标签:proxy dex sage UI doc ext error chm ops
场景:项目需要部署在生产环境中,这些新的工具都需要在生产环境中去实践练习。有时间再部署一套ELK的日志分析系统,这样的系统才算具有一定的应用价值。
用root用户安装,采用源代码编译的方式来进行安装,正式开始前,请确认gcc、g++开发库之类的已经预先安装好
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
先把nginx安装要用到的所有文件(“软件/nginx-1.8.0 下面的所有文件”)上传至服务器/root/nginx目录(没有该目录则新建)
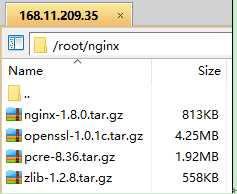
一般我们都需要先装pcre,zlib,前者用于url rewrite,后者用于gzip压缩,openssl用于后续可能升级到https时使用
首先切换到nginx目录
cd /root/nginx
tar -zxvf pcre-8.36.tar.gz cd pcre-8.36/ ./configure make make install
tar -zxvf zlib-1.2.8.tar.gz cd zlib-1.2.8/ ./configure make make install
tar -zxvf openssl-1.0.1c.tar.gz cd openssl-1.0.1c/ ./config make make install
tar -zxvf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz cd nginx-1.8.0/ #这里要根据自己安装软件的版本填写 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-pcre=../pcre-8.36 --with-zlib=../zlib-1.2.8 --with-openssl=../openssl-1.0.1c make make install
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin //启动 ./nginx ps –ef|grep nginx //关闭进程 kill -QUIT 主进程号(上面ps命令看到的带master字样的进程号)
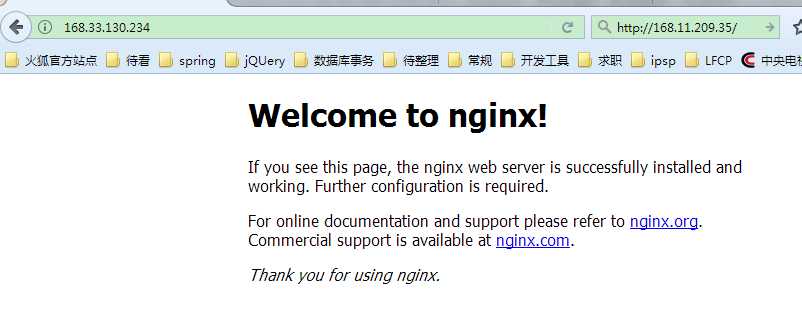
浏览器访问如:http://168.33.130.234/
如果能正常显示nginx首页,则表示安装成功,测试关闭
ps:这里看到很多清晰明白的nginx开机自启动教程,但是死活都安装不成功。最后询问运维人员发现是系统不一致造成的。这里我采用的suse系统,所以自启动脚本的制作过程不太一样。
常规自启动过程:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/FBva2i
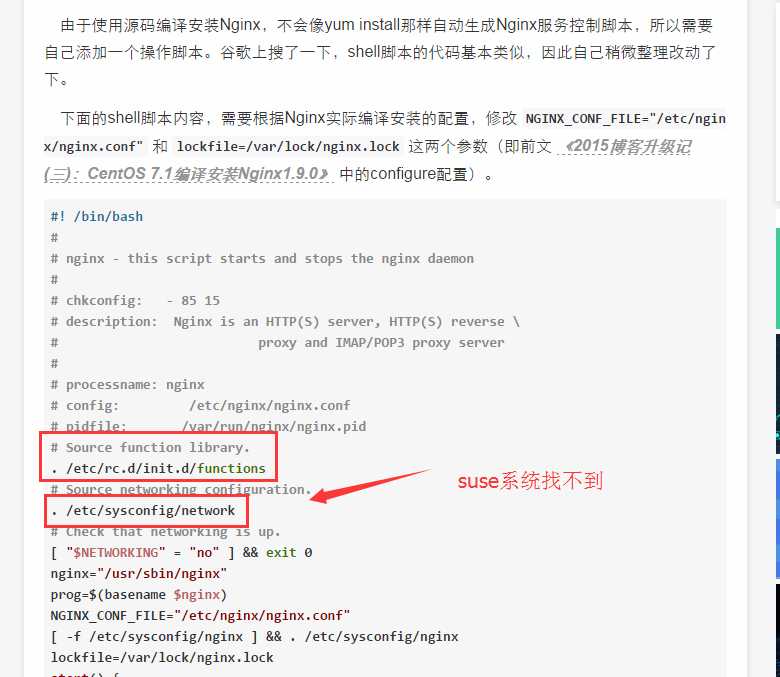
没办法,这里只能另外寻求解决办法:
[root@localhost nginx-1.0.15]# ln -sf /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/sbin
[root@linux nginx-1.0.15]# netstat -anpt|grep 80 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 16787/nginx [root@linux nginx-1.0.15]#
在客户端浏览器中执行:http://10.0.0.133(服务器IP地址)进行查看:
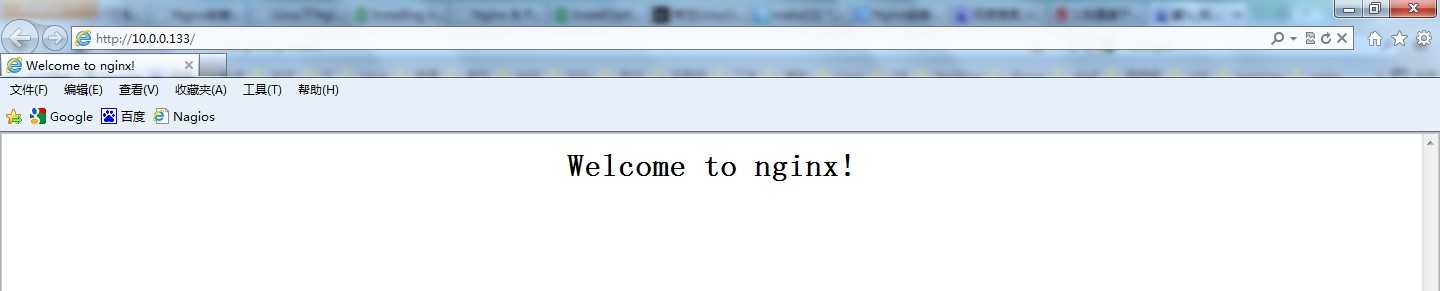
[root@localhost nginx-0.8.54]# elinks http://10.0.0.133
6.使用系统信号控制nginx进程:
启动:nginx
重启:kill -HUP `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`
#!/bin/bash #description: Nginx Service Control Script case "$1" in start) /usr/sbin/nginx ;; stop) /usr/bin/killall -s QUIT nginx ;; restart) $0 stop $0 start ;; reload) /usr/bin/killall -s HUP nginx ;; *) echo "Usage:$0 {start|stop|restart|reload}" exit 1 esac exit 0
接下来就可以使用service nginx stop|start|restart|reload对nginx服务进行控制:
[root@linux nginx-1.0.15]# service nginx restart
[root@linux nginx-1.0.15]# !nets
netstat -anpt|grep 80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 16787/nginx
[root@linux nginx-1.0.15]#
以root用户登录ssh
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
vi nginx.conf
