标签:core dump info valgrind 描述符 子线程 使用情况 using 默认 ref
最近老是遇上各种奇奇怪怪的core dump,不太会分析的情况下看到了这款工具。在这记录分享下。
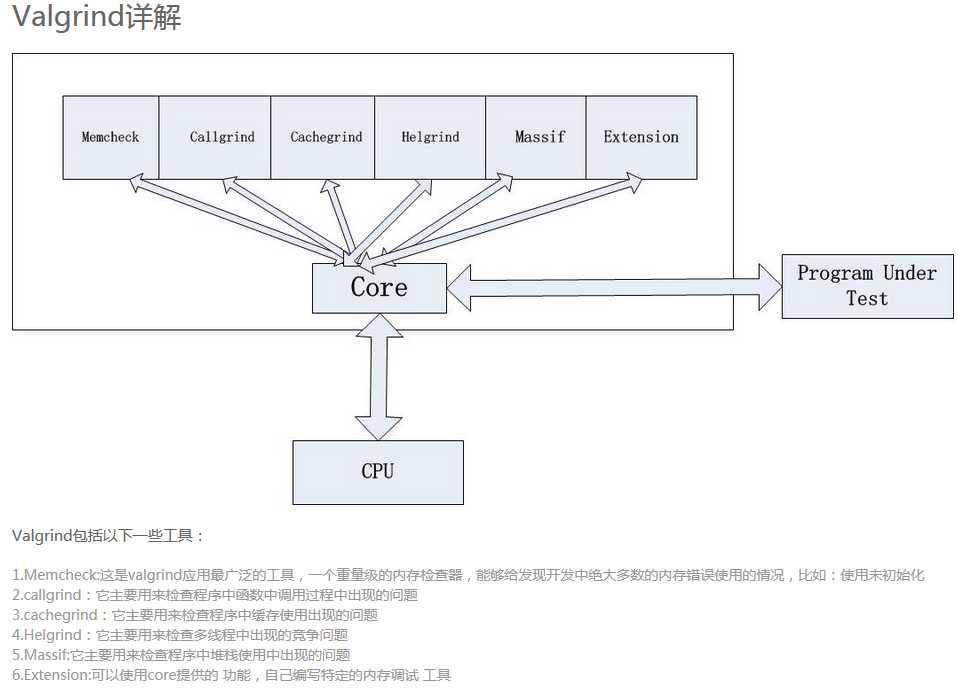
Valgrind 是个开源的工具,功能很多。例如检查内存泄漏工具---memcheck。
Valgrind 安装:
去官网下载: http://valgrind.org/downloads/current.html#current
安装过程:(可以直接查看README文档来确认安装过程)
tools/valgrind-3.12.0> pwd
/proj/MPS_DEV_REPO/xchonxu/tools
> tar -jxf valgrind-3.12.0.tar.bz2
> cd /proj/MPS_DEV_REPO/xchonxu/tools/valgrind-3.12.0
> vim README
> ls
> ./autogen.sh
> ./configure --prefix=/home/xchonxu/bin
> make
> make install
验证是否成功:
> cd ~
> ls
> cd bin/
> ls
> cd bin/
> ls
> ./valgrind ls -l
> ./valgrind --leak-check=full ls -l
Valgrind 命令介绍:
用法: valgrind [options] prog-and-args
[options]: 常用选项,适用于所有Valgrind工具
-tool=<name> 最常用的选项。运行 valgrind中名为toolname的工具。默认memcheck。
memcheck ------> 这是valgrind应用最广泛的工具,一个重量级的内存检查器,能够发现开发中绝大多数内存错误使用情况,比如:使用未初始化的内存,使用已经释放了的内存,内存访问越界等。
callgrind ------> 它主要用来检查程序中函数调用过程中出现的问题。
cachegrind ------> 它主要用来检查程序中缓存使用出现的问题。
helgrind ------> 它主要用来检查多线程程序中出现的竞争问题。
massif ------> 它主要用来检查程序中堆栈使用中出现的问题。
extension ------> 可以利用core提供的功能,自己编写特定的内存调试工具
-h –help 显示帮助信息。
-version 显示valgrind内核的版本,每个工具都有各自的版本。
-q –quiet 安静地运行,只打印错误信息。
-v –verbose 更详细的信息, 增加错误数统计。
-trace-children=no|yes 跟踪子线程? [no]
-track-fds=no|yes 跟踪打开的文件描述?[no]
-time-stamp=no|yes 增加时间戳到LOG信息? [no]
-log-fd=<number> 输出LOG到描述符文件 [2=stderr]
-log-file=<file> 将输出的信息写入到filename.PID的文件里,PID是运行程序的进行ID
-log-file-exactly=<file> 输出LOG信息到 file
-log-file-qualifier=<VAR> 取得环境变量的值来做为输出信息的文件名。 [none]
-log-socket=ipaddr:port 输出LOG到socket ,ipaddr:port
LOG信息输出
-xml=yes 将信息以xml格式输出,只有memcheck可用
-num-callers=<number> show <number> callers in stack traces [12]
-error-limit=no|yes 如果太多错误,则停止显示新错误? [yes]
-error-exitcode=<number> 如果发现错误则返回错误代码 [0=disable]
-db-attach=no|yes 当出现错误,valgrind会自动启动调试器gdb。[no]
-db-command=<command> 启动调试器的命令行选项[gdb -nw %f %p]
适用于Memcheck工具的相关选项:
-leak-check=no|summary|full 要求对leak给出详细信息? [summary]
-leak-resolution=low|med|high how much bt merging in leak check [low]
-show-reachable=no|yes show reachable blocks in leak check? [no]
最常用的命令格式:
valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full ./test
案例介绍:
申请内存未释放:
xchonxu/testCode> cat testValgrind.cc
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *a = new int(2);
//delete a;
return 0;
}
xchonxu/testCode> g++ -g -o testValgrind testValgrind.cc
xchonxu/testCode> ~/bin/bin/valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full ./testValgrind
==3598== Memcheck, a memory error detector
==3598== Copyright (C) 2002-2015, and GNU GPL‘d, by Julian Seward et al.
