标签:bin ranch sources statistic connect taf line lists ilo
| Population tables of world cities |
|---|
 |
A megalopolis (sometimes called a megapolis; also megaregion, or supercity)[1] is typically defined as a chain of roughly adjacent metropolitan areas. The term was used by Patrick Geddes in his 1915 book Cities in Evolution,[2] by Oswald Spengler in his 1918 book The Decline of the West, and Lewis Mumford in his 1938 book The Culture of Cities, which described it as the first stage in urban overdevelopment and social decline. Later, it was used by Jean Gottmann in his landmark 1961 study, Megalopolis: The Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States, to describe the chain of metropolitan areas along the northeastern seaboard of the U.S. extending from Boston, Massachusetts, through New York City, Philadelphia, Baltimore, and ending in Washington, D.C. and Northern Virginia.[3][4][5] The latter is sometimes called the "BosWash megalopolis".
Megalopolis is a Western deformation of the Greek word that derived from Greek: μ?γα? - ‘great‘ and Greek: π?λι? - ‘city‘, therefore literally a ‘great city‘. This term is closer in meaning to megacity. Because in Greek, π?λι? is feminine, the correct term is megalopolis.
A megalopolis, also known as a megaregion, is a clustered network of cities. Gottmann defined its population as 25 million.[6] Doxiadis defined a small megalopolis a similar cluster with a population of about 10 million.[7][8][9] America 2050,[10] a program of the Regional Plan Association, lists 11 megaregions in the United States and Canada.[7] Literally, megalopolis in Greek means a city of exaggerated size where the prefix megalo- represents a quantity of exaggerated size.[11] Megapolitan areas were explored in a July 2005 report by Robert E. Lang and Dawn Dhavale of the Metropolitan Institute at Virginia Tech.[12] A later 2007 article by Lang and Nelson uses 20 megapolitan areas grouped into 10 megaregions.[13] The concept is based on the original Megalopolis model.[9]
Modern interlinked ground transportation corridors, such as rail and highway, often aid in the development of megalopolises. Using these commuter passageways to travel throughout the megalopolis is informally called megaloping. This term was coined by Davide Gadren and Stefan Berteau.[14]
In July 2012, the Economist Intelligence Unit brought out a report entitled; Supersized cities: China’s 13 megalopolises, which pinpoints the 13 emerging megalopolises in China, and highlights the demographic and income trends that are shaping their development.
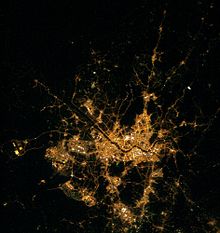


Karachi comprises six district municipal corporations. The total population is 24 million according to the 2011 estimate.
Kathmandu valley, which consists of 5 municipalities namely Kathmandu, Lalitpur, Bhaktapur, Kirtipur and Madhyapur Thimi, along with the peripheral cities of Banepa, Panauti and Dhulikhel.
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Country | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Java | 141[26] | Jakarta, Bandung, Surabaya, Yogyakarta, Bekasi, Bogor, Depok, Malang, Semarang, Tasikmalaya, Tangerang, Cirebon | |
| 2 | Mega Manila | 40+ | Manila, Calamba, Angeles, Baguio, Batangas, Dagupan, Olongapo, Bacoor | |
| 3 | Central Thailand | 25+ | Bangkok, Ayuthaya, Pattaya | |
| 4 | Southeast Economic Zone | 16+ | ??ng Nai, Bình D??ng, Ho Chi Minh City, Bà R?a–V?ng Tàu Province, Long An, Ti?n Giang |
Mega Manila is made up of 4 Regions:
(Regional Centers) San Fernando-Manila-Calamba-Calapan
Total Population of Mega Manila as of 2015: (40,624,035)[27]
(all figures extrapolated from end of 2014 and end of 2015 figures of,[30] to middle of year 2016)
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Greater Copenhagen | 3.9[35][36] | Copenhagen, Malm?, Helsingborg, Lund, and Roskilde |
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paris metropolitan area | 12.3[37] | Paris & most of ?le-de-France |
