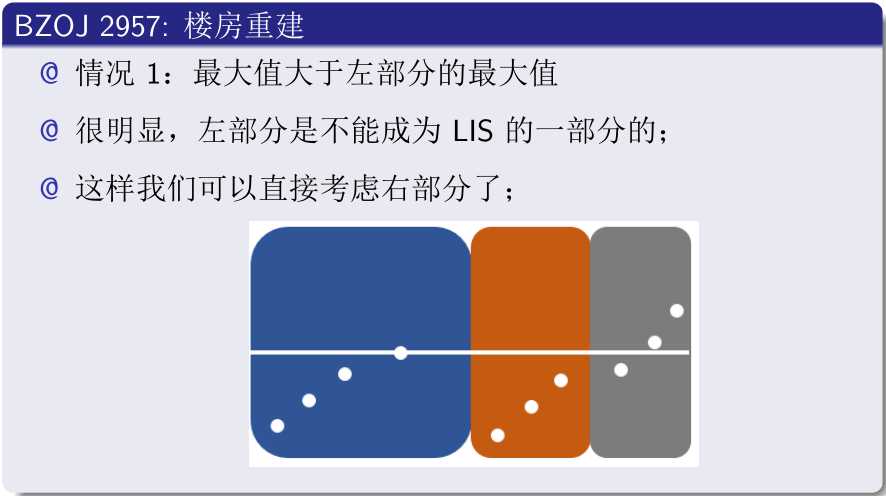
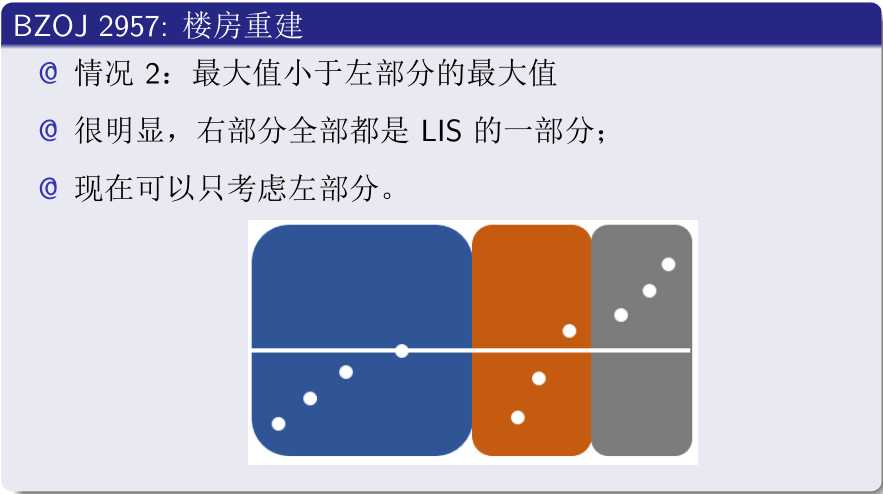
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define lc k<<1
#define rc k<<1|1
using namespace std;
int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘){if(ch==‘-‘)f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch-‘0‘;ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
const int M=1e5+10,N=M<<2;
struct node{int sum;double slop;}tr[N];
struct data{int x,y;}s[N];double a[N];
int solve(int k,int l,int r,double z){
if(l==r) return tr[k].slop>z;
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(tr[lc].slop<=z) return solve(rc,mid+1,r,z);
return tr[k].sum-tr[lc].sum+solve(lc,l,mid,z);
}
void updata(int k,int l,int r){
int mid=l+r>>1;
tr[k].slop=max(tr[lc].slop,tr[rc].slop);
tr[k].sum=tr[lc].sum+solve(rc,mid+1,r,tr[lc].slop);
}
void change(int k,int l,int r,int pos,double z){
if(l==r){
tr[k].slop=z;
tr[k].sum=1;
return ;
}
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(pos<=mid) change(lc,l,mid,pos,z);
else change(rc,mid+1,r,pos,z);
updata(k,l,r);
}
int main(){
int n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
s[i].x=read();s[i].y=read();
a[i]=(double)s[i].y/(double)s[i].x;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
change(1,1,n,s[i].x,a[i]);
printf("%d\n",tr[1].sum);
}
return 0;
}

 、
、