标签:新建 系统 预定义变量 环境 stat 目录 linu man 提示
CMake是一个跨平台的安装(编译)工具,可以用简单的语句来描述所有平台的安装(编译过程)。CMake不构建出最终的可执行文件,而是产生一个标准的建构档(即根据目标用户的平台进一步生成所需的本地化 Makefile 和工程文件),然后再依一般的建构方式使用,从而实现软件的跨平台。
<1>Linux下CMake的安装:
先到官网下载CMake源码包:https://cmake.org/download/
打开终端依次执行以下命令:
tar -xzvf cmake-2.6.4.tar.gz cd cmake-2.6.4 ./bootstrap make make install
cmake 会默认安装在 /usr/local/bin 下面。(windows下安装可以直接下载安装包进行安装)
<2>Linux下使用CMake生成makefile & 编译的大致流程如下:
1.编写CMake的配置文件CMakeLists.txt(组态档的命名和类型必须为这个);
2.然后在终端输入CMake <PATH>(PATH是 CMakeLists.txt 所在的目录)或者CMake .(如果是在当前目录下,注意CMake和.之间有空格)来生成Makefile;
3.最后在终端输入make命令进行编译(windows平台下会生成VS的工程文件,可以使用VS工具进行编译)输出可执行文件。
以上就是CMake简单使用步骤,下面本文将会通过一些简单的例子来讲解CMake的一个基本使用。
<3>实例解析
主题一:单个源文件
假设现在我们有个源文件demo1.c,该程序实现对某个数求绝对值
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int abs(int num){ return num>=0?num:-num; } void main(int argc, char* argv[]){ int num = 0; if(argc < 2){ printf("usage: %s number\n", argv[0]); } else{ num = atoi(argv[1]); printf("abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); } }
接着在demo1.c源文件的目录下,编写CMakeLists.txt
#CMake中#后面的语句解释为注释行
#指定cmake最低使用版本号,可以不设置,但是会有一个warnning cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) #设置项目工程的名称 project(Demo1) #将demo1.c源文件编译成一个名为Demo1的可执行文件 add_executable(Demo1 demo1.c)
然后在当前的目录下,输入cmake .命令生成makefile,最后再输入make命令(windows下使用VS打开.sln工程文件进行编译)来编译得到最后的可执行文件Demo1
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ cmake . -- The C compiler identification is GNU 4.4.7 -- The CXX compiler identification is GNU 4.4.7 -- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- works -- Detecting C compiler ABI info -- Detecting C compiler ABI info - done -- Detecting C compile features -- Detecting C compile features - done -- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- works -- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info -- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info - done -- Detecting CXX compile features -- Detecting CXX compile features - done -- Configuring done -- Generating done -- Build files have been written to: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ make Scanning dependencies of target Demo1 [ 50%] Building C object CMakeFiles/Demo1.dir/demo1.c.o [100%] Linking C executable Demo1 [100%] Built target Demo1 [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ ./Demo1 -5 abs(-5) = 5 [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$
主题二:多个源文件
(1)同一目录
假设现在我们把上面例子中的求绝对值abs单独编写一个另外一个源文件MyFunction.c中,如下形式(所有源文件都在同一目录demo_test下)
/demo_test
demo2.c
MyFunction.h
MyFunction.c
此时的CMakeLists.txt应修改如下
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo2) add_executable(Demo2 demo2.c MyFunction.c)
相对于上例的CMakeLists.txt,只是在add_executable中多添加了一个源文件。这样写过固然没有问题,但是考虑到多文件的情况,我们这样手动的添加多个源文件是不是太麻烦了呢?是的,这个时候我们可以这样来添加文件
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo2) #该指令会查找所指定目录下(. 代表当前目录)的所有源文件 #并把文件名赋值给变量DIR_SOURCE aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo2 ${DIR_SOURCE})
这样就可以顺利编译出可执行文件了。
(2)不同目录
现在在demo_test目录下新建一个子目录math,将我们的MyFunction.h和MyFunction.c文件移动math文件里面。这种情况下,我们就必须要为每个源文件目录编写一个CMakeLists.txt。文件结构如下
/demo_test demo03 /math MyFunction.h MyFunction.c
首先在子目录math里面,编写CMakeLists.txt
aux_source_directory(. DIR_LIB_SOURCE)
#将目录中的源文件编译为静态链接库
add_library(MyFunction ${DIR_LIB_SOURCE})
在根目录demo_test中的CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo3) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) #添加一个子目录math,这样子目录下的CMakeLists.txt也会被处理 add_subdirectory(math) add_executable(Demo3 ${DIR_SOURCE}) #为可执行文件添加我们所需要的链接库MyFunction target_link_libraries(Demo3 MyFunction)
接着我们再输入cmake命令:
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ cmake . -- The C compiler identification is GNU 4.4.7 -- The CXX compiler identification is GNU 4.4.7 -- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- works -- Detecting C compiler ABI info -- Detecting C compiler ABI info - done -- Detecting C compile features -- Detecting C compile features - done -- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- works -- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info -- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info - done -- Detecting CXX compile features -- Detecting CXX compile features - done -- Configuring done -- Generating done -- Build files have been written to: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test
这样根目录和子目录都会生成makefile,再make编译成可执行文件就可以了