| 2 | Lyon economic region | 5.5[32] | Lyon & Rh?ne-Alpes river area |
| 3 | Marseille metropolitan region | 1.8[32] | Marseille, Aix-en-Provence |
| 4 | Toulouse economic region | 1.5[32] | Toulouse, Andorra (independent state, not a part of France) |
| 5 | Nice economic region | 1.1[32] | Nice, Monaco (independent city state, not a part of France) |
| Rank | Megalopolis name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rhine-Ruhr | 13.5 | Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund, Essen |
| 2 | Berlin-Brandenburg | 5.95 | Berlin, Potsdam |
| 3 | Frankfurt Rhine-Main | 5.52 | Frankfurt, Wiesbaden, Mainz |
| 4 | Stuttgart Metropolitan Region | 5.29[32] | Stuttgart |
| 5 | Munich Metropolitan Region | 5.2[32] | Munich |
| 6 | Hamburg Metropolitan Region | 5.0 | Hamburg |
| 7 | Central German Metropolitan Region (Saxon triangle) | 4.36[32] | Leipzig, Halle, Dresden |
| 8 | Hannover–Braunschweig–G?ttingen–Wolfsburg Metropolitan Region | 3.91[32] | Hanover, Braunschweig, G?ttingen, Wolfsburg |
| 9 | Nuremberg Metropolitan Region | 3.5[32] | Nuremberg |
| 10 | Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region | 2.37[32] | Bremen, Oldenburg |
| Rank | Megalopolis name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grande Milano | 7.5 | Milan |
| 2 | Naples metropolitan area | 4.46 | Naples |
| 3 | Rome metropolitan area | 4.3 | Rome |
| 4 | Turin economic region | 4.1 | Turin & Piedmont centre and south area |
| 5 | Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area | 2.6 | Venice & Padua & Treviso central-eastern Veneto region |
| 6 | Genoa metropolitan region | 1.5 | Genoa |
| 7 | Conca d‘Oro | 1.1 | Palermo and neighboring cities |
Netherlands, Belgium & Luxembourg:[32]
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Randstad | 7.5 | Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht |
| 2 | Flemish Diamond | 5.5 | Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent, Leuven |
| 3 | Brabantse Stedenrij | 2.0 | Eindhoven, Tilburg, Breda, ‘s-Hertogenbosch, Helmond |
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Silesian Metropolis | 5.3 | Katowice, Ostrava |
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Madrid region | 6.3 | Madrid, Alcalá de Henares, Fuenlabrada, Getafe, Alcobendas, Alcorcón, Leganés, Móstoles |
| 2 | Barcelona | 5 | Barcelona |
| 3 | Valencia | 3 | Valencia, Alicante, Elche, Benidorm, Sagunto, Gandia, Castellón, Vinaròs, Burriana |
| 4 | Sevilla | 1.3 | Sevilla, Dos Hermanas, Utrera |
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | London commuter belt | 14.0[40] | London, Medway, Southend-on-Sea, Chelmsford, Basildon, Luton, Reading |
| 2 | Northern England | 9.4[32][41] | Manchester, Leeds, Liverpool, Sheffield, Warrington, Bradford, Birkenhead, Preston, Blackburn, Blackpool |
| 3 | English midlands | 6.3[32][41] | Birmingham, Nottingham, Coventry, Leicester, Wolverhampton, Derby, Stoke-on-Trent |
| 4 | Central Belt | 3.6[41] | Glasgow, Edinburgh |
| 5 | South Hampshire-Brighton | 2.8[32][41] | Southampton, Portsmouth, Brighton, Worthing, Littlehampton, Bournemouth |
| 6 | Tyne & Wear Region | 2.2[32][41] | Newcastle, Sunderland, Middlesbrough |
| 7 | Cardiff-Bristol-Swansea | 2.2[32][41] | Cardiff, Bristol, Swansea, Newport |
| Megalopolis name | Population in millions 2011 | Population in millions 2025 (projected) | Population percent growth 2011 - 2025 (projected) | Major cities | Related articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quebec City–Windsor Corridor | 18.4 | 21 | 14.1% | Hamilton, Kingston, Kitchener, London, Mississauga, Montreal, Oshawa, Ottawa, Peterborough, Quebec City, Toronto, Trois-Rivières, Windsor | Southern Ontario |
| Calgary–Edmonton Corridor | 2.7 | 4 | 48.1% | Calgary, Edmonton, Red Deer, St. Albert, Airdrie | Calgary Region, Edmonton Capital Region, Central Alberta |
