[list->length] = node; // 线性表长度加一 list->length++; return; } // 移动pos之后的数据 for (int i = list->length; i > pos-1; i--) { list->array[i] = list->array[i-1]; } // 插入数据 list->array[pos - 1] = node; // 线性表长度加一 list->length++; } /* 线性表的删除 */ Node * delete(List * list, int pos) { if (list == NULL) { printf("线性表为NULL\n"); return NULL; } if (pos > list->length) { printf("删除位置不存在\n"); return NULL; } // 返回的元素 Node * node = list->array[pos - 1];; // 删除元素后线性表长度减一 list->length--; // 删除最后一个 if (pos == list->length) { list->array[pos - 1] = NULL; return node; } // 删除 for (int i = pos - 1; i < list->length; i++) { list->array[i] = list->array[i + 1]; } return node; } /* 线性表的修改 */ Node * update(List * list, int pos, Node * node) { if (list == NULL) { printf("线性表为NULL\n"); return NULL; } // 返回修改前的对象 Node * result = list->array[pos - 1]; // 修改 list->array[pos - 1] = node; return result; } /* 线性表的获取 */ Node * get(List * list, int pos) { if (list == NULL) { printf("线性表为NULL\n"); return NULL; } return list->array[pos - 1]; }
3.测试程序实现
/* 测试程序 */ typedef struct Student { char name[64]; int age; }Student; int main() { // 创建线性表 List * list = createList(20); // 创建学生对象并初始化 Student s1 = { "刘备",42 }; Student s2 = { "关羽",38 }; Student s3 = { "张飞",32 }; Student s4 = { "赵云",36 }; Student s5 = { "马超",26 }; Student s6 = { "黄忠",59 }; // 头插法插入 insert(list, 1, &s1); insert(list, 2, &s2); insert(list, 3, &s3); insert(list, 4, &s4); insert(list, 5, &s5); insert(list, 19, &s6); // 获取长度 printf("############线性表长度############\n"); printf("length = %d\n", length(list)); // 获取容量 printf("############线性表容量############\n"); printf("capacity = %d\n", capacity(list)); // 遍历 printf("############线性表遍历############\n"); for (int i = 1; i <= length(list); i++) { Student * s = get(list, i); printf("name = %s,age = %d\n", s->name, s->age); } // 删除第一个元素 delete(list, 3); printf("############删除第三个元素############\n"); // 遍历 for (int i = 1; i <= length(list); i++) { Student * s = get(list, i); printf("name = %s,age = %d\n", s->name, s->age); } // 修改第一个元素 printf("############修改第一个元素############\n"); Student sss = { "刘备-汉中王",50 }; update(list, 1, &sss); // 遍历 for (int i = 1; i <= length(list); i++) { Student * s = get(list, i); printf("name = %s,age = %d\n", s->name, s->age); } // 清空线性表 printf("############清空线性表############\n"); clearList(list); // 遍历 for (int i = 1; i <= length(list); i++) { Student * s = get(list, i); printf("name = %s,age = %d\n", s->name, s->age); } // 销毁线性表 printf("############销毁线性表############\n"); destoryList(list); return 0; }
标签:ges color pac 初始化 student 多个 遍历 线性 free
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/metalsteel/p/6246365.html