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ make Scanning dependencies of target MyFunction [ 25%] Building C object math/CMakeFiles/MyFunction.dir/MyFunction.c.o [ 50%] Linking C static library libMyFunction.a [ 50%] Built target MyFunction Scanning dependencies of target Demo3 [ 75%] Building C object CMakeFiles/Demo3.dir/demo3.c.o [100%] Linking C executable Demo3 [100%] Built target Demo3 [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ ./Demo3 9 abs(9) = 9 [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$
主题三:自定义编译选项
CMake允许用户增加编译选项,可以根据用户的环境和需要选择最合适的编译方案
比如我们可以把demo3中的MyFunction库设计为一个可选链接库,CMakeLists.txt如下
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo4) #加入一个配置文件config.h,由CMake通过config.h.in生成 #这样的机制可以通过预定义一些参数和变量来控制代码的生成 configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") #添加一个USE_MYMATH控制变量,默认值为ON option(USE_MYMATH "USE MyFunction" ON) #根据是否定义USE_MYMATH进行条件编译 if(USE_MYMATH) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(USE_MYMATH) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo4 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo4 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB})
再修改源文件demo04.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
#include "config.h" #ifdef USE_MYMATH #include "math/MyFunction.h" #else #include <math.h> #endif(USE_MYMATH) void main(int argc, char* argv[]){ int num = 0; if(argc < 2){ printf("usage: %s number\n", argv[0]); } else{ num = atoi(argv[1]); #ifdef USE_MYMATH printf("MyFunction: abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); #else printf("SystemFunction: abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); #endif(USE_MYMATH) } }
编写config.h.in文件
#cmakedefine USE_MYMATH
生成makefile,因为上面我们定义了一个变量USE_MYMATH,其默认值为ON,但是如果我们想显式的修改该变量的值,可以输入cmake -DUSE_MYMATH=OFF命令来修改变量的值为OFF(cmake其他的一些用法可以键入cmake -help来查询),同样可以在cmake生成makefile之后输入命令make edit_cache或者ccmake .来激活一个配置窗口
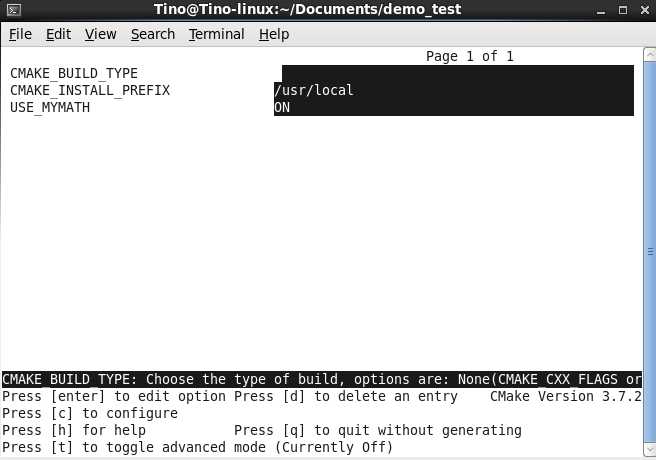
具体的操作在这里我就不细讲了(窗口底下有指令提示),当USE_MYMATH为ON时,config.h文件的内容为 #define USE_MYMATH,即执行我们自定的函数;当USE_MYMATH为OFF时,config.h文件的内容为/*#undef SE_MYMATH*/,执行系统库函数
主题四:安装和测试
CMake也可以指定安装规则和添加测试,下面来看看具体实现
(1)定制安装规则
现在math子目录下的CMakeLists.txt
aux_source_directory(. DIR_LIB_SOURCE) add_library(MyFunction ${DIR_LIB_SOURCE}) #指定MyFunction 安装路径为当前目录的bin子目录下 #直接写bin会默认安装在/usr/local/bin中 install(TARGETS MyFunction DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin") #指定MyFunction.h 安装路径为当前目录的include子目录下 #直接写include会默认安装在/usr/local/include中 install(FILES MyFunction.h DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include")
修改根目录demo_test下的CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo5) configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") option(USE_MYMATH "USE MyFunction" ON) if(USE_MYMATH) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(USE_MYMATH) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo5 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo5 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB}) install(TARGETS Demo5 DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin") install(FILES "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h" DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include")
键入make install命令来安装文件。这样,通过上面的定制,生成MyFunction.h和config.h就会包含在demo_test目录下的include文件中,而libMyFunction.o函数库文件和Demo5可执行文件就会包含在demo_test目录下的bin文件中
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ cmake . -- Configuring done -- Generating done -- Build files have been written to: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ cmake . -- The C compiler identification is GNU 4.4.7 -- The CXX compiler identification is GNU 4.4.7 -- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- works -- Detecting C compiler ABI info -- Detecting C compiler ABI info - done -- Detecting C compile features -- Detecting C compile features - done -- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- works -- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info -- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info - done -- Detecting CXX compile features -- Detecting CXX compile features - done -- Configuring done -- Generating done -- Build files have been written to: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ make install Scanning dependencies of target MyFunction [ 25%] Building C object math/CMakeFiles/MyFunction.dir/MyFunction.c.o [ 50%] Linking C static library libMyFunction.a [ 50%] Built target MyFunction Scanning dependencies of target Demo5 [ 75%] Building C object CMakeFiles/Demo5.dir/demo5.c.o /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/demo5.c:8:7: warning: extra tokens at end of #endif directive /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/demo5.c:21:15: warning: extra tokens at end of #endif directive [100%] Linking C executable Demo5 [100%] Built target Demo5 Install the project... -- Install configuration: "" -- Installing: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/bin/Demo5 -- Installing: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/include/config.h -- Installing: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/bin/libMyFunction.a -- Installing: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/include/MyFunction.h
(2)为工程添加测试
修改根目录下的CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo6) configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") option(USE_MYMATH "USE MyFunction" ON) if(USE_MYMATH) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(USE_MYMATH) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo6 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo6 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB}) install(TARGETS Demo6 DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin") install(FILES "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h" DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include")
#开始测试 enable_testing()
#添加一个测试(test_-9) add_test(test_-9 Demo6 -9)
#设置测试属性,PASS_REGULAR_EXPRESSION用来测试输出是否包含双引号里面的字符串 set_tests_properties(test_-9 PROPERTIES PASS_REGULAR_EXPRESSION "= 9")
#下同 add_test(test_8 Demo6 8) set_tests_properties(test_8 PROPERTIES PASS_REGULAR_EXPRESSION "= 8")
编译后执行make test如下
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ make test Running tests... Test project /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test Start 1: test_-9 1/2 Test #1: test_-9 .......................... Passed 0.00 sec Start 2: test_8 2/2 Test #2: test_8 ........................... Passed 0.00 sec 100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 2 Total Test time (real) = 0.01 sec [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$
通过上面例子我们已经知道可以通过CMake来进行测试,但是很多时候,我们测试的是要多次反复测量,才能尽可能避免bug的出现,所以这个时候用add_test来一个个添加测试就显得有力不从心了。因此,我们需要定义一个宏来实现测试
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo6) configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") option(USE_MYMATH "USE MyFunction" ON) if(USE_MYMATH) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(USE_MYMATH) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo6 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo6 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB}) install(TARGETS Demo6 DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin") install(FILES "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h" DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include") enable_testing() add_test(test_-9 Demo6 -9) set_tests_properties(test_-9 PROPERTIES PASS_REGULAR_EXPRESSION "= 9") add_test(test_8 Demo6 8) set_tests_properties(test_8 PROPERTIES PASS_REGULAR_EXPRESSION "= 8")
#定义一个宏 macro(do_test arg result) add_test(test_${arg} Demo6 ${arg}) set_tests_properties(test_${arg} PROPERTIES PASS_REGULAR_EXPRESSION ${result}) endmacro(do_test)
#使用宏进行测试 do_test(7 "= 7") do_test(-6 "= 6")
主题五:添加环境检查
有时候可能要对系统的环境做点检查,比如要使用一个平台的相关特性时。在以下例子中,我们要检查系统是否自带abs函数,有则使用,没有则使用自定义的abs函数。和上面我们自定义编译选项的做法类似
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo7)
#添加CheckFunctionExists.cmake宏 include(${CMAKE_ROOT}/Modules/CheckFunctionExists.cmake)
#调用check_function_exists命令测试链接器是否能够在链接阶段找到abs函数 check_function_exists(abs HAVE_ABS) configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") if(NOT HAVE_ABS) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(HAVE_ABS) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo7 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo7 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB})
修改config.h.in文件
#cmakedefine HAVE_ABS
最后修改demo7.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "config.h" #ifdef HAVE_ABS #include <math.h> #else #include "math/MyFunction.h" #endif void main(int argc, char* argv[]){ int num = 0; if(argc < 2){ printf("usage: %s number\n", argv[0]); } else{ num = atoi(argv[1]); #ifdef HAVE_ABS printf("SystemFunction: abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); #else printf("MyFunction: abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); #endif } }