| Megalopolis name | Population in millions 2015 | Population in millions 2025 (projected) | Population percent growth 2000 - 2025 (projected) | Major cities | Related articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bajío | 11 | ? | ?% | León, Querétaro, Aguascalientes, Celaya, Irapuato, San Juan del Río, Salamanca | Bajío |
| Mexico City megalopolis | 34 | ? | ?% | Mexico City, Puebla, Cuernavaca, Toluca, Pachuca, Tula, Tlaxcala, Cuautla, Tulancingo |
Constituent urban areas of each megalopolis are based on reckoning by a single American organization, the Regional Plan Association (RPA). The RPA definition of the Great Lakes Megalopolis includes some Canadian metropolitan areas with the United States, including some but not all major urban centres in the Windsor-Quebec City Corridor. Note that one city, Houston, is listed in two different Megalopolis regions as defined by the RPA, (the Gulf Coast and Texas Triangle).[7][42]
| Megalopolis Name | Population in millions | Major cities |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney Region[citation needed] | 5.6[45] | Greater Sydney (including Central Coast and Blue Mountains) (4.92 million), Newcastle and Lake Macquarie (370,000), Illawarra (300,000) |
| South East Queensland[citation needed] | 3.5[45] | Greater Brisbane (2.3 million), Gold Coast-Tweed Heads (662,000), Sunshine Coast (341,000), Toowoomba (152,000) |
| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2015[46] | Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expanded Metropolitan Complex of S?o Paulo | +32,200,000 | S?o Paulo and Campinas | Sorocaba, Jundiaí, S?o José dos Campos, Piracicaba and Santos |
| Greater Rio de Janeiro | +12,000,000 | Rio de Janeiro and S?o Gon?alo | Nova Igua?u, Duque de Caxias, Niterói and Petrópolis |
| Greater Belo Horizonte | +5,800,000 | Belo Horizonte and Contagem | Betim, Nova Lima and Sete Lagoas |
| Greater Porto Alegre | +4,200,000 | Porto Alegre and Canoas | S?o Leopoldo, Novo Hamburgo and Gravataí |
The following megaregions in Colombia are expected to have nearly 93% (55 Million people) of its population by 2030, up from the current 72%. There are currently 4 major megaregions in Colombia.
| Megalopolis name | Population in 2015 | Population in 2030 (projected) | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bogota National Capital Metropolis | 17,000,000 | 26,500,000 | Bogotá, Soacha, Facatativá, Chía, Tunja, Fusagasugá, Zipaquirá, Madrid, Funza, Cajicá, Ubaté, Sibaté, Guaduas, Villa de Leyva and Tocancipá |
| Pacific Belt | 9,000,000 | 14,000,000 | Medellín, Cali, Bello, Pereira, Colombia, Manizales, Armenia, Itagüí, Yumbo, and Palmira |
| Northeast Atlantic Region | 6,000,000 | 10,500,000 | Barranquilla, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Ciénaga, Malambo, Baranoa and Turbaco |
| Santander Belt | 3,000,000 | 5,200,000 | Bucaramanga, Cúcuta, Oca?a, and Pamplona |
Other sources[47] show that another megaregion may be considered:
| Megalopolis name | Population in 2015 | Population in 2030 (projected) | Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Golden Triangle | 29,500,000 | 41,000,000 | Bogotá, Soacha, Medellín, Cali, Bello, Manizales, Armenia |
| Megalopolis name | Population in 2013 | Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caracas-Valencia Megalopolis | +9,000,000 | Caracas, Valencia, and Maracay | Cagua, Maiquetía, and Guatire |

| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2013 | Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater Buenos Aires | 13,641,973 | Buenos Aires, Merlo, Buenos Aires, Quilmes, Banfield, Buenos Aires | Lanús, Hurlingham, Buenos Aires, and Avellaneda |
| Megalopolis name | Population in 2013 | Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lima-Callao Megalopolis | 10,523,796 | Lima and Callao | Cono Norte, Cono Sur, and Cono Este |
标签:bin ranch sources statistic connect taf line lists ilo
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/stevendes1/p/6683671.html