标签:区别 relative tps param ups each available str text
1、模块定义
用来从逻辑上组织python代码(变量,函数,类,逻辑:实现一个功能),本质上就是.py结尾python文件
分类:内置模块、开源模块、自定义模块
2、导入模块
本质:导入模块的本质就是把python文件解释一遍;导入包的本质就是把包文件下面的init.py文件运行一遍
① 同目录下模块的导入
#同级目录间import import module_name #直接导入模块 import module_name,module2_name #导入多个模块 使用:模块名.加函数名 from module_name import * #导入模块中所有函数和变量等。。不建议使用 from module_name import m1,m2,m3 #只导入模块中函数m1,m2,m3 使用:直接使用m1,m2,m3即可 from module_name import m1 as m #导入module_name模块中m1函数并且重新赋值给m 使用:直接输入m即可
② 不同目录下模块的导入
#不同目录之间import 当前文件main.py #目录结构 # ├── Credit_card # │ # ├── core # # │ ├── __init__.py # │ └── main.py # 当前文件 # ├── conf # # │ ├── __init__.py # │ └── setting.py # │ └── lzl.py import sys,os creditcard_path=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) #当前目录的上上级目录绝对路径,即Creditcard目录 sys.path.insert(0,creditcard_path) #把Creditcard目录加入到系统路径 print(sys.path) #打印系统环境路径 #[‘C:\\Users\\L\\PycharmProjects\\s14\\Day5\\Creditcard,.......] #import settings.py #无法直接import #ImportError: No module named ‘settings‘ from conf import settings #from目录import模块 settings.set() #执行settings下的函数 #in the settings
③ 不同目录下模块连环导入
不同目录多个模块之间相互导入,为什么要引入这个概念,虽然老师没讲,但这个很重要,当时做atm程序时一个很大的坑........
目录结构:

目录结构 ├── Credit_card │ ├── core # │ ├── __init__.py │ └── main.py # 当前文件 ├── conf # │ ├── __init__.py │ └── setting.py │ └── lzl.py
conf目录下的文件:

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #-Author-Lian #当前文件lzl.py def name(): print("name is lzl")

#当前文件settings,调用lzl.py模块 import lzl #导入模块lzl def set(): print("in the settings") lzl.name() #运行lzl模块下的函数 set() #执行函数set #in the settings #name is lzl
此时执行settings.py文件没有任何问题,就是同一目录下的模块之间的导入,关键来了,此刻croe目录下的main.py导入模块settings会出现什么状况呢??!
core目录下的文件:
#不同目录之间连环import 当前文件main.py import sys,os creditcard_path=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) #当前目录的上上级目录绝对路径,即Creditcard目录 sys.path.insert(0,creditcard_path) #把Creditcard目录加入到系统路径 from conf import settings settings.set() #执行settings下的函数 # import lzl #导入模块lzl #ImportError: No module named ‘lzl‘
可以看到直接报错:ImportError: No module named ‘lzl‘,想想什么会报错类?!刚才已经说到了,导入模块的本质就是把模块里的内容执行一遍,当main.py导入settings模块时,也会把settings里的内容执行一遍,即执行import lzl;但是对于main.py来说,不能直接import lzl,所有就出现了刚才的报错,那有什么办法可以解决?!
对conf目录下settings.py文件进行修改

#当前文件settings,调用lzl.py模块 from . import lzl #通过相对路径导入模块lzl def set(): print("in the settings") lzl.name() #运行lzl模块下的函数 set() #执行函数set #in the settings #name is lzl
此时执行main.py文件
#不同目录之间连环import 当前文件main.py import sys,os creditcard_path=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) #当前目录的上上级目录绝对路径,即Creditcard目录 sys.path.insert(0,creditcard_path) #把Creditcard目录加入到系统路径 from conf import settings settings.set() #执行settings下的函数 # in the settings # name is lzl # in the settings # name is lzl
没有任何报错,我们只对settings修改了lzl模块的调用方式,结果就完全不同,此时的from . import lzl 用到的是相对路径,这就是相对路径的优点所在
④ 不同目录多个模块相互导入,用相对路径
目录结构:

Day5 ├── Credit_card ├── README.md ├── core │ ├── __init__.py │ └── main.py ├── conf │ ├── __init__.py │ └── setting.py │ └── lzl.py
conf目录下的文件:

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #-Author-Lian #当前文件lzl.py 相对路径 def name(): print("name is lzl")

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #-Author-Lian #当前文件settings,调用lzl.py模块 相对路径 from . import lzl #通过相对路径导入模块lzl def set(): print("in the settings") lzl.name() #运行lzl模块下的函数 set() #执行函数set #in the settings #name is lzl
core目录下的文件:
#不同目录之间连环import 当前文件main.py 相对路径 from Day5.Credit_card.conf import settings settings.set() #执行settings下的函数 # in the settings # name is lzl # in the settings # name is lzl
lzl.py以及settings.py文件未变,main.py文件去掉了繁杂的sys.path添加的过程,直接执行from Day5.Credit_card.conf import settings,使用相对路径,更加简洁方便!
1、time和datatime模块
时间相关的操作,时间有三种表示方式:
time模块:
#time模块 import time print(time.time()) #时间戳 #1472037866.0750718 print(time.localtime()) #结构化时间 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2016, tm_mon=8, tm_mday=25, tm_hour=8, tm_min=44, tm_sec=46, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=238, tm_isdst=0) print(time.strftime(‘%Y-%m-%d‘)) #格式化的字符串 #2016-08-25 print(time.strftime(‘%Y-%m-%d‘,time.localtime())) #2016-08-25 print(time.gmtime()) #结构化时间 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2016, tm_mon=8, tm_mday=25, tm_hour=3, tm_min=8, tm_sec=48, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=238, tm_isdst=0) print(time.strptime(‘2014-11-11‘, ‘%Y-%m-%d‘)) #结构化时间 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2014, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=11, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=315, tm_isdst=-1) print(time.asctime()) #Thu Aug 25 11:15:10 2016 print(time.asctime(time.localtime())) #Thu Aug 25 11:15:10 2016 print(time.ctime(time.time())) #Thu Aug 25 11:15:10 2016
结构化时间:
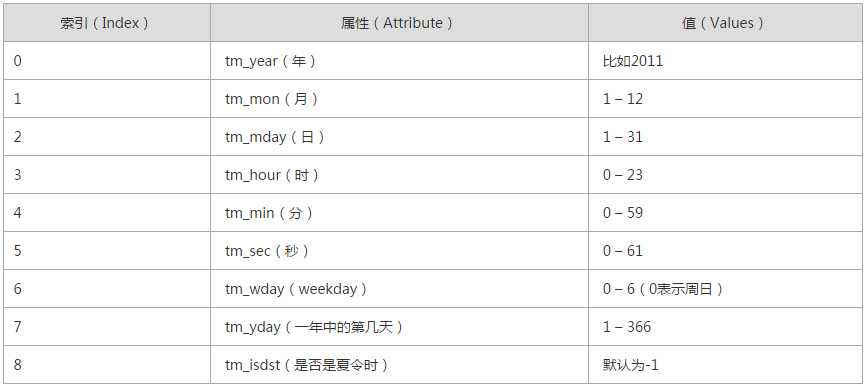
时间戳、格式化字符串、机构化时间相互转换:
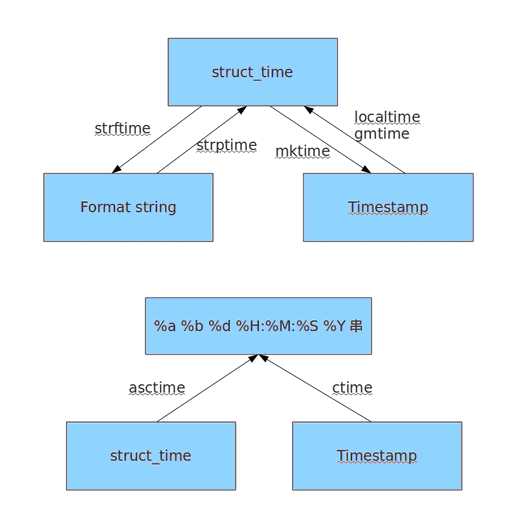
datetime:
import datetime print(datetime.date) #表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, day #<class ‘datetime.date‘> print(datetime.time) #表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microsecond #<class ‘datetime.time‘> print(datetime.datetime) #表示日期时间 #<class ‘datetime.datetime‘> print(datetime.timedelta) #表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度 #<class ‘datetime.timedelta‘> print(datetime.datetime.now()) #2016-08-25 14:21:07.722285 print(datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=5)) #2016-08-20 14:21:28.275460
更多-》》https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/23679915?utm_source=itdadao&utm_medium=referral
2、random模块
生成随机数:
#random随机数模块
import random
print(random.random()) #生成0到1的随机数
#0.7308387398872364
print(random.randint(1,3)) #生成1-3随机数
#3
print(random.randrange(1,3)) #生成1-2随机数,不包含3
#2
print(random.choice("hello")) #随机选取字符串
#e
print(random.sample("hello",2)) #随机选取特定的字符
#[‘l‘, ‘h‘]
items = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
random.shuffle(items)
print(items)
#[2, 3, 1, 6, 4, 7, 5]
验证码:
import random
checkcode = ‘‘
for i in range(4):
current = random.randrange(0,4)
if current != i:
temp = chr(random.randint(65,90))
else:
temp = random.randint(0,9)
checkcode += str(temp)
print(checkcode)
#51T6
3、os模块
用于提供系统级别的操作
#os模块
import os
os.getcwd() #获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径
os.chdir("dirname") #改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd
os.curdir #返回当前目录: (‘.‘)
os.pardir #获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:(‘..‘)
os.makedirs(‘dirname1/dirname2‘) #可生成多层递归目录
os.removedirs(‘dirname1‘) # 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
os.mkdir(‘dirname‘) # 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname
os.rmdir(‘dirname‘) #删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname
os.listdir(‘dirname‘) #列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
os.remove() # 删除一个文件
os.rename("oldname","newname") # 重命名文件/目录
os.stat(‘path/filename‘) # 获取文件/目录信息
os.sep #输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"
os.linesep #输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"
os.pathsep #输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
os.name #输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->‘nt‘; Linux->‘posix‘
os.system("bash command") #运行shell命令,直接显示
os.environ #获取系统环境变量
os.path.abspath(path) #返回path规范化的绝对路径
os.path.split(path) #将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
os.path.dirname(path) # 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
os.path.basename(path) # 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
os.path.exists(path) #如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
os.path.isabs(path) #如果path是绝对路径,返回True
os.path.isfile(path) #如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False
os.path.isdir(path) #如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) # 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) #返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间
os.path.getmtime(path) #返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
4、sys模块
用于提供对解释器相关的操作
#sys模块 import sys sys.argv #命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 sys.exit(n) #退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) sys.version # 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 sys.maxint #最大的Int值 sys.path #返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 sys.platform #返回操作系统平台名称 sys.stdout.write(‘please:‘) val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]
详情:->>http://www.cnblogs.com/lianzhilei/p/5724847.html
5、shutil模块
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
① shutil.copyfileobj 将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,可以部分内容

def copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst, length=16*1024): """copy data from file-like object fsrc to file-like object fdst""" while 1: buf = fsrc.read(length) if not buf: break fdst.write(buf)
#shutil 文件拷贝
import shutil
f1 = open("fsrc",encoding="utf-8")
f2 = open("fdst",encoding="utf-8")
shutil.copyfile(f1,f2)
#把文件f1里的内容拷贝到f2当中
② shutil.copyfile 文件拷贝

def copyfile(src, dst): """Copy data from src to dst""" if _samefile(src, dst): raise Error("`%s` and `%s` are the same file" % (src, dst)) for fn in [src, dst]: try: st = os.stat(fn) except OSError: # File most likely does not exist pass else: # XXX What about other special files? (sockets, devices...) if stat.S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode): raise SpecialFileError("`%s` is a named pipe" % fn) with open(src, ‘rb‘) as fsrc: with open(dst, ‘wb‘) as fdst: copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst)
#shutil.copyfile 文件拷贝
import shutil
shutil.copyfile("f1","f2")
#把文件f1里的内容拷贝到f2当中
③ shutil.copymode(src, dst) 仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变

def copymode(src, dst): """Copy mode bits from src to dst""" if hasattr(os, ‘chmod‘): st = os.stat(src) mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode) os.chmod(dst, mode)
④ shutil.copystat(src, dst) 拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags

def copystat(src, dst): """Copy all stat info (mode bits, atime, mtime, flags) from src to dst""" st = os.stat(src) mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode) if hasattr(os, ‘utime‘): os.utime(dst, (st.st_atime, st.st_mtime)) if hasattr(os, ‘chmod‘): os.chmod(dst, mode) if hasattr(os, ‘chflags‘) and hasattr(st, ‘st_flags‘): try: os.chflags(dst, st.st_flags) except OSError, why: for err in ‘EOPNOTSUPP‘, ‘ENOTSUP‘: if hasattr(errno, err) and why.errno == getattr(errno, err): break else: raise
⑤ shutil.copy(src, dst) 拷贝文件和权限

def copy(src, dst): """Copy data and mode bits ("cp src dst"). The destination may be a directory. """ if os.path.isdir(dst): dst = os.path.join(dst, os.path.basename(src)) copyfile(src, dst) copymode(src, dst)
⑥ shutil.copy2(src, dst) 拷贝文件和状态信息

def copy2(src, dst): """Copy data and all stat info ("cp -p src dst"). The destination may be a directory. """ if os.path.isdir(dst): dst = os.path.join(dst, os.path.basename(src)) copyfile(src, dst) copystat(src, dst)
⑦ shutil.copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None) 递归的去拷贝文件 拷贝多层目录

def ignore_patterns(*patterns): """Function that can be used as copytree() ignore parameter. Patterns is a sequence of glob-style patterns that are used to exclude files""" def _ignore_patterns(path, names): ignored_names = [] for pattern in patterns: ignored_names.extend(fnmatch.filter(names, pattern)) return set(ignored_names) return _ignore_patterns def copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None): """Recursively copy a directory tree using copy2(). The destination directory must not already exist. If exception(s) occur, an Error is raised with a list of reasons. If the optional symlinks flag is true, symbolic links in the source tree result in symbolic links in the destination tree; if it is false, the contents of the files pointed to by symbolic links are copied. The optional ignore argument is a callable. If given, it is called with the `src` parameter, which is the directory being visited by copytree(), and `names` which is the list of `src` contents, as returned by os.listdir(): callable(src, names) -> ignored_names Since copytree() is called recursively, the callable will be called once for each directory that is copied. It returns a list of names relative to the `src` directory that should not be copied. XXX Consider this example code rather than the ultimate tool. """ names = os.listdir(src) if ignore is not None: ignored_names = ignore(src, names) else: ignored_names = set() os.makedirs(dst) errors = [] for name in names: if name in ignored_names: continue srcname = os.path.join(src, name) dstname = os.path.join(dst, name) try: if symlinks and os.path.islink(srcname): linkto = os.readlink(srcname) os.symlink(linkto, dstname) elif os.path.isdir(srcname): copytree(srcname, dstname, symlinks, ignore) else: # Will raise a SpecialFileError for unsupported file types copy2(srcname, dstname) # catch the Error from the recursive copytree so that we can # continue with other files except Error, err: errors.extend(err.args[0]) except EnvironmentError, why: errors.append((srcname, dstname, str(why))) try: copystat(src, dst) except OSError, why: if WindowsError is not None and isinstance(why, WindowsError): # Copying file access times may fail on Windows pass else: errors.append((src, dst, str(why))) if errors: raise Error, errors
⑧ shutil.rmtree(path[, ignore_errors[, onerror]]) 递归的去删除文件

def rmtree(path, ignore_errors=False, onerror=None): """Recursively delete a directory tree. If ignore_errors is set, errors are ignored; otherwise, if onerror is set, it is called to handle the error with arguments (func, path, exc_info) where func is os.listdir, os.remove, or os.rmdir; path is the argument to that function that caused it to fail; and exc_info is a tuple returned by sys.exc_info(). If ignore_errors is false and onerror is None, an exception is raised. """ if ignore_errors: def onerror(*args): pass elif onerror is None: def onerror(*args): raise try: if os.path.islink(path): # symlinks to directories are forbidden, see bug #1669 raise OSError("Cannot call rmtree on a symbolic link") except OSError: onerror(os.path.islink, path, sys.exc_info()) # can‘t continue even if onerror hook returns return names = [] try: names = os.listdir(path) except os.error, err: onerror(os.listdir, path, sys.exc_info()) for name in names: fullname = os.path.join(path, name) try: mode = os.lstat(fullname).st_mode except os.error: mode = 0 if stat.S_ISDIR(mode): rmtree(fullname, ignore_errors, onerror) else: try: os.remove(fullname) except os.error, err: onerror(os.remove, fullname, sys.exc_info()) try: os.rmdir(path) except os.error: onerror(os.rmdir, path, sys.exc_info())
⑨ shutil.move(src, dst) 递归的去移动文件

def move(src, dst): """Recursively move a file or directory to another location. This is similar to the Unix "mv" command. If the destination is a directory or a symlink to a directory, the source is moved inside the directory. The destination path must not already exist. If the destination already exists but is not a directory, it may be overwritten depending on os.rename() semantics. If the destination is on our current filesystem, then rename() is used. Otherwise, src is copied to the destination and then removed. A lot more could be done here... A look at a mv.c shows a lot of the issues this implementation glosses over. """ real_dst = dst if os.path.isdir(dst): if _samefile(src, dst): # We might be on a case insensitive filesystem, # perform the rename anyway. os.rename(src, dst) return real_dst = os.path.join(dst, _basename(src)) if os.path.exists(real_dst): raise Error, "Destination path ‘%s‘ already exists" % real_dst try: os.rename(src, real_dst) except OSError: if os.path.isdir(src): if _destinsrc(src, dst): raise Error, "Cannot move a directory ‘%s‘ into itself ‘%s‘." % (src, dst) copytree(src, real_dst, symlinks=True) rmtree(src) else: copy2(src, real_dst) os.unlink(src)
⑩ shutil.make_archive(base_name, format,...) 创建压缩包并返回文件路径,例如:zip、tar
如:www =>保存至当前路径
如:/Users/wupeiqi/www =>保存至/Users/wupeiqi/

def make_archive(base_name, format, root_dir=None, base_dir=None, verbose=0, dry_run=0, owner=None, group=None, logger=None): """Create an archive file (eg. zip or tar). ‘base_name‘ is the name of the file to create, minus any format-specific extension; ‘format‘ is the archive format: one of "zip", "tar", "bztar" or "gztar". ‘root_dir‘ is a directory that will be the root directory of the archive; ie. we typically chdir into ‘root_dir‘ before creating the archive. ‘base_dir‘ is the directory where we start archiving from; ie. ‘base_dir‘ will be the common prefix of all files and directories in the archive. ‘root_dir‘ and ‘base_dir‘ both default to the current directory. Returns the name of the archive file. ‘owner‘ and ‘group‘ are used when creating a tar archive. By default, uses the current owner and group. """ save_cwd = os.getcwd() if root_dir is not None: if logger is not None: logger.debug("changing into ‘%s‘", root_dir) base_name = os.path.abspath(base_name) if not dry_run: os.chdir(root_dir) if base_dir is None: base_dir = os.curdir kwargs = {‘dry_run‘: dry_run, ‘logger‘: logger} try: format_info = _ARCHIVE_FORMATS[format] except KeyError: raise ValueError, "unknown archive format ‘%s‘" % format func = format_info[0] for arg, val in format_info[1]: kwargs[arg] = val if format != ‘zip‘: kwargs[‘owner‘] = owner kwargs[‘group‘] = group try: filename = func(base_name, base_dir, **kwargs) finally: if root_dir is not None: if logger is not None: logger.debug("changing back to ‘%s‘", save_cwd) os.chdir(save_cwd) return filename
shutil 对压缩包的处理是调用 ZipFile 和 TarFile 两个模块来进行的,详细:

import zipfile # 压缩 z = zipfile.ZipFile(‘laxi.zip‘, ‘w‘) z.write(‘a.log‘) z.write(‘data.data‘) z.close() # 解压 z = zipfile.ZipFile(‘laxi.zip‘, ‘r‘) z.extractall() z.close() zipfile 压缩解压

import tarfile # 压缩 tar = tarfile.open(‘your.tar‘,‘w‘) tar.add(‘/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/bbs2.zip‘, arcname=‘bbs2.zip‘) tar.add(‘/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/cmdb.zip‘, arcname=‘cmdb.zip‘) tar.close() # 解压 tar = tarfile.open(‘your.tar‘,‘r‘) tar.extractall() # 可设置解压地址 tar.close() tarfile 压缩解压