最后编译,这里我就不演示了,和上面例子类似
主题六:添加版本号
修改根目录demo_test里的CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo8)
#设定当前主、副版本号也就是变量的值 set(Demo8_VERSION_MAJOR 1) set(Demo8_VERSION_MINOR 0) include(${CMAKE_ROOT}/Modules/CheckFunctionExists.cmake) check_function_exists(abs HAVE_ABS) configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") if(NOT HAVE_ABS) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(NOT HAVE_ABS) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo8 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo8 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB}) install(TARGETS Demo8 DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin") install(FILES "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h" DESTINATION "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include")
然后在修改config.h.in内容
#cmakedefine HAVE_ABS
#添加两个预定义变量 #define Demo8_VERSION_MAJOR @Demo8_VERSION_MAJOR@ #define Demo8_VERSION_MINOR @Demo8_VERSION_MINOR@
在demo8.c里面打印出我们设置的版本信息
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "config.h" #ifdef HAVE_ABS #include <math.h> #else #include "math/MyFunction.h" #endif void main(int argc, char* argv[]){ int num = 0; printf("%s Version %d.%d\n", argv[0], Demo8_VERSION_MAJOR, Demo8_VERSION_MINOR); if(argc < 2){ printf("usage: %s number\n", argv[0]); } else{ num = atoi(argv[1]); #ifdef HAVE_ABS printf("SystemFunction: abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); #else printf("MyFunction: abs(%d) = %d\n", num, abs(num)); #endif } }
执行看下结果
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ ./Demo8 5 ./Demo8 Version 1.0 MyFunction: abs(5) = 5
主题七:生成安装包
利用CMake来配置生成各种平台上的安装包(二进制包和源码包)
修改主目录CMakeLists.txt文件
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8) project(Demo9) set(Demo9_VERSION_MAJOR 1) set(Demo9_VERSION_MINOR 0) include(${CMAKE_ROOT}/Modules/CheckFunctionExists.cmake) check_function_exists(abs HAVE_ABS) configure_file("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.in" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h") if(NOT HAVE_ABS) include_directories("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/math") add_subdirectory(math) set(EXTRA_LIBS ${EXTRA_LIB} MyFunction) endif(NOT HAVE_ABS) aux_source_directory(. DIR_SOURCE) add_executable(Demo9 ${DIR_SOURCE}) target_link_libraries(Demo9 MyFunction ${EXTRA_LIB})
#必须定制安装规则,否则安装包为空,注意存放路径 install(TARGETS Demo9 DESTINATION bin) install(FILES "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/config.h" DESTINATION include)
#构建一个CPack安装包
#导入InstallRequiredSystemLibraries模块,以便之后导入CPack模块 include(InstallRequiredSystemLibraries)
#设置CPack的基本信息 set(CPACK_RESOURCE_FILE_LICENSE "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/License.txt") set(CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MAJOR "${Demo9_VERSION_MAJOR}") set(CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MINOR "${Demo9_VERSION_MINOR}")
#导入CPack模块
include(CPack)
修改子目录math文件下的CMakeLists.txt
aux_source_directory(. DIR_LIB_SOURCE)
add_library(MyFunction ${DIR_LIB_SOURCE})
install(TARGETS MyFunction DESTINATION bin)
install(FILES MyFunction.h DESTINATION include)
上面有3个要注意的地方,1.首先必须要定制安装规则,即加入install指令;2.再者DESTINATION后面的文件存放路径不能是自定义的一个路径,比如主题四里面设置的当前文件目录,否则CPack出来的安装包都是空文件;3.License.txt只是你自己添加的信息文本,自己随意编写一个就好,如果没有会在cmake的时候出现错误导致不通过
接下来就是平常一样构建工程,make编译完成之后执行CPack命令:
1. cpack -C CpackConfig.cmake //生成二进制安装包
2. cpack -C CpackSourceConfig.cmake //生成源码安装包
下面键入cpack -C CpackSourceConfig.cmake试一试结果
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ cpack -C CpackSourceConfig.cmake CPack: Create package using STGZ CPack: Install projects CPack: - Run preinstall target for: Demo9 CPack: - Install project: Demo9 CPack: Create package CPack: - package: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.sh generated. CPack: Create package using TGZ CPack: Install projects CPack: - Run preinstall target for: Demo9 CPack: - Install project: Demo9 CPack: Create package CPack: - package: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.tar.gz generated. CPack: Create package using TZ CPack: Install projects CPack: - Run preinstall target for: Demo9 CPack: - Install project: Demo9 CPack: Create package CPack: - package: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.tar.Z generated.
