标签:span 树结构 接下来 tchar org 包含 swa http tor
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入格式:
第一行包含三个正整数N、M、S,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来N-1行每行包含两个正整数x、y,表示x结点和y结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来M行每行包含两个正整数a、b,表示询问a结点和b结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式:
输出包含M行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
5 5 4 3 1 2 4 5 1 1 4 2 4 3 2 3 5 1 2 4 5
4 4 1 4 4
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
对于30%的数据:N<=10,M<=10
对于70%的数据:N<=10000,M<=10000
对于100%的数据:N<=500000,M<=500000
样例说明:
该树结构如下:
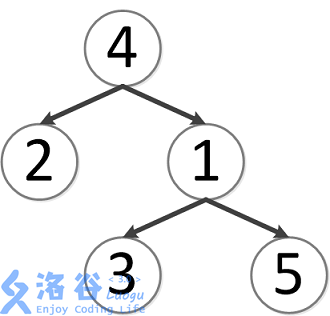
第一次询问:2、4的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第二次询问:3、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第三次询问:3、5的最近公共祖先,故为1。
第四次询问:1、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第五次询问:4、5的最近公共祖先,故为4。
故输出依次为4、4、1、4、4。
//就是个板子,但是各种卡还要用读入优化... //边不要用vector存会超时!!! #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #define maxn 500010 #define S 21 using namespace std; int deep[maxn],head[maxn],p1,p2,n,m,num,ans,s,x,y,fa[maxn][S+5]; struct node { int from; int to; int next; }e[maxn*2]; void add(int from,int to) { e[++num].from=from; e[num].to=to; e[num].next=head[from]; head[from]=num; } int init() { int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar(); while(c>‘9‘||c<‘0‘){if(c==‘-‘)f=-1;c=getchar();} while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){x=x*10+c-‘0‘;c=getchar();} return x*f; } void swap(int &a,int &b) { int t=a;a=b;b=t; } void get_fa() { for(int j=1;j<=S;j++) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) fa[i][j]=fa[fa[i][j-1]][j-1]; } void Dfs(int now,int from,int c) { fa[now][0]=from; deep[now]=c; for(int i=head[now];i;i=e[i].next) { int v=e[i].to; if(v!=from) Dfs(v,now,c+1); } } int get_same(int a,int t) { for(int i=0;i<S;i++) if(t&(1<<i)) a=fa[a][i]; return a; } int LCA(int a,int b) { if(deep[a]<deep[b]) swap(a,b); a=get_same(a,deep[a]-deep[b]); if(a==b) return a; for(int i=S;i>=0;i--) { if(fa[a][i]!=fa[b][i]) { a=fa[a][i]; b=fa[b][i]; } } return fa[a][0]; } int main() { n=init();m=init();s=init(); int x,y; for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { x=init();y=init(); add(x,y); add(y,x); } Dfs(s,s,0); get_fa(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { p1=init();p2=init(); int ans=LCA(p1,p2); printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }
标签:span 树结构 接下来 tchar org 包含 swa http tor
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/L-Memory/p/6363930.html