class ZipFile(object): """ Class with methods to open, read, write, close, list zip files. z = ZipFile(file, mode="r", compression=ZIP_STORED, allowZip64=False) file: Either the path to the file, or a file-like object. If it is a path, the file will be opened and closed by ZipFile. mode: The mode can be either read "r", write "w" or append "a". compression: ZIP_STORED (no compression) or ZIP_DEFLATED (requires zlib). allowZip64: if True ZipFile will create files with ZIP64 extensions when needed, otherwise it will raise an exception when this would be necessary. """ fp = None # Set here since __del__ checks it def __init__(self, file, mode="r", compression=ZIP_STORED, allowZip64=False): """Open the ZIP file with mode read "r", write "w" or append "a".""" if mode not in ("r", "w", "a"): raise RuntimeError(‘ZipFile() requires mode "r", "w", or "a"‘) if compression == ZIP_STORED: pass elif compression == ZIP_DEFLATED: if not zlib: raise RuntimeError, "Compression requires the (missing) zlib module" else: raise RuntimeError, "That compression method is not supported" self._allowZip64 = allowZip64 self._didModify = False self.debug = 0 # Level of printing: 0 through 3 self.NameToInfo = {} # Find file info given name self.filelist = [] # List of ZipInfo instances for archive self.compression = compression # Method of compression self.mode = key = mode.replace(‘b‘, ‘‘)[0] self.pwd = None self._comment = ‘‘ # Check if we were passed a file-like object if isinstance(file, basestring): self._filePassed = 0 self.filename = file modeDict = {‘r‘ : ‘rb‘, ‘w‘: ‘wb‘, ‘a‘ : ‘r+b‘} try: self.fp = open(file, modeDict[mode]) except IOError: if mode == ‘a‘: mode = key = ‘w‘ self.fp = open(file, modeDict[mode]) else: raise else: self._filePassed = 1 self.fp = file self.filename = getattr(file, ‘name‘, None) try: if key == ‘r‘: self._RealGetContents() elif key == ‘w‘: # set the modified flag so central directory gets written # even if no files are added to the archive self._didModify = True elif key == ‘a‘: try: # See if file is a zip file self._RealGetContents() # seek to start of directory and overwrite self.fp.seek(self.start_dir, 0) except BadZipfile: # file is not a zip file, just append self.fp.seek(0, 2) # set the modified flag so central directory gets written # even if no files are added to the archive self._didModify = True else: raise RuntimeError(‘Mode must be "r", "w" or "a"‘) except: fp = self.fp self.fp = None if not self._filePassed: fp.close() raise def __enter__(self): return self def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback): self.close() def _RealGetContents(self): """Read in the table of contents for the ZIP file.""" fp = self.fp try: endrec = _EndRecData(fp) except IOError: raise BadZipfile("File is not a zip file") if not endrec: raise BadZipfile, "File is not a zip file" if self.debug > 1: print endrec size_cd = endrec[_ECD_SIZE] # bytes in central directory offset_cd = endrec[_ECD_OFFSET] # offset of central directory self._comment = endrec[_ECD_COMMENT] # archive comment # "concat" is zero, unless zip was concatenated to another file concat = endrec[_ECD_LOCATION] - size_cd - offset_cd if endrec[_ECD_SIGNATURE] == stringEndArchive64: # If Zip64 extension structures are present, account for them concat -= (sizeEndCentDir64 + sizeEndCentDir64Locator) if self.debug > 2: inferred = concat + offset_cd print "given, inferred, offset", offset_cd, inferred, concat # self.start_dir: Position of start of central directory self.start_dir = offset_cd + concat fp.seek(self.start_dir, 0) data = fp.read(size_cd) fp = cStringIO.StringIO(data) total = 0 while total < size_cd: centdir = fp.read(sizeCentralDir) if len(centdir) != sizeCentralDir: raise BadZipfile("Truncated central directory") centdir = struct.unpack(structCentralDir, centdir) if centdir[_CD_SIGNATURE] != stringCentralDir: raise BadZipfile("Bad magic number for central directory") if self.debug > 2: print centdir filename = fp.read(centdir[_CD_FILENAME_LENGTH]) # Create ZipInfo instance to store file information x = ZipInfo(filename) x.extra = fp.read(centdir[_CD_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH]) x.comment = fp.read(centdir[_CD_COMMENT_LENGTH]) x.header_offset = centdir[_CD_LOCAL_HEADER_OFFSET] (x.create_version, x.create_system, x.extract_version, x.reserved, x.flag_bits, x.compress_type, t, d, x.CRC, x.compress_size, x.file_size) = centdir[1:12] x.volume, x.internal_attr, x.external_attr = centdir[15:18] # Convert date/time code to (year, month, day, hour, min, sec) x._raw_time = t x.date_time = ( (d>>9)+1980, (d>>5)&0xF, d&0x1F, t>>11, (t>>5)&0x3F, (t&0x1F) * 2 ) x._decodeExtra() x.header_offset = x.header_offset + concat x.filename = x._decodeFilename() self.filelist.append(x) self.NameToInfo[x.filename] = x # update total bytes read from central directory total = (total + sizeCentralDir + centdir[_CD_FILENAME_LENGTH] + centdir[_CD_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH] + centdir[_CD_COMMENT_LENGTH]) if self.debug > 2: print "total", total def namelist(self): """Return a list of file names in the archive.""" l = [] for data in self.filelist: l.append(data.filename) return l def infolist(self): """Return a list of class ZipInfo instances for files in the archive.""" return self.filelist def printdir(self): """Print a table of contents for the zip file.""" print "%-46s %19s %12s" % ("File Name", "Modified ", "Size") for zinfo in self.filelist: date = "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d" % zinfo.date_time[:6] print "%-46s %s %12d" % (zinfo.filename, date, zinfo.file_size) def testzip(self): """Read all the files and check the CRC.""" chunk_size = 2 ** 20 for zinfo in self.filelist: try: # Read by chunks, to avoid an OverflowError or a # MemoryError with very large embedded files. with self.open(zinfo.filename, "r") as f: while f.read(chunk_size): # Check CRC-32 pass except BadZipfile: return zinfo.filename def getinfo(self, name): """Return the instance of ZipInfo given ‘name‘.""" info = self.NameToInfo.get(name) if info is None: raise KeyError( ‘There is no item named %r in the archive‘ % name) return info def setpassword(self, pwd): """Set default password for encrypted files.""" self.pwd = pwd @property def comment(self): """The comment text associated with the ZIP file.""" return self._comment @comment.setter def comment(self, comment): # check for valid comment length if len(comment) > ZIP_MAX_COMMENT: import warnings warnings.warn(‘Archive comment is too long; truncating to %d bytes‘ % ZIP_MAX_COMMENT, stacklevel=2) comment = comment[:ZIP_MAX_COMMENT] self._comment = comment self._didModify = True def read(self, name, pwd=None): """Return file bytes (as a string) for name.""" return self.open(name, "r", pwd).read() def open(self, name, mode="r", pwd=None): """Return file-like object for ‘name‘.""" if mode not in ("r", "U", "rU"): raise RuntimeError, ‘open() requires mode "r", "U", or "rU"‘ if not self.fp: raise RuntimeError, "Attempt to read ZIP archive that was already closed" # Only open a new file for instances where we were not # given a file object in the constructor if self._filePassed: zef_file = self.fp should_close = False else: zef_file = open(self.filename, ‘rb‘) should_close = True try: # Make sure we have an info object if isinstance(name, ZipInfo): # ‘name‘ is already an info object zinfo = name else: # Get info object for name zinfo = self.getinfo(name) zef_file.seek(zinfo.header_offset, 0) # Skip the file header: fheader = zef_file.read(sizeFileHeader) if len(fheader) != sizeFileHeader: raise BadZipfile("Truncated file header") fheader = struct.unpack(structFileHeader, fheader) if fheader[_FH_SIGNATURE] != stringFileHeader: raise BadZipfile("Bad magic number for file header") fname = zef_file.read(fheader[_FH_FILENAME_LENGTH]) if fheader[_FH_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH]: zef_file.read(fheader[_FH_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH]) if fname != zinfo.orig_filename: raise BadZipfile, ‘File name in directory "%s" and header "%s" differ.‘ % ( zinfo.orig_filename, fname) # check for encrypted flag & handle password is_encrypted = zinfo.flag_bits & 0x1 zd = None if is_encrypted: if not pwd: pwd = self.pwd if not pwd: raise RuntimeError, "File %s is encrypted, " "password required for extraction" % name zd = _ZipDecrypter(pwd) # The first 12 bytes in the cypher stream is an encryption header # used to strengthen the algorithm. The first 11 bytes are # completely random, while the 12th contains the MSB of the CRC, # or the MSB of the file time depending on the header type # and is used to check the correctness of the password. bytes = zef_file.read(12) h = map(zd, bytes[0:12]) if zinfo.flag_bits & 0x8: # compare against the file type from extended local headers check_byte = (zinfo._raw_time >> 8) & 0xff else: # compare against the CRC otherwise check_byte = (zinfo.CRC >> 24) & 0xff if ord(h[11]) != check_byte: raise RuntimeError("Bad password for file", name) return ZipExtFile(zef_file, mode, zinfo, zd, close_fileobj=should_close) except: if should_close: zef_file.close() raise def extract(self, member, path=None, pwd=None): """Extract a member from the archive to the current working directory, using its full name. Its file information is extracted as accurately as possible. `member‘ may be a filename or a ZipInfo object. You can specify a different directory using `path‘. """ if not isinstance(member, ZipInfo): member = self.getinfo(member) if path is None: path = os.getcwd() return self._extract_member(member, path, pwd) def extractall(self, path=None, members=None, pwd=None): """Extract all members from the archive to the current working directory. `path‘ specifies a different directory to extract to. `members‘ is optional and must be a subset of the list returned by namelist(). """ if members is None: members = self.namelist() for zipinfo in members: self.extract(zipinfo, path, pwd) def _extract_member(self, member, targetpath, pwd): """Extract the ZipInfo object ‘member‘ to a physical file on the path targetpath. """ # build the destination pathname, replacing # forward slashes to platform specific separators. arcname = member.filename.replace(‘/‘, os.path.sep) if os.path.altsep: arcname = arcname.replace(os.path.altsep, os.path.sep) # interpret absolute pathname as relative, remove drive letter or # UNC path, redundant separators, "." and ".." components. arcname = os.path.splitdrive(arcname)[1] arcname = os.path.sep.join(x for x in arcname.split(os.path.sep) if x not in (‘‘, os.path.curdir, os.path.pardir)) if os.path.sep == ‘\\‘: # filter illegal characters on Windows illegal = ‘:<>|"?*‘ if isinstance(arcname, unicode): table = {ord(c): ord(‘_‘) for c in illegal} else: table = string.maketrans(illegal, ‘_‘ * len(illegal)) arcname = arcname.translate(table) # remove trailing dots arcname = (x.rstrip(‘.‘) for x in arcname.split(os.path.sep)) arcname = os.path.sep.join(x for x in arcname if x) targetpath = os.path.join(targetpath, arcname) targetpath = os.path.normpath(targetpath) # Create all upper directories if necessary. upperdirs = os.path.dirname(targetpath) if upperdirs and not os.path.exists(upperdirs): os.makedirs(upperdirs) if member.filename[-1] == ‘/‘: if not os.path.isdir(targetpath): os.mkdir(targetpath) return targetpath with self.open(member, pwd=pwd) as source, file(targetpath, "wb") as target: shutil.copyfileobj(source, target) return targetpath def _writecheck(self, zinfo): """Check for errors before writing a file to the archive.""" if zinfo.filename in self.NameToInfo: import warnings warnings.warn(‘Duplicate name: %r‘ % zinfo.filename, stacklevel=3) if self.mode not in ("w", "a"): raise RuntimeError, ‘write() requires mode "w" or "a"‘ if not self.fp: raise RuntimeError, "Attempt to write ZIP archive that was already closed" if zinfo.compress_type == ZIP_DEFLATED and not zlib: raise RuntimeError, "Compression requires the (missing) zlib module" if zinfo.compress_type not in (ZIP_STORED, ZIP_DEFLATED): raise RuntimeError, "That compression method is not supported" if not self._allowZip64: requires_zip64 = None if len(self.filelist) >= ZIP_FILECOUNT_LIMIT: requires_zip64 = "Files count" elif zinfo.file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT: requires_zip64 = "Filesize" elif zinfo.header_offset > ZIP64_LIMIT: requires_zip64 = "Zipfile size" if requires_zip64: raise LargeZipFile(requires_zip64 + " would require ZIP64 extensions") def write(self, filename, arcname=None, compress_type=None): """Put the bytes from filename into the archive under the name arcname.""" if not self.fp: raise RuntimeError( "Attempt to write to ZIP archive that was already closed") st = os.stat(filename) isdir = stat.S_ISDIR(st.st_mode) mtime = time.localtime(st.st_mtime) date_time = mtime[0:6] # Create ZipInfo instance to store file information if arcname is None: arcname = filename arcname = os.path.normpath(os.path.splitdrive(arcname)[1]) while arcname[0] in (os.sep, os.altsep): arcname = arcname[1:] if isdir: arcname += ‘/‘ zinfo = ZipInfo(arcname, date_time) zinfo.external_attr = (st[0] & 0xFFFF) << 16L # Unix attributes if compress_type is None: zinfo.compress_type = self.compression else: zinfo.compress_type = compress_type zinfo.file_size = st.st_size zinfo.flag_bits = 0x00 zinfo.header_offset = self.fp.tell() # Start of header bytes self._writecheck(zinfo) self._didModify = True if isdir: zinfo.file_size = 0 zinfo.compress_size = 0 zinfo.CRC = 0 zinfo.external_attr |= 0x10 # MS-DOS directory flag self.filelist.append(zinfo) self.NameToInfo[zinfo.filename] = zinfo self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(False)) return with open(filename, "rb") as fp: # Must overwrite CRC and sizes with correct data later zinfo.CRC = CRC = 0 zinfo.compress_size = compress_size = 0 # Compressed size can be larger than uncompressed size zip64 = self._allowZip64 and zinfo.file_size * 1.05 > ZIP64_LIMIT self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(zip64)) if zinfo.compress_type == ZIP_DEFLATED: cmpr = zlib.compressobj(zlib.Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION, zlib.DEFLATED, -15) else: cmpr = None file_size = 0 while 1: buf = fp.read(1024 * 8) if not buf: break file_size = file_size + len(buf) CRC = crc32(buf, CRC) & 0xffffffff if cmpr: buf = cmpr.compress(buf) compress_size = compress_size + len(buf) self.fp.write(buf) if cmpr: buf = cmpr.flush() compress_size = compress_size + len(buf) self.fp.write(buf) zinfo.compress_size = compress_size else: zinfo.compress_size = file_size zinfo.CRC = CRC zinfo.file_size = file_size if not zip64 and self._allowZip64: if file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT: raise RuntimeError(‘File size has increased during compressing‘) if compress_size > ZIP64_LIMIT: raise RuntimeError(‘Compressed size larger than uncompressed size‘) # Seek backwards and write file header (which will now include # correct CRC and file sizes) position = self.fp.tell() # Preserve current position in file self.fp.seek(zinfo.header_offset, 0) self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(zip64)) self.fp.seek(position, 0) self.filelist.append(zinfo) self.NameToInfo[zinfo.filename] = zinfo def writestr(self, zinfo_or_arcname, bytes, compress_type=None): """Write a file into the archive. The contents is the string ‘bytes‘. ‘zinfo_or_arcname‘ is either a ZipInfo instance or the name of the file in the archive.""" if not isinstance(zinfo_or_arcname, ZipInfo): zinfo = ZipInfo(filename=zinfo_or_arcname, date_time=time.localtime(time.time())[:6]) zinfo.compress_type = self.compression if zinfo.filename[-1] == ‘/‘: zinfo.external_attr = 0o40775 << 16 # drwxrwxr-x zinfo.external_attr |= 0x10 # MS-DOS directory flag else: zinfo.external_attr = 0o600 << 16 # ?rw------- else: zinfo = zinfo_or_arcname if not self.fp: raise RuntimeError( "Attempt to write to ZIP archive that was already closed") if compress_type is not None: zinfo.compress_type = compress_type zinfo.file_size = len(bytes) # Uncompressed size zinfo.header_offset = self.fp.tell() # Start of header bytes self._writecheck(zinfo) self._didModify = True zinfo.CRC = crc32(bytes) & 0xffffffff # CRC-32 checksum if zinfo.compress_type == ZIP_DEFLATED: co = zlib.compressobj(zlib.Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION, zlib.DEFLATED, -15) bytes = co.compress(bytes) + co.flush() zinfo.compress_size = len(bytes) # Compressed size else: zinfo.compress_size = zinfo.file_size zip64 = zinfo.file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT or zinfo.compress_size > ZIP64_LIMIT if zip64 and not self._allowZip64: raise LargeZipFile("Filesize would require ZIP64 extensions") self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(zip64)) self.fp.write(bytes) if zinfo.flag_bits & 0x08: # Write CRC and file sizes after the file data fmt = ‘<LQQ‘ if zip64 else ‘<LLL‘ self.fp.write(struct.pack(fmt, zinfo.CRC, zinfo.compress_size, zinfo.file_size)) self.fp.flush() self.filelist.append(zinfo) self.NameToInfo[zinfo.filename] = zinfo def __del__(self): """Call the "close()" method in case the user forgot.""" self.close() def close(self): """Close the file, and for mode "w" and "a" write the ending records.""" if self.fp is None: return try: if self.mode in ("w", "a") and self._didModify: # write ending records pos1 = self.fp.tell() for zinfo in self.filelist: # write central directory dt = zinfo.date_time dosdate = (dt[0] - 1980) << 9 | dt[1] << 5 | dt[2] dostime = dt[3] << 11 | dt[4] << 5 | (dt[5] // 2) extra = [] if zinfo.file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT or zinfo.compress_size > ZIP64_LIMIT: extra.append(zinfo.file_size) extra.append(zinfo.compress_size) file_size = 0xffffffff compress_size = 0xffffffff else: file_size = zinfo.file_size compress_size = zinfo.compress_size if zinfo.header_offset > ZIP64_LIMIT: extra.append(zinfo.header_offset) header_offset = 0xffffffffL else: header_offset = zinfo.header_offset extra_data = zinfo.extra if extra: # Append a ZIP64 field to the extra‘s extra_data = struct.pack( ‘<HH‘ + ‘Q‘*len(extra), 1, 8*len(extra), *extra) + extra_data extract_version = max(45, zinfo.extract_version) create_version = max(45, zinfo.create_version) else: extract_version = zinfo.extract_version create_version = zinfo.create_version try: filename, flag_bits = zinfo._encodeFilenameFlags() centdir = struct.pack(structCentralDir, stringCentralDir, create_version, zinfo.create_system, extract_version, zinfo.reserved, flag_bits, zinfo.compress_type, dostime, dosdate, zinfo.CRC, compress_size, file_size, len(filename), len(extra_data), len(zinfo.comment), 0, zinfo.internal_attr, zinfo.external_attr, header_offset) except DeprecationWarning: print >>sys.stderr, (structCentralDir, stringCentralDir, create_version, zinfo.create_system, extract_version, zinfo.reserved, zinfo.flag_bits, zinfo.compress_type, dostime, dosdate, zinfo.CRC, compress_size, file_size, len(zinfo.filename), len(extra_data), len(zinfo.comment), 0, zinfo.internal_attr, zinfo.external_attr, header_offset) raise self.fp.write(centdir) self.fp.write(filename) self.fp.write(extra_data) self.fp.write(zinfo.comment) pos2 = self.fp.tell() # Write end-of-zip-archive record centDirCount = len(self.filelist) centDirSize = pos2 - pos1 centDirOffset = pos1 requires_zip64 = None if centDirCount > ZIP_FILECOUNT_LIMIT: requires_zip64 = "Files count" elif centDirOffset > ZIP64_LIMIT: requires_zip64 = "Central directory offset" elif centDirSize > ZIP64_LIMIT: requires_zip64 = "Central directory size" if requires_zip64: # Need to write the ZIP64 end-of-archive records if not self._allowZip64: raise LargeZipFile(requires_zip64 + " would require ZIP64 extensions") zip64endrec = struct.pack( structEndArchive64, stringEndArchive64, 44, 45, 45, 0, 0, centDirCount, centDirCount, centDirSize, centDirOffset) self.fp.write(zip64endrec) zip64locrec = struct.pack( structEndArchive64Locator, stringEndArchive64Locator, 0, pos2, 1) self.fp.write(zip64locrec) centDirCount = min(centDirCount, 0xFFFF) centDirSize = min(centDirSize, 0xFFFFFFFF) centDirOffset = min(centDirOffset, 0xFFFFFFFF) endrec = struct.pack(structEndArchive, stringEndArchive, 0, 0, centDirCount, centDirCount, centDirSize, centDirOffset, len(self._comment)) self.fp.write(endrec) self.fp.write(self._comment) self.fp.flush() finally: fp = self.fp self.fp = None if not self._filePassed: fp.close() ZipFile