==3598== Using Valgrind-3.12.0 and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==3598== Command: ./testValgrind
==3598==
==3598==
==3598== HEAP SUMMARY:
==3598== in use at exit: 4 bytes in 1 blocks
==3598== total heap usage: 1 allocs, 0 frees, 4 bytes allocated
==3598==
==3598== 4 bytes in 1 blocks are definitely lost in loss record 1 of 1
==3598== at 0x4C292DF: operator new(unsigned long) (vg_replace_malloc.c:332)
==3598== by 0x4007AF: main (testValgrind.cc:7)
==3598==
==3598== LEAK SUMMARY:
==3598== definitely lost: 4 bytes in 1 blocks
==3598== indirectly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==3598== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==3598== still reachable: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==3598== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==3598==
==3598== For counts of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -v
==3598== ERROR SUMMARY: 1 errors from 1 contexts (suppressed: 2 from 2)
Memcheck将内存泄露分为两种,一种是可能的内存泄露(Possibly lost),另外一种是确定的内存泄露(Definitely lost)。Possibly lost 是指仍然存在某个指针能够访问某块内存,但该指针指向的已经不是该内存首地址。Definitely lost 是指已经不能够访问这块内存。而Definitely lost又分为两种:直接的(direct)和间接的(indirect)。直接和间接的区别就是,直接是没有任何指针指向该内存,间接是指指向该内存的指针都位于内存泄露处。在上述的例子中,根节点是directly lost,而其他节点是indirectly lost
原理:
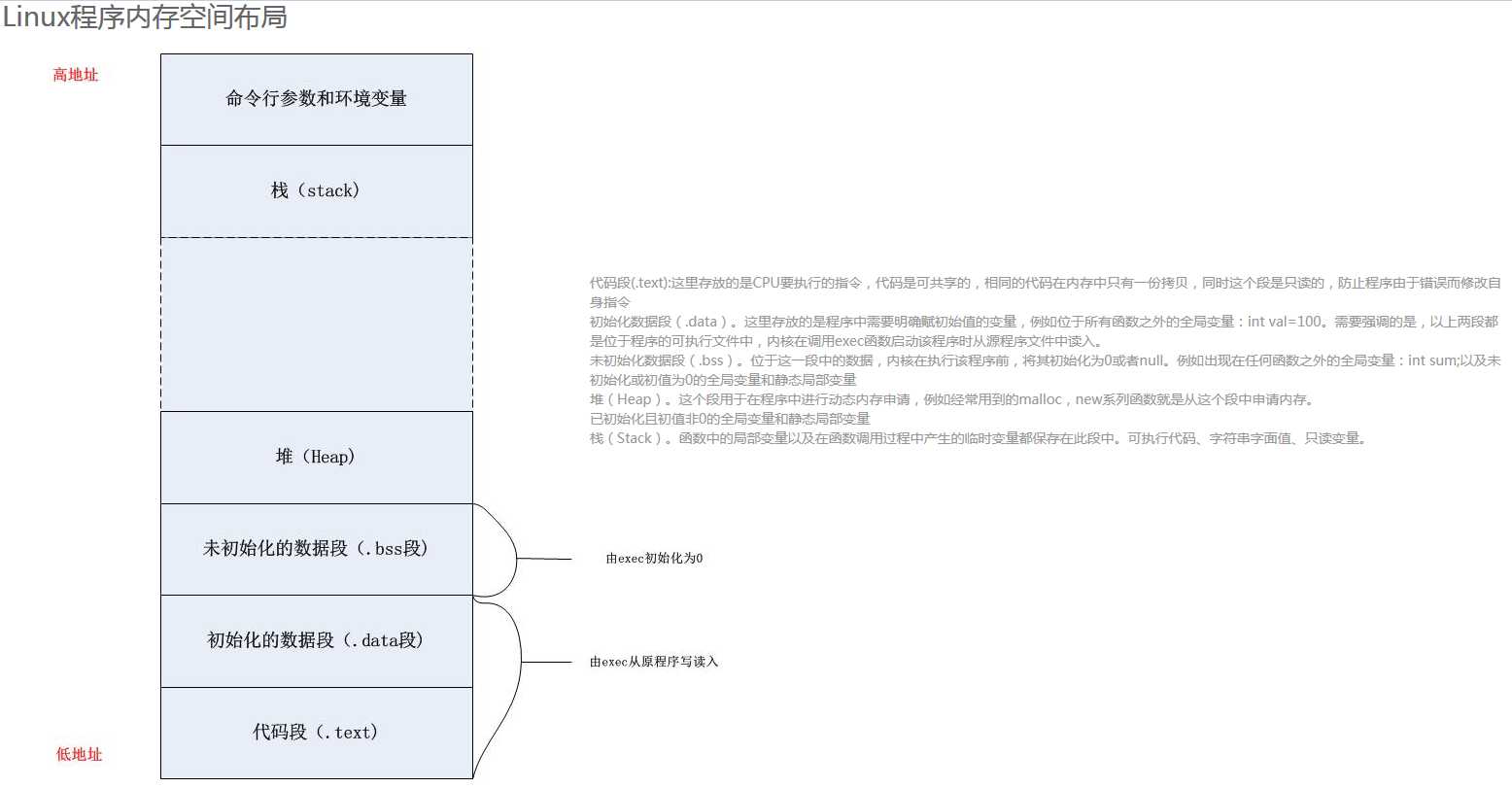
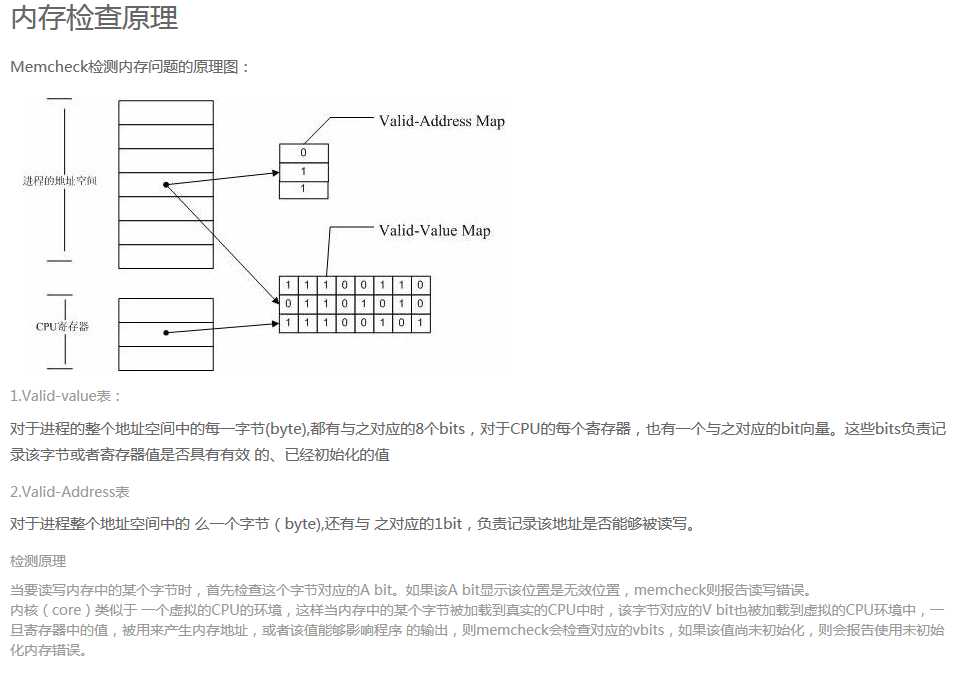
参考网站:
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-06/63754.htm
http://elinux.org/Valgrind (wiki)
http://blog.csdn.net/sduliulun/article/details/7732906
http://blog.csdn.net/gatieme/article/details/51959654(比较全面的介绍)
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-06/63754.htm (非常详细的介绍了每个工具的使用)
标签:core dump info valgrind 描述符 子线程 使用情况 using 默认 ref
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/AndyStudy/p/6409287.html