#修改配置 worker_processes 4; events { use epoll; worker_connections 65535; } #生产虚拟机为4个物理cpu,32GB内存,使用epoll事件模型,最大连接数为65535 #在http{}里面配置增加 client_max_body_size 200m; client_header_buffer_size 16k; large_client_header_buffers 4 64k; keepalive_timeout 900; gzip on; gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml; #负载均衡配置 upstream opss.web{ ip_hash; server 168.11.209.37:80; server 168.11.209.42:80; } #在server{}里面增加配置 location ^~ /opssweb/ { proxy_pass http://opss.web; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; client_max_body_size 10m; client_body_buffer_size 128k; proxy_connect_timeout 900; proxy_send_timeout 900; proxy_read_timeout 900; proxy_buffer_size 4k; proxy_buffers 4 32k; proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; }
配置也很简单,upstream中配置轮询策略和服务器的ip、端口(端口可以去tomcat的server.xml中查看),绿色部分随意命名,只要一只即可。
upstream 那里随便命名 和下面server里面的proxy_pass名称对应上就可以了
nginx通过ip和端口 会自动找到tomcat部署的应用程序 ,与server.xml中的<Context path= 配置无关。
这里附上自己的配置示例nginx.conf:
#user nobody; worker_processes 8; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { use epoll; worker_connections 65535; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; client_max_body_size 200m; client_header_buffer_size 16k; large_client_header_buffers 4 64k; #log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ # ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘ # ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 900; gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml; gzip on; upstream nginxweb{
ip_hash; #轮询侧率(如果省略就执行轮换轮询)
#这里的ip和端口随意添加,和tomcat中的应用保持一只 server 168.33.131.126:8088; server 168.33.130.234:8088; } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root # concurs with nginx‘s one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} location ^~ /lfcpweb/ { proxy_pass http://nginxweb; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; client_max_body_size 10m; client_body_buffer_size 128k; proxy_connect_timeout 900; proxy_send_timeout 900; proxy_read_timeout 900; proxy_buffer_size 4k; proxy_buffers 4 32k; proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; } } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }
配置完成后,只要server端的应用正常启动,就可以通过
http://168.33.130.234/lfcpweb/login来访问
server 168.33.131.126:8088;
server 168.33.130.234:8088;两台服务器上的应用,这里我是通过改变轮询侧率,然后在两台服务器上查看日志打印来确定nginx能够正常的工作
1
标签:proxy dex sage UI doc ext error chm ops
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lixuwu/p/6567793.html