class TarFile(object): """The TarFile Class provides an interface to tar archives. """ debug = 0 # May be set from 0 (no msgs) to 3 (all msgs) dereference = False # If true, add content of linked file to the # tar file, else the link. ignore_zeros = False # If true, skips empty or invalid blocks and # continues processing. errorlevel = 1 # If 0, fatal errors only appear in debug # messages (if debug >= 0). If > 0, errors # are passed to the caller as exceptions. format = DEFAULT_FORMAT # The format to use when creating an archive. encoding = ENCODING # Encoding for 8-bit character strings. errors = None # Error handler for unicode conversion. tarinfo = TarInfo # The default TarInfo class to use. fileobject = ExFileObject # The default ExFileObject class to use. def __init__(self, name=None, mode="r", fileobj=None, format=None, tarinfo=None, dereference=None, ignore_zeros=None, encoding=None, errors=None, pax_headers=None, debug=None, errorlevel=None): """Open an (uncompressed) tar archive `name‘. `mode‘ is either ‘r‘ to read from an existing archive, ‘a‘ to append data to an existing file or ‘w‘ to create a new file overwriting an existing one. `mode‘ defaults to ‘r‘. If `fileobj‘ is given, it is used for reading or writing data. If it can be determined, `mode‘ is overridden by `fileobj‘s mode. `fileobj‘ is not closed, when TarFile is closed. """ modes = {"r": "rb", "a": "r+b", "w": "wb"} if mode not in modes: raise ValueError("mode must be ‘r‘, ‘a‘ or ‘w‘") self.mode = mode self._mode = modes[mode] if not fileobj: if self.mode == "a" and not os.path.exists(name): # Create nonexistent files in append mode. self.mode = "w" self._mode = "wb" fileobj = bltn_open(name, self._mode) self._extfileobj = False else: if name is None and hasattr(fileobj, "name"): name = fileobj.name if hasattr(fileobj, "mode"): self._mode = fileobj.mode self._extfileobj = True self.name = os.path.abspath(name) if name else None self.fileobj = fileobj # Init attributes. if format is not None: self.format = format if tarinfo is not None: self.tarinfo = tarinfo if dereference is not None: self.dereference = dereference if ignore_zeros is not None: self.ignore_zeros = ignore_zeros if encoding is not None: self.encoding = encoding if errors is not None: self.errors = errors elif mode == "r": self.errors = "utf-8" else: self.errors = "strict" if pax_headers is not None and self.format == PAX_FORMAT: self.pax_headers = pax_headers else: self.pax_headers = {} if debug is not None: self.debug = debug if errorlevel is not None: self.errorlevel = errorlevel # Init datastructures. self.closed = False self.members = [] # list of members as TarInfo objects self._loaded = False # flag if all members have been read self.offset = self.fileobj.tell() # current position in the archive file self.inodes = {} # dictionary caching the inodes of # archive members already added try: if self.mode == "r": self.firstmember = None self.firstmember = self.next() if self.mode == "a": # Move to the end of the archive, # before the first empty block. while True: self.fileobj.seek(self.offset) try: tarinfo = self.tarinfo.fromtarfile(self) self.members.append(tarinfo) except EOFHeaderError: self.fileobj.seek(self.offset) break except HeaderError, e: raise ReadError(str(e)) if self.mode in "aw": self._loaded = True if self.pax_headers: buf = self.tarinfo.create_pax_global_header(self.pax_headers.copy()) self.fileobj.write(buf) self.offset += len(buf) except: if not self._extfileobj: self.fileobj.close() self.closed = True raise def _getposix(self): return self.format == USTAR_FORMAT def _setposix(self, value): import warnings warnings.warn("use the format attribute instead", DeprecationWarning, 2) if value: self.format = USTAR_FORMAT else: self.format = GNU_FORMAT posix = property(_getposix, _setposix) #-------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Below are the classmethods which act as alternate constructors to the # TarFile class. The open() method is the only one that is needed for # public use; it is the "super"-constructor and is able to select an # adequate "sub"-constructor for a particular compression using the mapping # from OPEN_METH. # # This concept allows one to subclass TarFile without losing the comfort of # the super-constructor. A sub-constructor is registered and made available # by adding it to the mapping in OPEN_METH. @classmethod def open(cls, name=None, mode="r", fileobj=None, bufsize=RECORDSIZE, **kwargs): """Open a tar archive for reading, writing or appending. Return an appropriate TarFile class. mode: ‘r‘ or ‘r:*‘ open for reading with transparent compression ‘r:‘ open for reading exclusively uncompressed ‘r:gz‘ open for reading with gzip compression ‘r:bz2‘ open for reading with bzip2 compression ‘a‘ or ‘a:‘ open for appending, creating the file if necessary ‘w‘ or ‘w:‘ open for writing without compression ‘w:gz‘ open for writing with gzip compression ‘w:bz2‘ open for writing with bzip2 compression ‘r|*‘ open a stream of tar blocks with transparent compression ‘r|‘ open an uncompressed stream of tar blocks for reading ‘r|gz‘ open a gzip compressed stream of tar blocks ‘r|bz2‘ open a bzip2 compressed stream of tar blocks ‘w|‘ open an uncompressed stream for writing ‘w|gz‘ open a gzip compressed stream for writing ‘w|bz2‘ open a bzip2 compressed stream for writing """ if not name and not fileobj: raise ValueError("nothing to open") if mode in ("r", "r:*"): # Find out which *open() is appropriate for opening the file. for comptype in cls.OPEN_METH: func = getattr(cls, cls.OPEN_METH[comptype]) if fileobj is not None: saved_pos = fileobj.tell() try: return func(name, "r", fileobj, **kwargs) except (ReadError, CompressionError), e: if fileobj is not None: fileobj.seek(saved_pos) continue raise ReadError("file could not be opened successfully") elif ":" in mode: filemode, comptype = mode.split(":", 1) filemode = filemode or "r" comptype = comptype or "tar" # Select the *open() function according to # given compression. if comptype in cls.OPEN_METH: func = getattr(cls, cls.OPEN_METH[comptype]) else: raise CompressionError("unknown compression type %r" % comptype) return func(name, filemode, fileobj, **kwargs) elif "|" in mode: filemode, comptype = mode.split("|", 1) filemode = filemode or "r" comptype = comptype or "tar" if filemode not in ("r", "w"): raise ValueError("mode must be ‘r‘ or ‘w‘") stream = _Stream(name, filemode, comptype, fileobj, bufsize) try: t = cls(name, filemode, stream, **kwargs) except: stream.close() raise t._extfileobj = False return t elif mode in ("a", "w"): return cls.taropen(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs) raise ValueError("undiscernible mode") @classmethod def taropen(cls, name, mode="r", fileobj=None, **kwargs): """Open uncompressed tar archive name for reading or writing. """ if mode not in ("r", "a", "w"): raise ValueError("mode must be ‘r‘, ‘a‘ or ‘w‘") return cls(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs) @classmethod def gzopen(cls, name, mode="r", fileobj=None, compresslevel=9, **kwargs): """Open gzip compressed tar archive name for reading or writing. Appending is not allowed. """ if mode not in ("r", "w"): raise ValueError("mode must be ‘r‘ or ‘w‘") try: import gzip gzip.GzipFile except (ImportError, AttributeError): raise CompressionError("gzip module is not available") try: fileobj = gzip.GzipFile(name, mode, compresslevel, fileobj) except OSError: if fileobj is not None and mode == ‘r‘: raise ReadError("not a gzip file") raise try: t = cls.taropen(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs) except IOError: fileobj.close() if mode == ‘r‘: raise ReadError("not a gzip file") raise except: fileobj.close() raise t._extfileobj = False return t @classmethod def bz2open(cls, name, mode="r", fileobj=None, compresslevel=9, **kwargs): """Open bzip2 compressed tar archive name for reading or writing. Appending is not allowed. """ if mode not in ("r", "w"): raise ValueError("mode must be ‘r‘ or ‘w‘.") try: import bz2 except ImportError: raise CompressionError("bz2 module is not available") if fileobj is not None: fileobj = _BZ2Proxy(fileobj, mode) else: fileobj = bz2.BZ2File(name, mode, compresslevel=compresslevel) try: t = cls.taropen(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs) except (IOError, EOFError): fileobj.close() if mode == ‘r‘: raise ReadError("not a bzip2 file") raise except: fileobj.close() raise t._extfileobj = False return t # All *open() methods are registered here. OPEN_METH = { "tar": "taropen", # uncompressed tar "gz": "gzopen", # gzip compressed tar "bz2": "bz2open" # bzip2 compressed tar } #-------------------------------------------------------------------------- # The public methods which TarFile provides: def close(self): """Close the TarFile. In write-mode, two finishing zero blocks are appended to the archive. """ if self.closed: return if self.mode in "aw": self.fileobj.write(NUL * (BLOCKSIZE * 2)) self.offset += (BLOCKSIZE * 2) # fill up the end with zero-blocks # (like option -b20 for tar does) blocks, remainder = divmod(self.offset, RECORDSIZE) if remainder > 0: self.fileobj.write(NUL * (RECORDSIZE - remainder)) if not self._extfileobj: self.fileobj.close() self.closed = True def getmember(self, name): """Return a TarInfo object for member `name‘. If `name‘ can not be found in the archive, KeyError is raised. If a member occurs more than once in the archive, its last occurrence is assumed to be the most up-to-date version. """ tarinfo = self._getmember(name) if tarinfo is None: raise KeyError("filename %r not found" % name) return tarinfo def getmembers(self): """Return the members of the archive as a list of TarInfo objects. The list has the same order as the members in the archive. """ self._check() if not self._loaded: # if we want to obtain a list of self._load() # all members, we first have to # scan the whole archive. return self.members def getnames(self): """Return the members of the archive as a list of their names. It has the same order as the list returned by getmembers(). """ return [tarinfo.name for tarinfo in self.getmembers()] def gettarinfo(self, name=None, arcname=None, fileobj=None): """Create a TarInfo object for either the file `name‘ or the file object `fileobj‘ (using os.fstat on its file descriptor). You can modify some of the TarInfo‘s attributes before you add it using addfile(). If given, `arcname‘ specifies an alternative name for the file in the archive. """ self._check("aw") # When fileobj is given, replace name by # fileobj‘s real name. if fileobj is not None: name = fileobj.name # Building the name of the member in the archive. # Backward slashes are converted to forward slashes, # Absolute paths are turned to relative paths. if arcname is None: arcname = name drv, arcname = os.path.splitdrive(arcname) arcname = arcname.replace(os.sep, "/") arcname = arcname.lstrip("/") # Now, fill the TarInfo object with # information specific for the file. tarinfo = self.tarinfo() tarinfo.tarfile = self # Use os.stat or os.lstat, depending on platform # and if symlinks shall be resolved. if fileobj is None: if hasattr(os, "lstat") and not self.dereference: statres = os.lstat(name) else: statres = os.stat(name) else: statres = os.fstat(fileobj.fileno()) linkname = "" stmd = statres.st_mode if stat.S_ISREG(stmd): inode = (statres.st_ino, statres.st_dev) if not self.dereference and statres.st_nlink > 1 and inode in self.inodes and arcname != self.inodes[inode]: # Is it a hardlink to an already # archived file? type = LNKTYPE linkname = self.inodes[inode] else: # The inode is added only if its valid. # For win32 it is always 0. type = REGTYPE if inode[0]: self.inodes[inode] = arcname elif stat.S_ISDIR(stmd): type = DIRTYPE elif stat.S_ISFIFO(stmd): type = FIFOTYPE elif stat.S_ISLNK(stmd): type = SYMTYPE linkname = os.readlink(name) elif stat.S_ISCHR(stmd): type = CHRTYPE elif stat.S_ISBLK(stmd): type = BLKTYPE else: return None # Fill the TarInfo object with all # information we can get. tarinfo.name = arcname tarinfo.mode = stmd tarinfo.uid = statres.st_uid tarinfo.gid = statres.st_gid if type == REGTYPE: tarinfo.size = statres.st_size else: tarinfo.size = 0L tarinfo.mtime = statres.st_mtime tarinfo.type = type tarinfo.linkname = linkname if pwd: try: tarinfo.uname = pwd.getpwuid(tarinfo.uid)[0] except KeyError: pass if grp: try: tarinfo.gname = grp.getgrgid(tarinfo.gid)[0] except KeyError: pass if type in (CHRTYPE, BLKTYPE): if hasattr(os, "major") and hasattr(os, "minor"): tarinfo.devmajor = os.major(statres.st_rdev) tarinfo.devminor = os.minor(statres.st_rdev) return tarinfo def list(self, verbose=True): """Print a table of contents to sys.stdout. If `verbose‘ is False, only the names of the members are printed. If it is True, an `ls -l‘-like output is produced. """ self._check() for tarinfo in self: if verbose: print filemode(tarinfo.mode), print "%s/%s" % (tarinfo.uname or tarinfo.uid, tarinfo.gname or tarinfo.gid), if tarinfo.ischr() or tarinfo.isblk(): print "%10s" % ("%d,%d" % (tarinfo.devmajor, tarinfo.devminor)), else: print "%10d" % tarinfo.size, print "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d" % time.localtime(tarinfo.mtime)[:6], print tarinfo.name + ("/" if tarinfo.isdir() else ""), if verbose: if tarinfo.issym(): print "->", tarinfo.linkname, if tarinfo.islnk(): print "link to", tarinfo.linkname, print def add(self, name, arcname=None, recursive=True, exclude=None, filter=None): """Add the file `name‘ to the archive. `name‘ may be any type of file (directory, fifo, symbolic link, etc.). If given, `arcname‘ specifies an alternative name for the file in the archive. Directories are added recursively by default. This can be avoided by setting `recursive‘ to False. `exclude‘ is a function that should return True for each filename to be excluded. `filter‘ is a function that expects a TarInfo object argument and returns the changed TarInfo object, if it returns None the TarInfo object will be excluded from the archive. """ self._check("aw") if arcname is None: arcname = name # Exclude pathnames. if exclude is not None: import warnings warnings.warn("use the filter argument instead", DeprecationWarning, 2) if exclude(name): self._dbg(2, "tarfile: Excluded %r" % name) return # Skip if somebody tries to archive the archive... if self.name is not None and os.path.abspath(name) == self.name: self._dbg(2, "tarfile: Skipped %r" % name) return self._dbg(1, name) # Create a TarInfo object from the file. tarinfo = self.gettarinfo(name, arcname) if tarinfo is None: self._dbg(1, "tarfile: Unsupported type %r" % name) return # Change or exclude the TarInfo object. if filter is not None: tarinfo = filter(tarinfo) if tarinfo is None: self._dbg(2, "tarfile: Excluded %r" % name) return # Append the tar header and data to the archive. if tarinfo.isreg(): with bltn_open(name, "rb") as f: self.addfile(tarinfo, f) elif tarinfo.isdir(): self.addfile(tarinfo) if recursive: for f in os.listdir(name): self.add(os.path.join(name, f), os.path.join(arcname, f), recursive, exclude, filter) else: self.addfile(tarinfo) def addfile(self, tarinfo, fileobj=None): """Add the TarInfo object `tarinfo‘ to the archive. If `fileobj‘ is given, tarinfo.size bytes are read from it and added to the archive. You can create TarInfo objects using gettarinfo(). On Windows platforms, `fileobj‘ should always be opened with mode ‘rb‘ to avoid irritation about the file size. """ self._check("aw") tarinfo = copy.copy(tarinfo) buf = tarinfo.tobuf(self.format, self.encoding, self.errors) self.fileobj.write(buf) self.offset += len(buf) # If there‘s data to follow, append it. if fileobj is not None: copyfileobj(fileobj, self.fileobj, tarinfo.size) blocks, remainder = divmod(tarinfo.size, BLOCKSIZE) if remainder > 0: self.fileobj.write(NUL * (BLOCKSIZE - remainder)) blocks += 1 self.offset += blocks * BLOCKSIZE self.members.append(tarinfo) def extractall(self, path=".", members=None): """Extract all members from the archive to the current working directory and set owner, modification time and permissions on directories afterwards. `path‘ specifies a different directory to extract to. `members‘ is optional and must be a subset of the list returned by getmembers(). """ directories = [] if members is None: members = self for tarinfo in members: if tarinfo.isdir(): # Extract directories with a safe mode. directories.append(tarinfo) tarinfo = copy.copy(tarinfo) tarinfo.mode = 0700 self.extract(tarinfo, path) # Reverse sort directories. directories.sort(key=operator.attrgetter(‘name‘)) directories.reverse() # Set correct owner, mtime and filemode on directories. for tarinfo in directories: dirpath = os.path.join(path, tarinfo.name) try: self.chown(tarinfo, dirpath) self.utime(tarinfo, dirpath) self.chmod(tarinfo, dirpath) except ExtractError, e: if self.errorlevel > 1: raise else: self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s" % e) def extract(self, member, path=""): """Extract a member from the archive to the current working directory, using its full name. Its file information is extracted as accurately as possible. `member‘ may be a filename or a TarInfo object. You can specify a different directory using `path‘. """ self._check("r") if isinstance(member, basestring): tarinfo = self.getmember(member) else: tarinfo = member # Prepare the link target for makelink(). if tarinfo.islnk(): tarinfo._link_target = os.path.join(path, tarinfo.linkname) try: self._extract_member(tarinfo, os.path.join(path, tarinfo.name)) except EnvironmentError, e: if self.errorlevel > 0: raise else: if e.filename is None: self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s" % e.strerror) else: self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s %r" % (e.strerror, e.filename)) except ExtractError, e: if self.errorlevel > 1: raise else: self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s" % e) def extractfile(self, member): """Extract a member from the archive as a file object. `member‘ may be a filename or a TarInfo object. If `member‘ is a regular file, a file-like object is returned. If `member‘ is a link, a file-like object is constructed from the link‘s target. If `member‘ is none of the above, None is returned. The file-like object is read-only and provides the following methods: read(), readline(), readlines(), seek() and tell() """ self._check("r") if isinstance(member, basestring): tarinfo = self.getmember(member) else: tarinfo = member if tarinfo.isreg(): return self.fileobject(self, tarinfo) elif tarinfo.type not in SUPPORTED_TYPES: # If a member‘s type is unknown, it is treated as a # regular file. return self.fileobject(self, tarinfo) elif tarinfo.islnk() or tarinfo.issym(): if isinstance(self.fileobj, _Stream): # A small but ugly workaround for the case that someone tries # to extract a (sym)link as a file-object from a non-seekable # stream of tar blocks. raise StreamError("cannot extract (sym)link as file object") else: # A (sym)link‘s file object is its target‘s file object. return self.extractfile(self._find_link_target(tarinfo)) else: # If there‘s no data associated with the member (directory, chrdev, # blkdev, etc.), return None instead of a file object. return None def _extract_member(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Extract the TarInfo object tarinfo to a physical file called targetpath. """ # Fetch the TarInfo object for the given name # and build the destination pathname, replacing # forward slashes to platform specific separators. targetpath = targetpath.rstrip("/") targetpath = targetpath.replace("/", os.sep) # Create all upper directories. upperdirs = os.path.dirname(targetpath) if upperdirs and not os.path.exists(upperdirs): # Create directories that are not part of the archive with # default permissions. os.makedirs(upperdirs) if tarinfo.islnk() or tarinfo.issym(): self._dbg(1, "%s -> %s" % (tarinfo.name, tarinfo.linkname)) else: self._dbg(1, tarinfo.name) if tarinfo.isreg(): self.makefile(tarinfo, targetpath) elif tarinfo.isdir(): self.makedir(tarinfo, targetpath) elif tarinfo.isfifo(): self.makefifo(tarinfo, targetpath) elif tarinfo.ischr() or tarinfo.isblk(): self.makedev(tarinfo, targetpath) elif tarinfo.islnk() or tarinfo.issym(): self.makelink(tarinfo, targetpath) elif tarinfo.type not in SUPPORTED_TYPES: self.makeunknown(tarinfo, targetpath) else: self.makefile(tarinfo, targetpath) self.chown(tarinfo, targetpath) if not tarinfo.issym(): self.chmod(tarinfo, targetpath) self.utime(tarinfo, targetpath) #-------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Below are the different file methods. They are called via # _extract_member() when extract() is called. They can be replaced in a # subclass to implement other functionality. def makedir(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Make a directory called targetpath. """ try: # Use a safe mode for the directory, the real mode is set # later in _extract_member(). os.mkdir(targetpath, 0700) except EnvironmentError, e: if e.errno != errno.EEXIST: raise def makefile(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Make a file called targetpath. """ source = self.extractfile(tarinfo) try: with bltn_open(targetpath, "wb") as target: copyfileobj(source, target) finally: source.close() def makeunknown(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Make a file from a TarInfo object with an unknown type at targetpath. """ self.makefile(tarinfo, targetpath) self._dbg(1, "tarfile: Unknown file type %r, " "extracted as regular file." % tarinfo.type) def makefifo(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Make a fifo called targetpath. """ if hasattr(os, "mkfifo"): os.mkfifo(targetpath) else: raise ExtractError("fifo not supported by system") def makedev(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Make a character or block device called targetpath. """ if not hasattr(os, "mknod") or not hasattr(os, "makedev"): raise ExtractError("special devices not supported by system") mode = tarinfo.mode if tarinfo.isblk(): mode |= stat.S_IFBLK else: mode |= stat.S_IFCHR os.mknod(targetpath, mode, os.makedev(tarinfo.devmajor, tarinfo.devminor)) def makelink(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Make a (symbolic) link called targetpath. If it cannot be created (platform limitation), we try to make a copy of the referenced file instead of a link. """ if hasattr(os, "symlink") and hasattr(os, "link"): # For systems that support symbolic and hard links. if tarinfo.issym(): if os.path.lexists(targetpath): os.unlink(targetpath) os.symlink(tarinfo.linkname, targetpath) else: # See extract(). if os.path.exists(tarinfo._link_target): if os.path.lexists(targetpath): os.unlink(targetpath) os.link(tarinfo._link_target, targetpath) else: self._extract_member(self._find_link_target(tarinfo), targetpath) else: try: self._extract_member(self._find_link_target(tarinfo), targetpath) except KeyError: raise ExtractError("unable to resolve link inside archive") def chown(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Set owner of targetpath according to tarinfo. """ if pwd and hasattr(os, "geteuid") and os.geteuid() == 0: # We have to be root to do so. try: g = grp.getgrnam(tarinfo.gname)[2] except KeyError: g = tarinfo.gid try: u = pwd.getpwnam(tarinfo.uname)[2] except KeyError: u = tarinfo.uid try: if tarinfo.issym() and hasattr(os, "lchown"): os.lchown(targetpath, u, g) else: if sys.platform != "os2emx": os.chown(targetpath, u, g) except EnvironmentError, e: raise ExtractError("could not change owner") def chmod(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Set file permissions of targetpath according to tarinfo. """ if hasattr(os, ‘chmod‘): try: os.chmod(targetpath, tarinfo.mode) except EnvironmentError, e: raise ExtractError("could not change mode") def utime(self, tarinfo, targetpath): """Set modification time of targetpath according to tarinfo. """ if not hasattr(os, ‘utime‘): return try: os.utime(targetpath, (tarinfo.mtime, tarinfo.mtime)) except EnvironmentError, e: raise ExtractError("could not change modification time") #-------------------------------------------------------------------------- def next(self): """Return the next member of the archive as a TarInfo object, when TarFile is opened for reading. Return None if there is no more available. """ self._check("ra") if self.firstmember is not None: m = self.firstmember self.firstmember = None return m # Read the next block. self.fileobj.seek(self.offset) tarinfo = None while True: try: tarinfo = self.tarinfo.fromtarfile(self) except EOFHeaderError, e: if self.ignore_zeros: self._dbg(2, "0x%X: %s" % (self.offset, e)) self.offset += BLOCKSIZE continue except InvalidHeaderError, e: if self.ignore_zeros: self._dbg(2, "0x%X: %s" % (self.offset, e)) self.offset += BLOCKSIZE continue elif self.offset == 0: raise ReadError(str(e)) except EmptyHeaderError: if self.offset == 0: raise ReadError("empty file") except TruncatedHeaderError, e: if self.offset == 0: raise ReadError(str(e)) except SubsequentHeaderError, e: raise ReadError(str(e)) break if tarinfo is not None: self.members.append(tarinfo) else: self._loaded = True return tarinfo #-------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Little helper methods: def _getmember(self, name, tarinfo=None, normalize=False): """Find an archive member by name from bottom to top. If tarinfo is given, it is used as the starting point. """ # Ensure that all members have been loaded. members = self.getmembers() # Limit the member search list up to tarinfo. if tarinfo is not None: members = members[:members.index(tarinfo)] if normalize: name = os.path.normpath(name) for member in reversed(members): if normalize: member_name = os.path.normpath(member.name) else: member_name = member.name if name == member_name: return member def _load(self): """Read through the entire archive file and look for readable members. """ while True: tarinfo = self.next() if tarinfo is None: break self._loaded = True def _check(self, mode=None): """Check if TarFile is still open, and if the operation‘s mode corresponds to TarFile‘s mode. """ if self.closed: raise IOError("%s is closed" % self.__class__.__name__) if mode is not None and self.mode not in mode: raise IOError("bad operation for mode %r" % self.mode) def _find_link_target(self, tarinfo): """Find the target member of a symlink or hardlink member in the archive. """ if tarinfo.issym(): # Always search the entire archive. linkname = "/".join(filter(None, (os.path.dirname(tarinfo.name), tarinfo.linkname))) limit = None else: # Search the archive before the link, because a hard link is # just a reference to an already archived file. linkname = tarinfo.linkname limit = tarinfo member = self._getmember(linkname, tarinfo=limit, normalize=True) if member is None: raise KeyError("linkname %r not found" % linkname) return member def __iter__(self): """Provide an iterator object. """ if self._loaded: return iter(self.members) else: return TarIter(self) def _dbg(self, level, msg): """Write debugging output to sys.stderr. """ if level <= self.debug: print >> sys.stderr, msg def __enter__(self): self._check() return self def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback): if type is None: self.close() else: # An exception occurred. We must not call close() because # it would try to write end-of-archive blocks and padding. if not self._extfileobj: self.fileobj.close() self.closed = True # class TarFile TarFile
6、json 和 pickle模块
文件只能存二进制或字符串,不能存其他类型,所以用到了用于序列化的两个模块:
json,用于字符串和python数据类型间进行转换,将数据通过特殊的形式转换为所有语言都认识的字符串(字典,变量,列表)
pickle,用于python特有的类型和python的数据类型间进行转换,将数据通过特殊的形式转换为只有python认识的字符串(函数,类)
① json模块:
#json 序列化和反序列化
import json
info ={ #字典
"name":"lzl",
"age":"18"
}
with open("test","w") as f:
f.write(json.dumps(info)) #用json把info写入到文件test中
with open("test","r") as f:
info = json.loads(f.read())
print(info["name"])
#lzl
② pickle模块:
#pickle 序列化和反序列化
import pickle #pickle支持python特有的所有类型
def func(): #函数
info ={
"name":"lzl",
"age":"18"
}
print(info,type(info))
func()
#{‘age‘: ‘18‘, ‘name‘: ‘lzl‘} <class ‘dict‘>
with open("test","wb") as f:
f.write(pickle.dumps(func)) #用pickle把func写入到文件test中 如果用json此时会报错
with open("test","rb") as f:
func_new = pickle.loads(f.read())
func_new()
#{‘age‘: ‘18‘, ‘name‘: ‘lzl‘} <class ‘dict‘>
更多内容-》》http://openskill.cn/article/472
7、shelve模块
shelve模块内部对pickle进行了封装,shelve模块是一个简单的k,v将内存数据通过文件持久化的模块,可以持久化任何pickle可支持的python数据格式
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#-Author-Lian
import shelve
# k,v方式存储数据
s = shelve.open("shelve_test") # 打开一个文件
tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4)
list = [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘, ‘d‘]
info = {"name": "lzl", "age": 18}
s["tuple"] = tuple # 持久化元组
s["list"] = list
s["info"] = info
s.close()
# 通过key获取value值
d = shelve.open("shelve_test") # 打开一个文件
print(d["tuple"]) # 读取
print(d.get("list"))
print(d.get("info"))
# (1, 2, 3, 4)
# [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘, ‘d‘]
# {‘name‘: ‘lzl‘, ‘age‘: 18}
d.close()
# 循环打印key值
s = shelve.open("shelve_test") # 打开一个文件
for k in s.keys(): # 循环key值
print(k)
# list
# tuple
# info
s.close()
# 更新key的value值
s = shelve.open("shelve_test") # 打开一个文件
s.update({"list":[22,33]}) #重新赋值或者s["list"] = [22,33]
print(s["list"])
#[22, 33]
s.close()
8、xml模块
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟json差不多,但json使用起来更简单,不过,古时候,在json还没诞生的黑暗年代,大家只能选择用xml呀,至今很多传统公司如金融行业的很多系统的接口还主要是xml
xml的格式如下,就是通过<>节点来区别数据结构的:

<?xml version="1.0"?> <data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2008</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/> <neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/> <neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/> </country> </data>
xml协议在各个语言里的都是支持的,在python中可以用以下模块操作xml
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml")
root = tree.getroot()
print(root.tag)
#遍历xml文档
for child in root:
print(child.tag, child.attrib)
for i in child:
print(i.tag,i.text)
#只遍历year 节点
for node in root.iter(‘year‘):
print(node.tag,node.text)
修改和删除xml文档内容
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml")
root = tree.getroot()
#修改
for node in root.iter(‘year‘):
new_year = int(node.text) + 1
node.text = str(new_year)
node.set("updated","yes")
tree.write("xmltest.xml")
#删除node
for country in root.findall(‘country‘):
rank = int(country.find(‘rank‘).text)
if rank > 50:
root.remove(country)
tree.write(‘output.xml‘)
自己创建xml文档
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
new_xml = ET.Element("namelist")
name = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"yes"})
age = ET.SubElement(name,"age",attrib={"checked":"no"})
sex = ET.SubElement(name,"sex")
sex.text = ‘33‘
name2 = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"no"})
age = ET.SubElement(name2,"age")
age.text = ‘19‘
et = ET.ElementTree(new_xml) #生成文档对象
et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True)
ET.dump(new_xml) #打印生成的格式
9、configparser模块
用于生成和修改常见配置文档,当前模块的名称在 python 3.x 版本中变更为 configparser
来看一个好多软件的常见文档格式如下:

[DEFAULT] ServerAliveInterval = 45 Compression = yes CompressionLevel = 9 ForwardX11 = yes [bitbucket.org] User = hg [topsecret.server.com] Port = 50022 ForwardX11 = no
如果想用python生成一个这样的文档怎么做呢?
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config["DEFAULT"] = {‘ServerAliveInterval‘: ‘45‘,
‘Compression‘: ‘yes‘,
‘CompressionLevel‘: ‘9‘}
config[‘bitbucket.org‘] = {}
config[‘bitbucket.org‘][‘User‘] = ‘hg‘
config[‘topsecret.server.com‘] = {}
topsecret = config[‘topsecret.server.com‘]
topsecret[‘Host Port‘] = ‘50022‘ # mutates the parser
topsecret[‘ForwardX11‘] = ‘no‘ # same here
config[‘DEFAULT‘][‘ForwardX11‘] = ‘yes‘
with open(‘example.ini‘, ‘w‘) as configfile:
config.write(configfile)
写完了还可以再读出来哈:
>>> import configparser >>> config = configparser.ConfigParser() >>> config.sections() [] >>> config.read(‘example.ini‘) [‘example.ini‘] >>> config.sections() [‘bitbucket.org‘, ‘topsecret.server.com‘] >>> ‘bitbucket.org‘ in config True >>> ‘bytebong.com‘ in config False >>> config[‘bitbucket.org‘][‘User‘] ‘hg‘ >>> config[‘DEFAULT‘][‘Compression‘] ‘yes‘ >>> topsecret = config[‘topsecret.server.com‘] >>> topsecret[‘ForwardX11‘] ‘no‘ >>> topsecret[‘Port‘] ‘50022‘ >>> for key in config[‘bitbucket.org‘]: print(key) ... user compressionlevel serveraliveinterval compression forwardx11 >>> config[‘bitbucket.org‘][‘ForwardX11‘] ‘yes‘
configparser增删改查语法:
[section1] k1 = v1 k2:v2 [section2] k1 = v1 import ConfigParser config = ConfigParser.ConfigParser() config.read(‘i.cfg‘) # ########## 读 ########## #secs = config.sections() #print secs #options = config.options(‘group2‘) #print options #item_list = config.items(‘group2‘) #print item_list #val = config.get(‘group1‘,‘key‘) #val = config.getint(‘group1‘,‘key‘) # ########## 改写 ########## #sec = config.remove_section(‘group1‘) #config.write(open(‘i.cfg‘, "w")) #sec = config.has_section(‘wupeiqi‘) #sec = config.add_section(‘wupeiqi‘) #config.write(open(‘i.cfg‘, "w")) #config.set(‘group2‘,‘k1‘,11111) #config.write(open(‘i.cfg‘, "w")) #config.remove_option(‘group2‘,‘age‘) #config.write(open(‘i.cfg‘, "w"))
10、hashlib模块
用于加密相关的操作,3.x里代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法
import hashlib
m = hashlib.md5()
m.update(b"Hello")
m.update(b"It‘s me")
print(m.digest())
m.update(b"It‘s been a long time since last time we ...")
print(m.digest()) #2进制格式hash
print(len(m.hexdigest())) #16进制格式hash
‘‘‘
def digest(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return the digest value as a string of binary data. """
pass
def hexdigest(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return the digest value as a string of hexadecimal digits. """
pass
‘‘‘
import hashlib
# ######## md5 ########
hash = hashlib.md5()
hash.update(‘admin‘)
print(hash.hexdigest())
# ######## sha1 ########
hash = hashlib.sha1()
hash.update(‘admin‘)
print(hash.hexdigest())
# ######## sha256 ########
hash = hashlib.sha256()
hash.update(‘admin‘)
print(hash.hexdigest())
# ######## sha384 ########
hash = hashlib.sha384()
hash.update(‘admin‘)
print(hash.hexdigest())
# ######## sha512 ########
hash = hashlib.sha512()
hash.update(‘admin‘)
print(hash.hexdigest())
还不够吊?python 还有一个 hmac 模块,它内部对我们创建 key 和 内容 再进行处理然后再加密
import hmac h = hmac.new(‘wueiqi‘) h.update(‘hellowo‘) print h.hexdigest()
11、re模块
re模块用于对python的正则表达式的操作
‘.‘ 默认匹配除\n之外的任意一个字符,若指定flag DOTALL,则匹配任意字符,包括换行
‘^‘ 匹配字符开头,若指定flags MULTILINE,这种也可以匹配上(r"^a","\nabc\neee",flags=re.MULTILINE)
‘$‘ 匹配字符结尾,或e.search("foo$","bfoo\nsdfsf",flags=re.MULTILINE).group()也可以
‘*‘ 匹配*号前的字符0次或多次,re.findall("ab*","cabb3abcbbac") 结果为[‘abb‘, ‘ab‘, ‘a‘]
‘+‘ 匹配前一个字符1次或多次,re.findall("ab+","ab+cd+abb+bba") 结果[‘ab‘, ‘abb‘]
‘?‘ 匹配前一个字符1次或0次
‘{m}‘ 匹配前一个字符m次
‘{n,m}‘ 匹配前一个字符n到m次,re.findall("ab{1,3}","abb abc abbcbbb") 结果‘abb‘, ‘ab‘, ‘abb‘]
‘|‘ 匹配|左或|右的字符,re.search("abc|ABC","ABCBabcCD").group() 结果‘ABC‘
‘(...)‘ 分组匹配,re.search("(abc){2}a(123|456)c", "abcabca456c").group() 结果 abcabca456c
‘[a-z]‘ 匹配a到z任意一个字符
‘[^()]‘ 匹配除()以外的任意一个字符
r‘ ‘ 转义引号里的字符 针对\字符 详情查看⑦
‘\A‘ 只从字符开头匹配,re.search("\Aabc","alexabc") 是匹配不到的
‘\Z‘ 匹配字符结尾,同$
‘\d‘ 匹配数字0-9
‘\D‘ 匹配非数字
‘\w‘ 匹配[A-Za-z0-9]
‘\W‘ 匹配非[A-Za-z0-9]
‘\s‘ 匹配空白字符、\t、\n、\r , re.search("\s+","ab\tc1\n3").group() 结果 ‘\t‘
‘(?P<name>...)‘ 分组匹配 re.search("(?P<province>[0-9]{4})(?P<city>[0-9]{2})(?P<birthday>[0-9]{4})","371481199306143242").groupdict("city")
结果{‘province‘: ‘3714‘, ‘city‘: ‘81‘, ‘birthday‘: ‘1993‘}
标志位:

# flags I = IGNORECASE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_IGNORECASE # ignore case L = LOCALE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_LOCALE # assume current 8-bit locale U = UNICODE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_UNICODE # assume unicode locale M = MULTILINE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_MULTILINE # make anchors look for newline S = DOTALL = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_DOTALL # make dot match newline X = VERBOSE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_VERBOSE # ignore whitespace and comments flags
①、match
从起始位置开始根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容:
#match
import re
obj = re.match(‘\d+‘, ‘123uua123sf‘) #从第一个字符开始匹配一个到多个数字
print(obj)
#<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 3), match=‘123‘>
if obj: #如果有匹配到字符则执行,为空不执行
print(obj.group()) #打印匹配到的内容
#123
匹配ip地址:
import re
ip = ‘255.255.255.253‘
result=re.match(r‘^([1-9]?\d|1\d\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.([1-9]?\d|1\d\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.‘
r‘([1-9]?\d|1\d\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.([1-9]?\d|1\d\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])$‘,ip)
print(result)
# <_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 15), match=‘255.255.255.253‘>
②、search
根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容(不一定是最开始位置),匹配最前
#search
import re
obj = re.search(‘\d+‘, ‘a123uu234asf‘) #从数字开始匹配一个到多个数字
print(obj)
#<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(1, 4), match=‘123‘>
if obj: #如果有匹配到字符则执行,为空不执行
print(obj.group()) #打印匹配到的内容
#123
import re
obj = re.search(‘\([^()]+\)‘, ‘sdds(a1fwewe2(3uusfdsf2)34as)f‘) #匹配最里面()的内容
print(obj)
#<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(13, 24), match=‘(3uusfdsf2)‘>
if obj: #如果有匹配到字符则执行,为空不执行
print(obj.group()) #打印匹配到的内容
#(3uusfdsf2)
③、group与groups的区别
#group与groups的区别
import re
a = "123abc456"
b = re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a)
print(b)
#<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 9), match=‘123abc456‘>
print(b.group())
#123abc456
print(b.group(0))
#123abc456
print(b.group(1))
#123
print(b.group(2))
#abc
print(b.group(3))
#456
print(b.groups())
#(‘123‘, ‘abc‘, ‘456‘)
④、findall
上述两中方式均用于匹配单值,即:只能匹配字符串中的一个,如果想要匹配到字符串中所有符合条件的元素,则需要使用 findall;findall没有group用法
#findall
import re
obj = re.findall(‘\d+‘, ‘a123uu234asf‘) #匹配多个
if obj: #如果有匹配到字符则执行,为空不执行
print(obj) #生成的内容为列表
#[‘123‘, ‘234‘]
⑤、sub
用于替换匹配的字符串(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
#sub import re content = "123abc456" new_content = re.sub(‘\d+‘, ‘ABC‘, content) print(new_content) #ABCabcABC
⑥、split
根据指定匹配进行分组(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
#split
import re
content = "1 - 2 * ((60-30+1*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2) )"
new_content = re.split(‘\*‘, content) #用*进行分割,分割为列表
print(new_content)
#[‘1 - 2 ‘, ‘ ((60-30+1‘, ‘(9-2‘, ‘5/3+7/3‘, ‘99/4‘, ‘2998+10‘, ‘568/14))-(-4‘, ‘3)/(16-3‘, ‘2) )‘]
content = "‘1 - 2 * ((60-30+1*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2) )‘"
new_content = re.split(‘[\+\-\*\/]+‘, content)
# new_content = re.split(‘\*‘, content, 1)
print(new_content)
#["‘1 ", ‘ 2 ‘, ‘ ((60‘, ‘30‘, ‘1‘, ‘(9‘, ‘2‘, ‘5‘, ‘3‘, ‘7‘, ‘3‘, ‘99‘, ‘4‘, ‘2998‘, ‘10‘, ‘568‘, ‘14))‘,
# ‘(‘, ‘4‘, ‘3)‘, ‘(16‘, ‘3‘, "2) )‘"]
inpp = ‘1-2*((60-30 +(-40-5)*(9-2*5/3 + 7 /3*99/4*2998 +10 * 568/14 )) - (-4*3)/ (16-3*2))‘
inpp = re.sub(‘\s*‘,‘‘,inpp) #把空白字符去掉
print(inpp)
new_content = re.split(‘\(([\+\-\*\/]?\d+[\+\-\*\/]?\d+){1}\)‘, inpp, 1)
print(new_content)
#[‘1-2*((60-30+‘, ‘-40-5‘, ‘*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2))‘]
⑦、补充r‘ ‘ 转义

