标签:二维数组 输出 software 记录 基于 else 参数 tps 开始
看了大家对于本课程的目标和规划,很多同学都希望能提高自己的实践能力,没有捷径可走,就是练习、练习再练习!那么就从第一个个人项目开始吧,用一周的时间完成一个基于控制台的四则运算程序,实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序
从《构建之法》第一章的 “程序” 例子出发,像阿超那样,花二十分钟写一个能自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行 “软件”,满足以下需求:
1、自动生成题目
2、除了整数,还要支持真分数运算
3、判断答案正确与否(可以识别真分数答案)
4、可以控制生成题目数量实现步骤
5、化简分数成最简结果
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; void DealFenshu(int m, int a[][2]) { for(int p=0;p<m;p++) { int i=(int)rand()%10; int j=(int)rand()%10; while(j==0||i>=j) { i=(int)rand()%10; j=(int)rand()%10; } int x=(int)rand()%10; int y=(int)rand()%10; while(y==0||x>=y) { x=(int)rand()%10; y=(int)rand()%10; } int k=(int)rand()%100/25; switch(k) { case 0: cout<<"("<<i<<"/"<<j<<")"<<"+"<<"("<<x<<"/"<<y<<")"<<"="; a[p][0]=i*y+x*j; a[p][1]=j*y; break; case 1: cout<<"("<<i<<"/"<<j<<")"<<"-"<<"("<<x<<"/"<<y<<")"<<"="; a[p][0]=i*y-x*j; a[p][1]=j*y; break; case 2: cout<<"("<<i<<"/"<<j<<")"<<"*"<<"("<<x<<"/"<<y<<")"<<"="; a[p][0]=i*x; a[p][1]=j*y; break; case 3: a[p][0]=i*y; a[p][1]=j*x; cout<<"("<<i<<"/"<<j<<")"<<"/"<<"("<<x<<"/"<<y<<")"<<"="; } if(p%5==4) { cout<<endl; } else { cout<<‘\t‘; } } } void DisplayFenshu(int a[][2],int w,int m) { if(w==1) { for(int q=0;q<m;q++) { if(a[q][0]==0) cout<<"0"<<‘\t‘; else cout<<a[q][0]<<"/"<<a[q][1]<<‘\t‘; if(q%5==4) { cout<<endl; } } } else {}; } void DealInt(int m,int a[]) { for(int p=0;p<m;p++) { int i=(int)rand()%10; int j=(int)rand()%10; int k=(int)rand()%100/25; switch(k) { case 0: cout<<i<<"+"<<j<<"="; a[p]=i+j; break; case 1: cout<<i<<"-"<<j<<"="; a[p]=i-j; break; case 2: cout<<i<<"*"<<j<<"="; a[p]=i*j; break; case 3: try { a[p]=i/j; cout<<i<<"/"<<j<<"="; } catch(...) { p--; } } if(p%5==4) { cout<<endl; } else { cout<<‘\t‘; } } } void DisplayInt(int a[],int w,int m) { if(w==1) { for(int q=0;q<m;q++) { cout<<a[q]<<‘\t‘; if(q%5==4) { cout<<endl; } } } else {}; } int main() { int p; do { system("cls"); int a[1000],b[1000][2]; int m,n,w; cout<<"请输入生成的四则运算题个数:"; cin>>m; cout<<endl; cout<<"请输入要生成的四则运算种类(输入1为整数,否则为真分数):"; cin>>n; cout<<endl; if(n==1) { DealInt(m,a); cout<<endl; } else { DealFenshu(m,b); cout<<endl; } cout<<"是否输出答案(输入1则输出答案否则不输出答案)"<<endl; cin>>w; if(n==1) { DisplayInt(a,w,m); } else { DisplayFenshu(b,w,m); } cout<<endl; cout<<"是否继续生成运算题(输入1则生成否则不生成)"<<endl; cin>>p; cout<<endl; }while(1==p); }
测试运行:
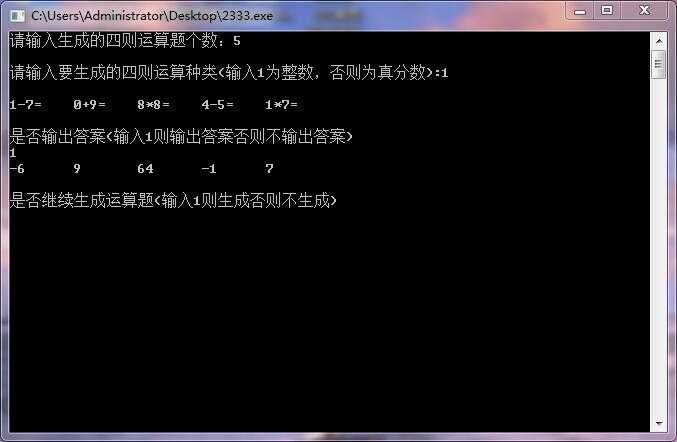
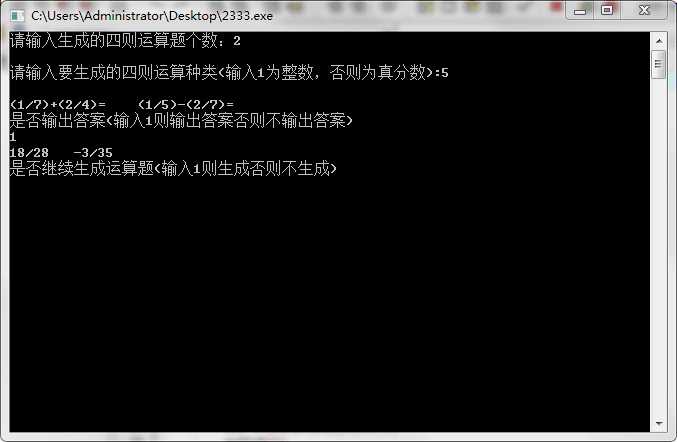
展示PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | Time (m) Senior Student | Time (m) |
| Planning | 计划 | 8 | 6 |
| · Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 8 | 6 |
| Development | 开发 | 82 | 88 |
| · Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 6 | 10 |
| · Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 5 | 6 |
| · Design Review | 设计复审 | 4 | 6 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 3 | 3 |
| · Design | 具体设计 | 10 | 12 |
| · Coding | 具体编码 | 36 | 21 |
| · Code Review | 代码复审 | 7 | 9 |
| · Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 13 | 21 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 9 | 6 |
| · | 测试报告 | 3 | 2 |
| · | 计算工作量 | 2 | 1 |
| · | 并提出过程改进计划 | 3 | 3 |
标签:二维数组 输出 software 记录 基于 else 参数 tps 开始
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Mr-zfmmm/p/6518532.html