标签:结束 相加 plist 相等 ipo 数据 include 第一个 排列
在《数据结构与算法分析--c语言描述》一书中,作者指出了使用单向链表作为实现多项式的方法。但是没有给出具体实现。下面自己对其进行实现。只考虑功能。对其他细节不暂时不考虑。程序完成两个功能,使用单向链表完成多项式的加法和乘法。首先看加法,解决加法问题的思想在于对表示进行操作的两个链表表示的多项式按照指数递减的结构排列,每个节点的数据域存储着多项式某一项的系数(Coefficient)和指数(Exponent),还有一个指向后继节点的指针。节点的实现如下:
1 typedef struct Node* PtrToNode; 2 struct Node 3 { 4 int Coefficient; 5 int Exponent; 6 PtrToNode Next; 7 };
为多项式定义以下操作:
1 #ifndef POLY_H_ 2 #define POLY_H_ 3 4 typedef struct Node* PtrToNode; 5 typedef PtrToNode Polynomial; 6 7 Polynomial CreatePoly(); 8 void Insert(int Coe,int Exp,Polynomial P); 9 Polynomial AddPoly(Polynomial P1,Polynomial P2); 10 Polynomial MultiPoly(Polynomial P1,Polynomial P2); 11 void PrintPoly(Polynomial P); 12 13 #endif
下面是每个函数的实现:
1 #include<stdlib.h> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 typedef struct Node* PtrToNode; 4 struct Node 5 { 6 int Coefficient; 7 int Exponent; 8 PtrToNode Next; 9 }; 10 11 typedef PtrToNode Polynomial; 12 13 14 Polynomial CreatePoly() 15 { 16 Polynomial P = malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 17 P->Next = NULL; 18 return P; 19 } 20 21 void Insert(int Coe,int Exp,Polynomial P) 22 { 23 PtrToNode Temp = malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 24 Temp->Coefficient = Coe; 25 Temp->Exponent = Exp; 26 PtrToNode Pt = P; 27 28 while(Pt->Next != NULL && Exp < Pt->Next->Exponent) 29 { 30 Pt= Pt->Next; 31 } 32 Temp->Next = Pt->Next; 33 Pt->Next = Temp; 34 } 35 36 void PrintPoly(Polynomial P) 37 { 38 PtrToNode Pt = P->Next; 39 while(Pt!= NULL) 40 { 41 printf("Coe: %d,Exp: %d ",Pt->Coefficient,Pt->Exponent); 42 Pt = Pt->Next; 43 } 44 } 45 46 Polynomial AddPoly(Polynomial P1,Polynomial P2) 47 { 48 Polynomial Pt1,Pt2,PA,Pt; 49 Pt1 = P1->Next; 50 Pt2 = P2->Next; 51 PA = CreatePoly(); 52 Pt = PA; 53 while(Pt2 != NULL && Pt1 != NULL) 54 { 55 Polynomial Tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 56 Tmp->Next = NULL; 57 if(Pt1->Exponent > Pt2->Exponent) 58 { 59 Tmp->Coefficient = Pt1->Coefficient; 60 Tmp->Exponent = Pt1->Exponent; 61 Pt1 = Pt1->Next; 62 } 63 else if(Pt1->Exponent < Pt2->Exponent) 64 { 65 Tmp->Coefficient = Pt2->Coefficient; 66 Tmp->Exponent = Pt2->Exponent; 67 Pt2 = Pt2->Next; 68 } 69 else 70 { 71 Tmp->Coefficient = Pt1->Coefficient + Pt2->Coefficient; 72 Tmp->Exponent = Pt2->Exponent; 73 Pt1 = Pt1->Next; 74 Pt2 = Pt2->Next; 75 } 76 Pt->Next = Tmp; 77 Pt = Pt->Next; 78 } 79 80 if(Pt1 == NULL) 81 { 82 while(Pt2 != NULL) 83 { 84 Polynomial Tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 85 Tmp->Coefficient = Pt2->Coefficient; 86 Tmp->Exponent = Pt2->Exponent; 87 Pt->Next = Tmp; 88 Pt = Pt->Next; 89 Pt->Next = NULL; 90 Pt2 = Pt2->Next; 91 } 92 } 93 94 if(Pt2 == NULL) 95 { 96 while(Pt1 != NULL) 97 { 98 Polynomial Tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 99 Tmp->Coefficient = Pt1->Coefficient; 100 Tmp->Exponent = Pt1->Exponent; 101 Pt->Next = Tmp; 102 Pt = Pt->Next; 103 Pt->Next = NULL; 104 Pt1 = Pt1->Next; 105 } 106 } 107 108 return PA; 109 } 110 111 112 Polynomial MultiPoly(Polynomial P1,Polynomial P2) 113 { 114 Polynomial Pt1,P; 115 P = CreatePoly(); 116 Pt1 = P1->Next; 117 while(Pt1 != NULL) 118 { 119 Polynomial TmpList = CreatePoly(); 120 Polynomial Tp = TmpList; 121 Polynomial Pt2 = P2->Next; 122 while(Pt2 != NULL) 123 { 124 Polynomial TmNode = malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 125 TmNode->Exponent = (Pt1->Exponent) + (Pt2->Exponent); 126 TmNode->Coefficient = (Pt1->Coefficient) * (Pt2->Coefficient); 127 Tp->Next = TmNode; 128 Tp = Tp->Next; 129 Tp->Next = NULL; 130 Pt2 = Pt2->Next; 131 } 132 133 P = AddPoly(P,TmpList); 134 135 Pt1=Pt1->Next; 136 } 137 return P; 138 }
其中加法函数的计算思想是:用两个移动指针分别指向两个链表的第一个数据节点,比较两个节点中指数的大小,如果某个节点大,则将该节点复制出来,加入结果链表,如果相等,则对系数进行相加,指数不变进行复制,加入结果链表,如果某个链表先扫描完,将另一个没有扫描结束的链表复制到结果链表的后面。使用流程图表示:
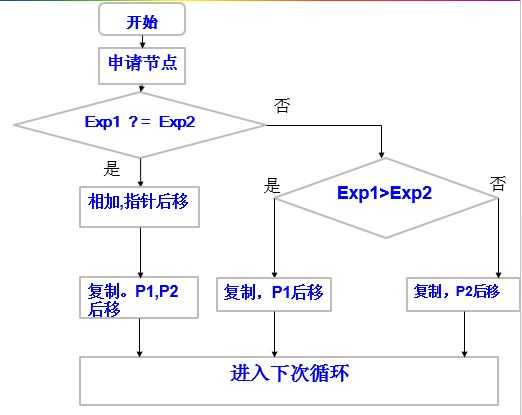
以上即为加法运算的流程图。
乘法运算的流程是:使用嵌套的while循环,使链表1的每个节点都和链表2的每个节点相乘,指数相加,系数相乘,将结果保存在一个新节点中,在链表2的每次遍历中创建一个临时链表,将计算结果保存在临时链表中,内层每循环结束一次,将临时链表和要返回的链表相加一次,这样总共相加的次数是外层循环的次数。
某种程度上将乘法运算分解成了加法运算。
标签:结束 相加 plist 相等 ipo 数据 include 第一个 排列
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangxiaoyong/p/6791595.html