标签:全局变量 对象 span 实现 new collect cte stat tor
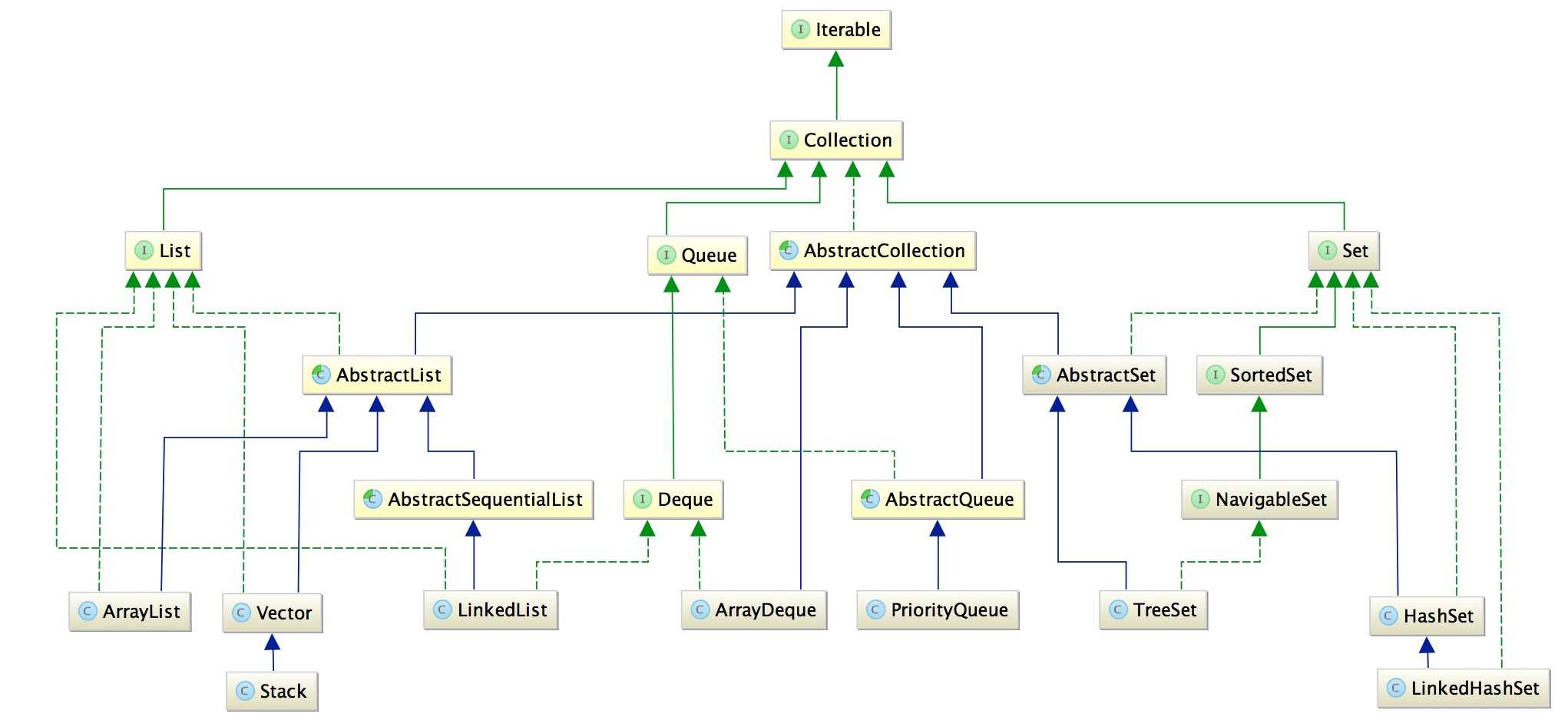
图中的绿色的虚线代表实现,绿色实线代表接口之间的继承,蓝色实线代表类之间的继承。
1)AbstractCollection:提供了大量的Collectin实现
两个抽象方法:
public abstract Iterator<E> iterator();
public abstract int size();
2)AbstractList:随机访问列表,内部提供了Iterator,ListIterator迭代器的实现,分别为Itr和ListItr(继承Itr),ListItr多了向前和set操作
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
//类似于游标 int cursor = 0; //上一次迭代到的元素的位置 int lastRet = -1; // modCount是一个全局变量,表示该List对象修改的次数 int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size(); } public E next() {
//这个方法时检测modCount与expectedModCount是否相等,是否有并发修改操作 checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor;
//get(i)是abstract方法 E next = get(i);
//记录上次迭代的位置 lastRet = i; cursor = i + 1; return next; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet); if (lastRet < cursor) cursor--; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
此外,还有两个类:SubList和RandomAccessSubList,这两个类的用处是什么呢?
在AbstractList中,有subList这样一个方法
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { return (this instanceof RandomAccess ? new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) : new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex)); }
RandomAccess:标识某个类是否支持随机访问,在这里是判断这个List是否是RandomAccess的实例
RandomAccessSubList:只是加了RandomAccess标识,重点看SubList
1 class RandomAccessSubList<E> extends SubList<E> implements RandomAccess { 2 RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 3 super(list, fromIndex, toIndex); 4 } 5 6 public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 7 return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex); 8 } 9 }
SubList:
标签:全局变量 对象 span 实现 new collect cte stat tor
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cxxblog/p/6677961.html