fdfdsfds\fds
sfdsfds& @$
首先要清楚,程序读取文件里的\字符时,添加到列表里面的是\\:
import re,sys
li = []
with open(‘lzl.txt‘,‘r‘,encoding="utf-8") as file:
for line in file:
li.append(line)
print(li) # 注意:文件中的单斜杠,读出来后会变成双斜杠
# [‘fdfdsfds\\fds\n‘, ‘sfdsfds& @$‘]
print(li[0]) # print打印的时候还是单斜杠
# fdfdsfds\fds
r字符的意义,对字符\进行转义,\只做为字符出现:
import re,sys
li = []
with open(‘lzl.txt‘,‘r‘,encoding="utf-8") as file:
for line in file:
print(re.findall(r‘s\\f‘, line)) #第一种方式匹配
# print(re.findall(‘\\\\‘, line)) #第二种方式匹配
li.append(line)
print(li) # 注意:文件中的单斜杠,读出来后会变成双斜杠
# [‘s\\f‘]
# []
# [‘fdfdsfds\\fds\n‘, ‘sfdsfds& @$‘]
补充:看完下面的代码你可能更懵了
import re re.findall(r‘\\‘, line) # 正则中只能这样写 不能写成 r‘\‘ 这样 print(r‘\\‘) # 只能这样写 不能写成r‘\‘ \只能是双数 # \\ 结果 # 如果想值打印单个\ 写成如下 print(‘\\‘) # 只能是双数 # \ 结果
总结:文件中的单斜杠\,读出到程序中时是双斜杠\\,print打印出来是单斜杠\;正则匹配文件但斜杠\时,用r‘\\‘双斜杠去匹配,或者不用r直接用‘\\\\‘四个斜杠去匹配
⑧、compile函数
说明:
Python通过re模块提供对正则表达式的支持。使用re的一般步骤是先使用re.compile()函数,将正则表达式的字符串形式编译为Pattern实例, 然后使用Pattern实例处理文本并获得匹配结果(一个Match实例),最后使用Match实例获得信息,进行其他的操作
举一个简单的例子,在寻找一个字符串中所有的英文字符:
import re pattern = re.compile(‘[a-zA-Z]‘) result = pattern.findall(‘as3SiOPdj#@23awe‘) print(result) # [‘a‘, ‘s‘, ‘S‘, ‘i‘, ‘O‘, ‘P‘, ‘d‘, ‘j‘, ‘a‘, ‘w‘, ‘e‘]
匹配IP地址(255.255.255.255):
import re
pattern = re.compile(r‘^(([1-9]?\d|1\d\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.){3}([1-9]?\d|1\d\d|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])$‘)
result = pattern.match(‘255.255.255.255‘)
print(result)
# <_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 15), match=‘255.255.255.255‘>
12、urllib模块
在能使用的各种网络函数库中,功能最强大的可能是urllib和urllib2(python2.0)了。通过他们在网络上访问文件,就好像访问本地电脑的文件一样,通过一个简单的函数调用,几乎可以把任何URL执行的东西用做程序的输入,想象一下这个模块和re模块集合:可以下载web页面,提前信息,以及自动生成报告等。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#-Author-Lian
import urllib.request
def getdata():
url = "http://www.baidu.com"
data = urllib.request.urlopen(url).read()
data = data.decode("utf-8")
print(data)
getdata()
urlopen返回的类文件对象支持close、read、readline、和readlines方法
标签:区别 relative tps param ups each available str text
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lixiaomingpython/p/6802328.html