执行完CPack命令之后,根目录下会有三个文件不同格式的二进制包文件:Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.sh,Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.tar.gz,Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.tar.Z 这几个文件所包含的内容是完全一致的。我们执行其中一个文件,此时会弹出一个交互界面,看到红色标记处,那就是我们编写的License.txt文件内容,然后下面依据提示来UnPacking包文件
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ sh Demo0-1.0.1-Linux.sh sh: Demo0-1.0.1-Linux.sh: No such file or directory [Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ sh Demo9-1.0.1-Linux.sh Demo9 Installer Version: 1.0.1, Copyright (c) Humanity This is a self-extracting archive. The archive will be extracted to: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test If you want to stop extracting, please press <ctrl-C>. Tino 2017-1-22 CPack Do you accept the license? [yN]: y By default the Demo9 will be installed in: "/home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/Demo9-1.0.1-Linux" Do you want to include the subdirectory Demo9-1.0.1-Linux? Saying no will install in: "/home/Tino/Documents/demo_test" [Yn]: y Using target directory: /home/Tino/Documents/demo_test/Demo9-1.0.1-Linux Extracting, please wait... Unpacking finished successfully
然后我们浏览下UnPacking出来的Demo9-1.0.1-Linux文件里面的内容
[Tino@Tino-linux demo_test]$ cd Demo9-1.0.1-Linux [Tino@Tino-linux Demo9-1.0.1-Linux]$ ls bin include [Tino@Tino-linux Demo9-1.0.1-Linux]$ cd bin [Tino@Tino-linux bin]$ ls Demo9 libMyFunction.a [Tino@Tino-linux bin]$ ./Demo9 -100 ./Demo9 Version 1.0 MyFunction: abs(-100) = 100
我们所需的可执行文件就安静的躺在里面了,就可以执行改程序了~
题外话:
CMake我就为大家介绍到这里了,再深入的话博主暂时也没有办法,因为博主也是刚开始学习CMake,写这篇文章最主要的目的还是想以一个笔记的形式来加深理解、印象,也希望同是新手的朋友在检索相关信息的时候能便利一下吧,希望对大家有点小帮助。等博主学习到一定程度之后会再次更新此文章,逐步完善内容的。
文中若有任何错误不正确的地方,请大家为我指出,以免错误引导网友,谢谢啦!
同时也要感谢那些经常写博客的大牛们,为我提供了那么多好的技术资料,Thx~向他们看齐!!哈哈~为大家多做贡献。
写博客太累了,累死我~以后查阅资料的时候真的怀着感恩的心,因为他们都是耗费自己的时间、精力无偿为大家提供帮助。
声明:本文没有任何形式上的获益,只是看了多篇博客资料加上自己的一些实践理解,借鉴采纳来为大家服务。
相关链接:
CMAKE官方文档(想要深入全面的了解CMake建议去阅读官方文档,受益匪浅)
某位大牛写的文章http://www.hahack.com/codes/cmake/
可以查看一些基本指令 https://my.oschina.net/zhangxu0512/blog/222741
http://m.blog.csdn.net/article/details?id=51289404
标签:新建 系统 预定义变量 环境 stat 目录 linu man 提示
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tino-memo-2017-1-20/p/6338061.html